
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781285869759
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.12P
14-12 Write the 1UPAC name of each compound.
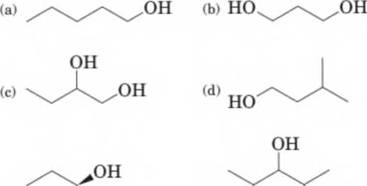
(e) (f)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Select the product for the following reaction.
HO
HO
PCC
OH
○
OH
O HO
○ HO
HO
HO
5:45
Х
Select the final product for the following reaction sequence.
O
O
1. Mg. ether
2.D.O
Based on the chart
Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages.
Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages.
Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.1PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.2PCh. 14.2 - Problem 14-3 Draw structural formulas for the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.4PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.5PCh. 14.3 - Problem 14-6 Write the common name for each ether.Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 14.7PCh. 14 - 14-8 Answer true or false. The functional group of...Ch. 14 - 14-9 What is the difference in structure between a...Ch. 14 - 14-10 Which of the following are secondary...
Ch. 14 - 14-11 Which of the alcohols in Problem 14-10 are...Ch. 14 - 14-12 Write the 1UPAC name of each compound. (e)...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.13PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.14PCh. 14 - 14-15 Both alcohols and phenols contain an —OH...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14 - 14-17 Explain in terms of noncovalent interactions...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.18PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.19PCh. 14 - 14-20 Show hydrogen bonding between methanol and...Ch. 14 - 14-21 Show hydrogen bonding between the oxygen of...Ch. 14 - 14-22 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 14 - 14-23 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 14 - 14-24 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) is commonly...Ch. 14 - 14-25 Explain why glycerol is much thicker (more...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.26PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.27PCh. 14 - 14-28 Give the structural formula of an alkene or...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14 - 14-30 Show how to distinguish between cyclohexanol...Ch. 14 - 14-31 Compare the acidity of alcohols and phenols,...Ch. 14 - 14-32 Both 2,6-diisopropylcyclohexanol and the...Ch. 14 - 14-33 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 14 - 14-34 Write equations for the reaction of...Ch. 14 - 14-35 Write equations for the reaction of each of...Ch. 14 - 14-36 Show how to convert cyclohexanol to these...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.38PCh. 14 - 14-39 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 14 - 14-40 Name two important alcohols derived from...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14 - 14-42 Write the common name for each ether. ch3...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14 - 14-44 Answer true or false. (a) The functional...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14 - 14-47 Following are structural formulas for...Ch. 14 - 14-48 Explain why methanethiol, CH3SH, has a lower...Ch. 14 - 14-49 Answer true or false. Today, the major...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.50PCh. 14 - 14-51 (Chemical Connections 14B) When was...Ch. 14 - 14-52 (Chemical Connections 14B) What was Alfred...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.53PCh. 14 - 14-54 (Chemical Connections 14C) What is the color...Ch. 14 - 14-55 (Chemical Connections 140 The legal...Ch. 14 - 14-56 (Chemical Connections 14D) What does it mean...Ch. 14 - 14-57 (Chemical Connections 14E) What are the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.58PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.59PCh. 14 - 14-60 Write a balanced equation for the complete...Ch. 14 - 14-61 Knowing what you do about electronegativity,...Ch. 14 - 14-62 Draw structural formulas and write IUPAC...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14 - 14-64 Explain why the boiling point of ethylene...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14 - 14-66 1,4-Butanediol, hexane, and 1-pentanol have...Ch. 14 - 14-67 Of the three compounds given in Problem...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14 - 14-69 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 14 - 14-70 Show how to prepare each compound from...Ch. 14 - 14-71 The mechanism of the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14 - 14-73 Lipoic acid is a growth factor for many...Ch. 14 - 14-74 Following is a structural formula for the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14 - Prob. 14.77PCh. 14 - 14-78 Consider alkenes A, B, and C. each of which...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.79P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- What is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward. M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forward
- Please use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forwardBriefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forward
- Answe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY