
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The two most important reactions of alcohols are their acid-catalyzed dehydration to give
Concept Introduction:
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
True.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohols are organic compounds containing -OH group. It undergoes in the presence of acid to form an alkene. Dehydration is the removal of water from alcohol.
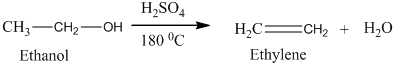
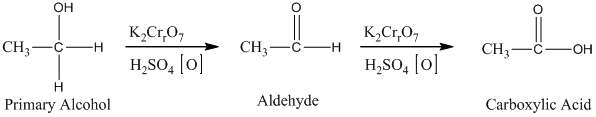
Alcohols undergo oxidation to yield aldehyde, ketone, and carboxylic acid. The primary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation gives an aldehyde and further acid catalyzed oxidation gives a corresponding acid.
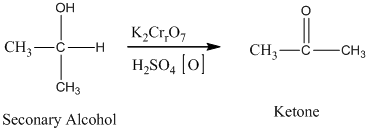
The secondary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation fives a ketone.
Therefore, this statement is True.
(b)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The acidity of alcohols is comparable to that of water.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
True.
Explanation of Solution
The strength of an acid can be measured by the acid dissociation constant Ka while the pKa value is logarithmic value of the acid dissociation constant. So, the alcohol has the nearly same pKa value as of water.
Therefore, this statement is True.
(c)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Water-insoluble alcohols and water-insoluble phenols react with string bases to give water soluble salts.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohol is a water-soluble compound. It is soluble in water because of the hydrogen bonding between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of water and alcohol molecules. Phenol is also water soluble because of hydrogen bonding. Water-soluble alcohol and water-insoluble phenol react with string bases to form water-soluble salt.
Therefore, this statement is False.
(d)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Acid catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol gives cyclohexene.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol gives corresponding alkene. In the presence of sulfuric acid, cyclohexanol gives cyclohexene.
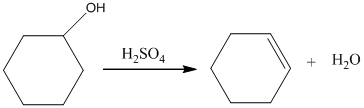
Therefore, this statement is False.
(e)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
When the acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alkene can yield isomeric alkenes, the alkene with the greater number of hydrogens in the carbons of the double bond generally predominates.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol gives an isomeric alkene. The isomeric alkene, which has a lower number of hydrogen atoms in the double bond, has a grater yield. Hence, when butanol undergoes an acid-catalyzed dehydration, 2-butene is the major product.
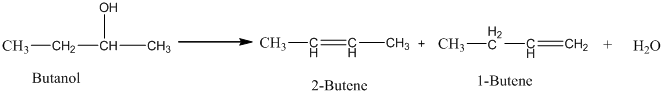
Therefore, this statement is False.
(f)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-butanol gives predominantly 1-butene.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
An acid catalyzed dehydration of butanol gives predominantly 2-butene. The yield of 1-butene is approximately because in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reaction of an alcohol, the major product has the lower number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms with double bonds. Thus, 2-Butene is the major product.
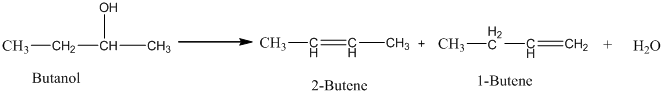
Therefore, this statement is False.
(g)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The oxidation of a primary alcohol gives either an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid depending on experimental conditions.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
True.
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation of the primary alcohols gives either aldehyde or carboxylic acid, depending on the experimental condition. For illustration, the primary alcohol in an acid catalyzed oxidation gives an aldehyde and further acid catalyzed oxidation gives a corresponding acid.
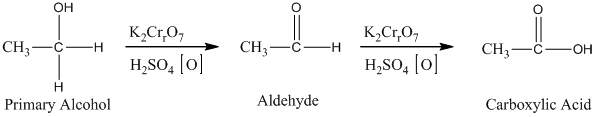
Therefore, this statement is True.
(h)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
The oxidation of a secondary alcohol gives a carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
The secondary alcohol in an acid-catalyzed oxidation gives ketone. The oxidation of the secondary alcohol gives ketone in the presence of potassium chromate as an oxidizing agent. It does not produce carboxylic acid because it lacks a hydrogen atom.
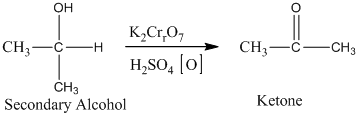
Therefore, this statement is false.
(i)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Acetic acid, CH3 COOH, can be prepared from ethylene, CH2 =CH2, by treatment of ethylene with H2 O/H2 SO4, followed by treatment with K2 Cr2 O7 /H2 SO4.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
True.
Explanation of Solution
Ethylene undergoes acid catalyzed hydration to produce ethanol. This, ethanol, in further treatment with potassium dichromate, undergoes oxidation to form acetic acid. The reaction is.
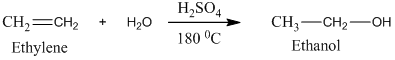
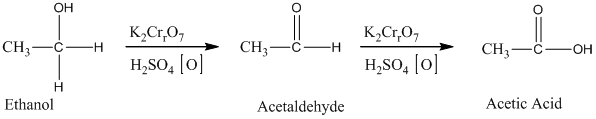
Therefore, this statement is True.
(j)
Interpretation:
State True or false.
Treatment of propene, CH3 CH=CH2, with H2 O/H2 SO4, followed by treatment with K2 Cr2 O7 /H2 SO4 gives propanoic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Answer to Problem 14.29P
False.
Explanation of Solution
The hydration of propene with water in the presence of sulfuric acid produces propanol. It is a secondary alcohol. Propanol undergoes oxidation in the presence of potassium chromate and produces propanone. There is no hydrogen atom present in propanone. So, it does not produce propanoic acid in oxidation.
Therefore, this statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- If we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forward
- You need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forward
- Give the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forwardQ14. Fill this chart: (please refer to ppt notes/browser to answer these questions) What alcohol is also called wood alcohol? What is the common name of ethanol? Draw the structure of phenol and thiophene? Are bigger chain alcohol like heptanol and octanol are soluble or insoluble in water and explain it ? Are ethers soluble or insoluble in water? What suffix and prefix are used for alcohol while naming alcohol and ether? What the process called when we add water to any alkene to make alcohol? Q16. Draw the diagram of following aromatic compound (practice from previous module) Aniline Phenol Benzoic acid Methyl benzoate Q17. a. Write the oxidation reactions for the 2 propanol. b. Write the oxidation reaction of the ethanol.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning



