
Identify each of the following compounds as an
a.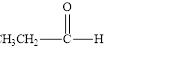 d.
d.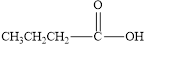
b.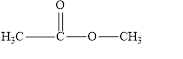 e.
e.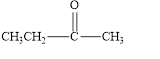
c.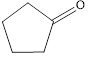 f.
f.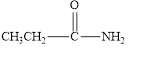
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is an aldehyde.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
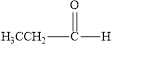
Figure 1
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to one carbon atom and one hydrogen atom. Hence, it is an aldehyde.
The given compound is an aldehyde.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
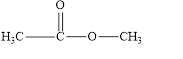
Figure 2
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is a ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
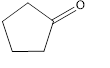
Figure 3
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to two carbon atoms in the ring. Hence, it is a ketone.
The given compound is a ketone.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
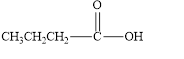
Figure 4
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is a ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
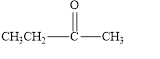
Figure 5
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to two carbon atoms. Hence, it is a ketone.
The given compound is a ketone.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
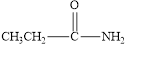
Figure 6
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. The carbonyl group is attached to one nitrogen atom and one carbon atom. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General Organic and Biochemistry
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward3. Devise a retrosynthesis for the problem given below and then provide the corresponding synthesis with all necessary reagents/reactants: RETROSYNTHESIS: SYNTHESIS: Brarrow_forwardSeveral square planar complexes are known for Gold (III) ions but not for Silver (III) why?arrow_forward
- Aiter running various experiments, you determine that the mechanism for the following reaction is bimolecular. CI Using this information, draw the correct mechanism in the space below. X Explanation Check C Cl OH + CI Add/Remove step Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Carrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the fewest number of steps as possible, Draw all intermediates (In the same form as the picture provided) and provide all reagents.arrow_forwardPlease provide steps to work for complete understanding.arrow_forward
- Please provide steps to work for complete understanding.arrow_forwardIdentify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forwardIdentify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




