
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether dehydrogenase is involved in (1) glycerol
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.48EP
Dehydrogenase is involved in (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. In step 1, glycerol-3-phosphate is formed as the intermediate compound that further reacts to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate in step 2. The reaction for the conversion of glycerol is as follows:
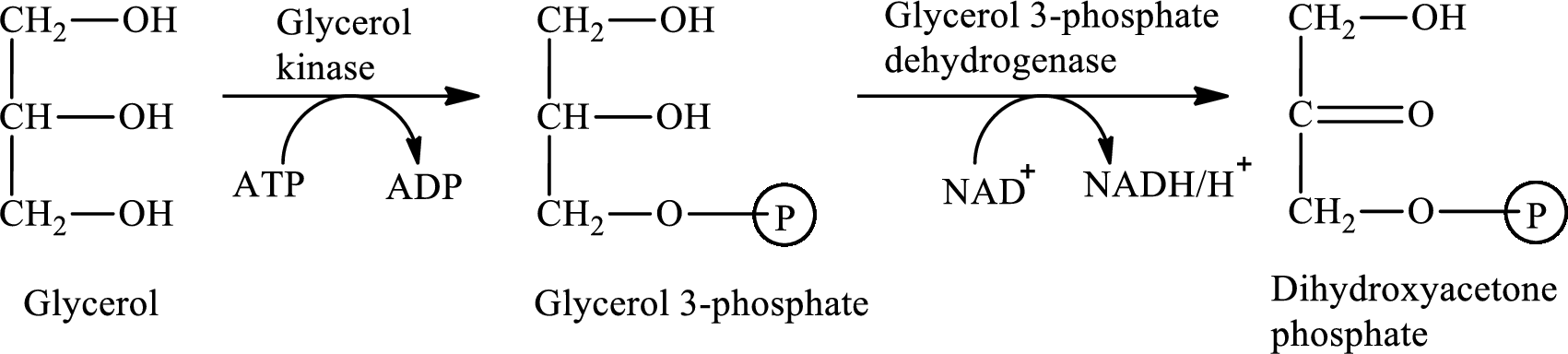
Here, represents
represents
In step 2 of glycerol metabolism, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase enzymes catalyzed the conversion of glycerol-3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Therefore, dehydrogenase is involved in glycerol metabolism.
The reaction in step 1 of a turn of the β-oxidation pathway is a dehydrogenation reaction in which hydrogen atoms from
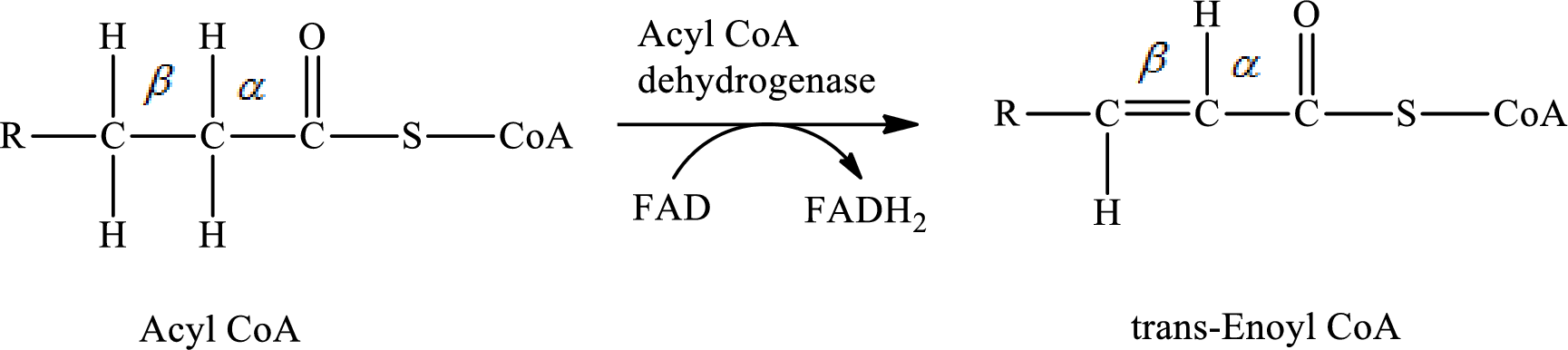
The reaction in step 1 of a turn of the β-oxidation pathway is catalyzed by acyl CoA dehydrogenase enzyme.
Hence, dehydrogenase is involved in (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether AMP is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
AMP (adenosine monophosphate) is an important
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.48EP
AMP is involved in (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of fatty acid metabolism is the activation of fatty acids in the outer mitochondrial membrane. The fatty acid is activated by coenzyme A and ATP. The activation reaction of fatty acid is as follows:
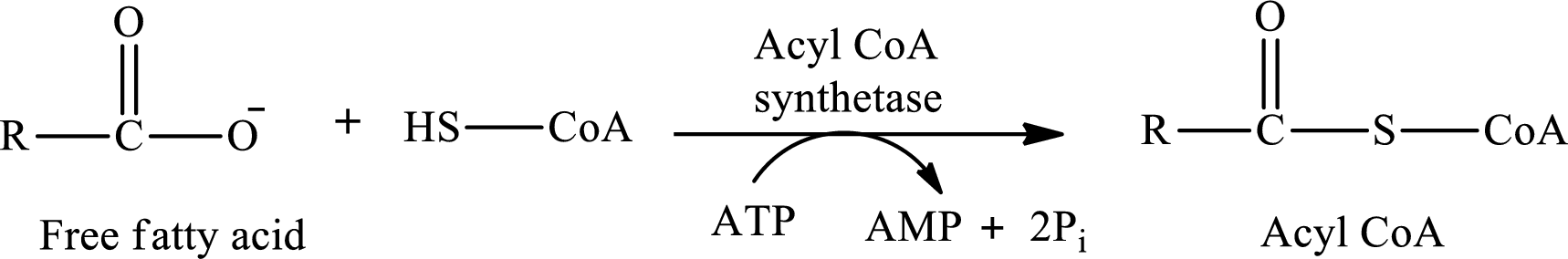
ATP is converted to AMP. Hence, AMP is involved in fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether acyl CoA is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.48EP
Acyl CoA is involved in (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of fatty acid metabolism is the activation of fatty acids in the outer mitochondrial membrane. The fatty acid is activated by coenzyme A and ATP. ATP is converted to AMP. The activation reaction of fatty acid is as follows:
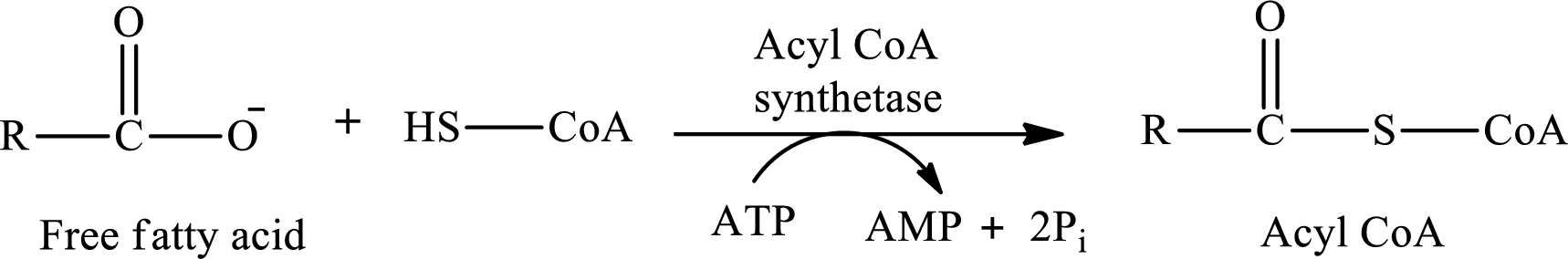
The activated fatty acid-CoA that is formed after the activation of the fatty acid molecule in the oxidation process of fatty acids is called acyl CoA.
The enzymes that are needed for the oxidation of fatty acid are located in the mitochondrial matrix. Acyl CoA cannot pass through the inner mitochondrial membrane to the mitochondrial matrix because it is too large. A shuttle mechanism that involves the molecule carnitine effects the entry of acyl CoA into the mitochondrial matrix. After this process, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA through a series of four biochemical reactions. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
Hence, acyl CoA is involved in fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether glycerol-3-phosphate is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) fatty acid metabolism to acetyl CoA, or (3) both glycerol metabolism and fatty acid metabolism has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney. The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. After the first stage, the remaining stages of glycerol metabolism are the same as glucose pathways. The overall equation for glycerol metabolism is as follows:
Fatty acids are molecules that are long hydrocarbon chain of carboxylic acid. They are building blocks of fat in humans and animals.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as a β-oxidation pathway. Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH are produced in this pathway.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.48EP
Glycerol-3-phosphate is involved in (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The first stage of glycerol metabolism is a two-step process. In step 1, glycerol-3-phosphate is formed as the intermediate compound that further reacts to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate in step 2. The reaction for the conversion of glycerol is as follows:
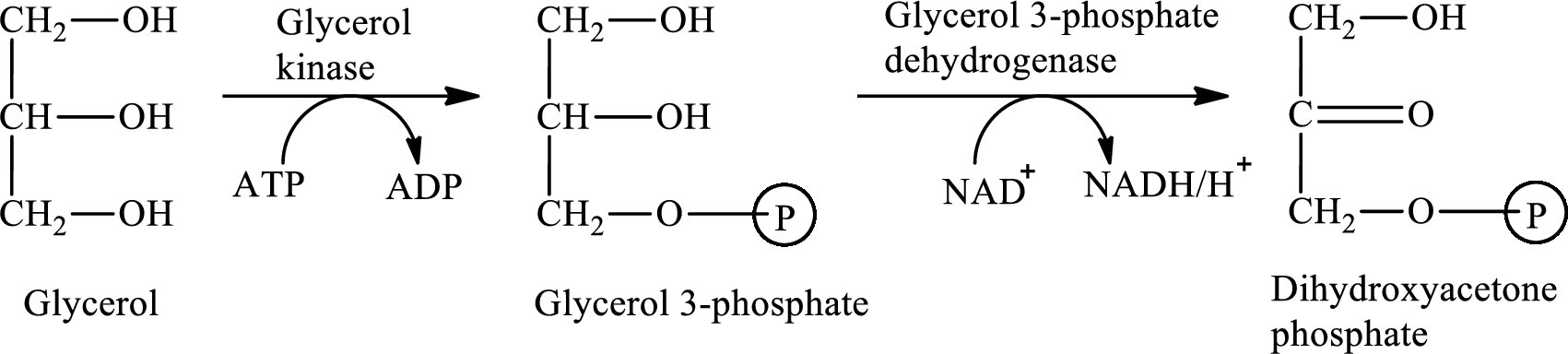
Here, represents
represents
Therefore, glycerol-3-phosphate is involved in glycerol metabolism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- What will the enolate for this be using LDA, THF, and cold temperatures? What will it be using NaOEt at rt?arrow_forwardHelp me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forward
- CHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forwardCan anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



