
Concept explainers
14-8 Answer true or false.
- The
functional group of an alcohol is the —OH (hydroxyl) group.
(h, The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The functional group of any alcohol is the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group.Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest.
carbon chain that contains the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: A primary alcohol contains one −OH group, and a tertiary alcohol contains three-OH groups, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol contains only one -OH groups but the connectivity of carbon atoms bearing −OH group is different. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Primary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to only one carbon atom. It has like -CH2 OH group in molecule. Secondary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to two other carbon atoms. Tertiary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to three other carbon atoms. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols have only one -OH group in their molecule but the connectivity of carbon atom bearing -OH group is different. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In IUPAC nomenclature, the presence of three -OH groups is shown by the ending triol Therefore, the given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Explanation of Solution
Glycol is a compound that has two -OH groups attached to carbon atoms. Ethyl glycol is the simplest form of glycol. Its structural formula is:
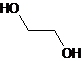
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: Because of the presence of an-OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
Because of the presence of an -OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Polar molecules have polar covalent bonds connected between the atoms. Methanol is an example of alcohol. Here, the O-C bond and O-H bond are polar covalent bonds. In methanol, there is a difference in electronegativity between the O-C bond (3.5-2.5 = 1.0) and O-H bond (3.5-2.1 = 1.4) Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. Due to the presence of the O-H bond, all alcohols are polar molecules.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The temperature at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure is known as boiling point. As the molecular weight increases, more atoms are involved in the non-covalent interaction. Due to this tact, more energy (more temperature) is required to break this non-covalent interactions.Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The solubility of alcohols in water decreases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohols are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons. This is due to the presence of the O-H group in alcohol. The O-H group undergoes hydrogen bonding with a hydrogen atom in the water molecule.
As the molecular weight increases, simultaneously the hydrocarbon chain in alcohol will also increase. Now the alcohol stars behaving more like hydrocarbons. Therefore, the solubility decreases with the increase in molecular weight.
Therefore, the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- 1. Give the structures of the products obtained when the following are heated. Include stereochemistry where relevant. A NO2 + NO2 B + C N=C CEN + { 2. Which compounds would you heat together in order to synthesize the following?arrow_forwardExplain how myo-inositol is different from D-chiro-inositol. use scholarly sources and please hyperlink.arrow_forwardWhat is the molarisuty of a 0.396 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 /mol.arrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC or common name for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly. Br ......Im OHarrow_forwardCan you please help me solve this problems. The top one is just drawing out the skeletal correct and then the bottom one is just very confusing to me and its quite small in the images. Can you enlarge it and explain it to me please. Thank You much (ME EX1) Prblm #33arrow_forwardI'm trying to memorize VESPR Shapes to solve problems like those. I need help making circles like the second image in blue or using an x- and y-axis plane to memorize these and solve those types of problems, especially the ones given in the top/first image (180, 120, 109.5). Can you help me with this? or is their any other efficient method do soarrow_forward
- Can you please explain this problems to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 27arrow_forwardQuestion 6 of 7 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of 1 = 1 ✓2 ✓ 3 ✓ 4 ✓ 5 6 ✓ 7 This organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution: Jen ✓ ? A short time later sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C-OH stretch absorption. That is, must now be a new molecule present with at least one C- OH bond. there 18 In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule Ar © + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Add/Remove step Click and drawing Save For Later Submit Assignmentarrow_forwardCan you please explain this problem to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 22arrow_forward
- Can you please explain this problems to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 30arrow_forwardThis organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution: O ? olo RET A short time later sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C-OH stretch absorption. That is, there Ar must now be a new molecule present with at least one C - OH bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule. $ Add/Remove steparrow_forwardSo the thing is im trying to memorize VESPR Shapes in order to be able to solve problems like so, and I need help with making circles like the second image that's in blue or using an x and y axis plane in order to memorize these and be able to solve those type of problems. Especially like the ones given in the top / first image. (180 , 120 , 109.5) Can you help me with this.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

