
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether crotonate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
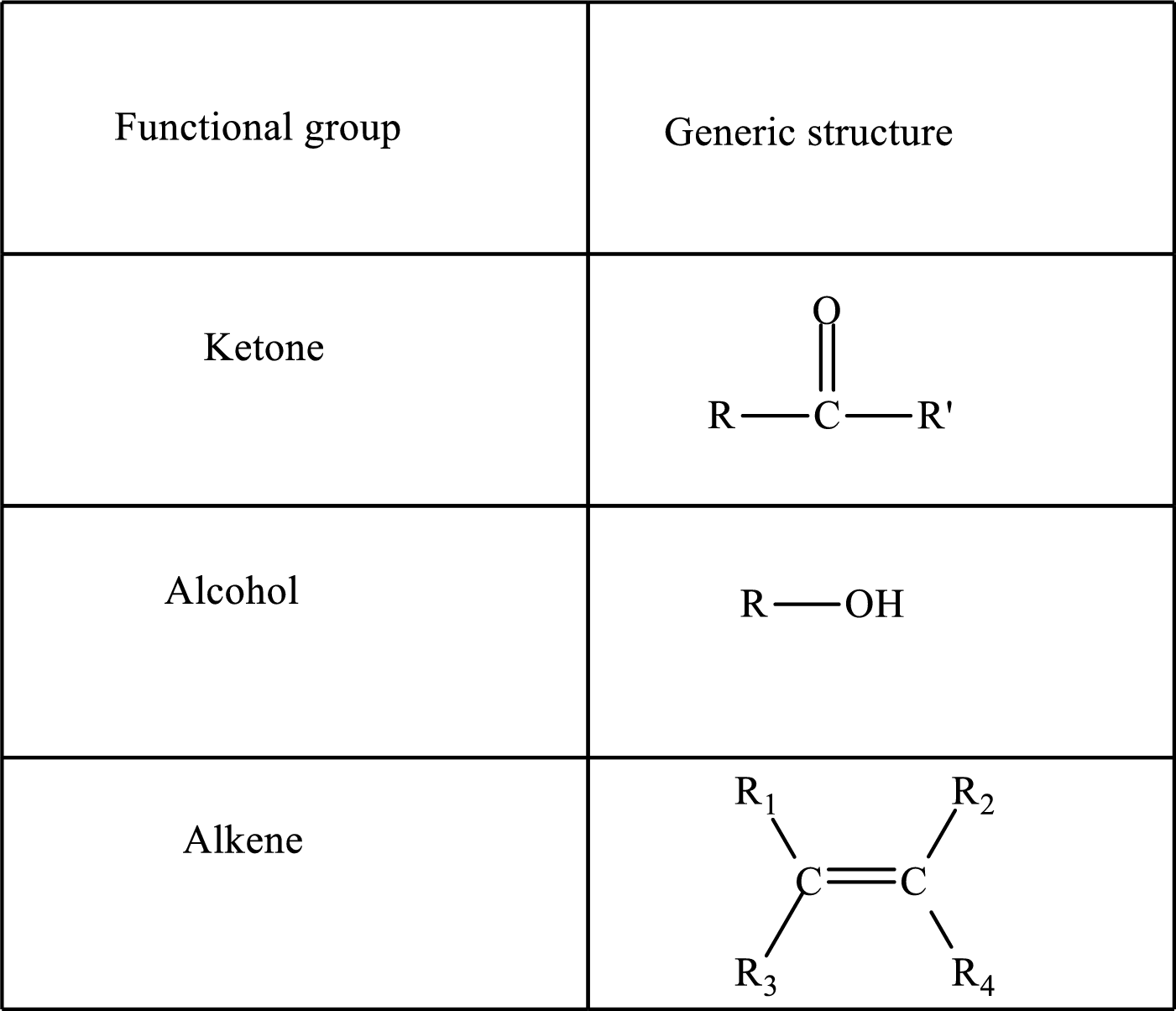
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Keto acid has a
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether oxaloacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
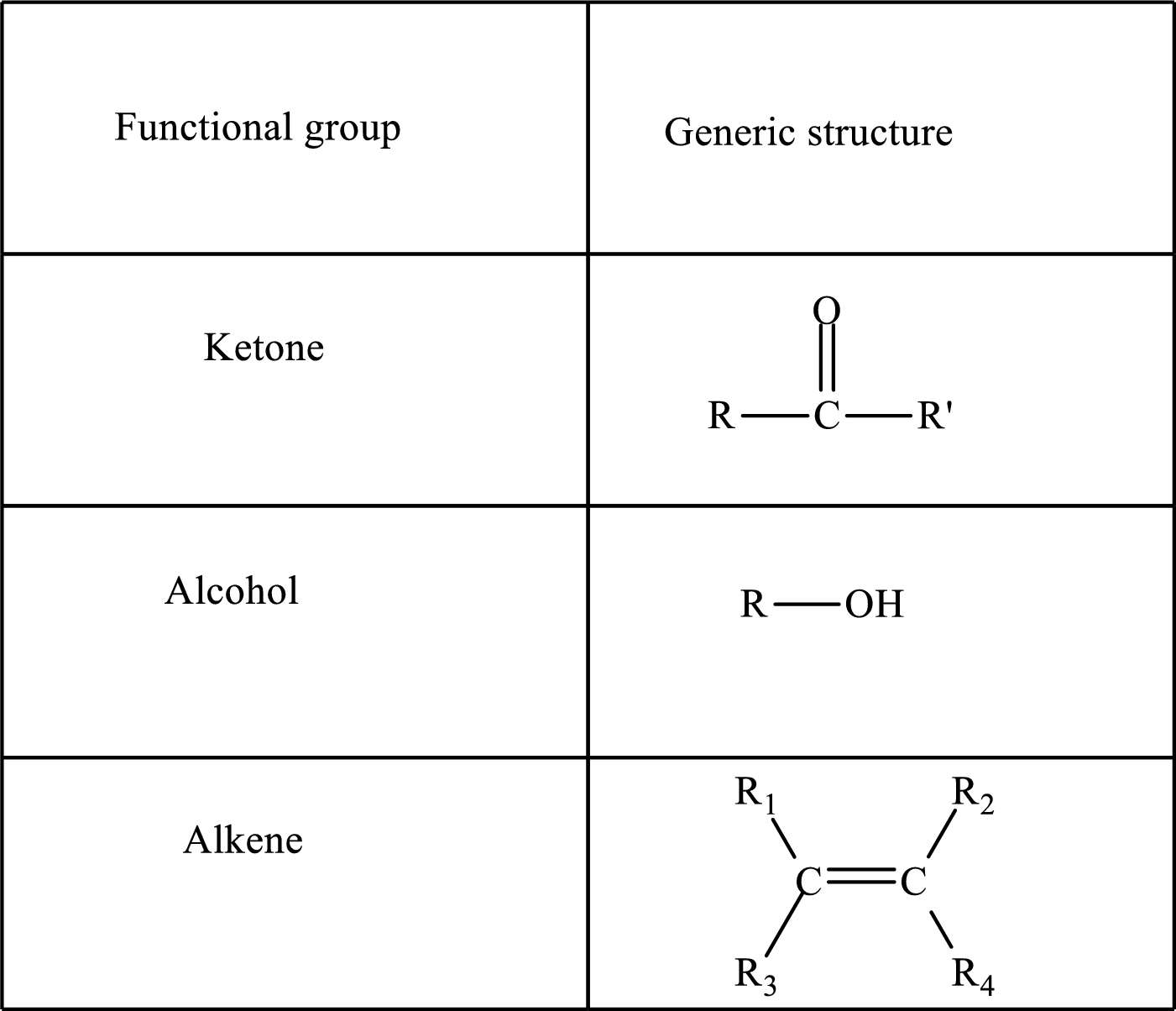
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether acetoacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
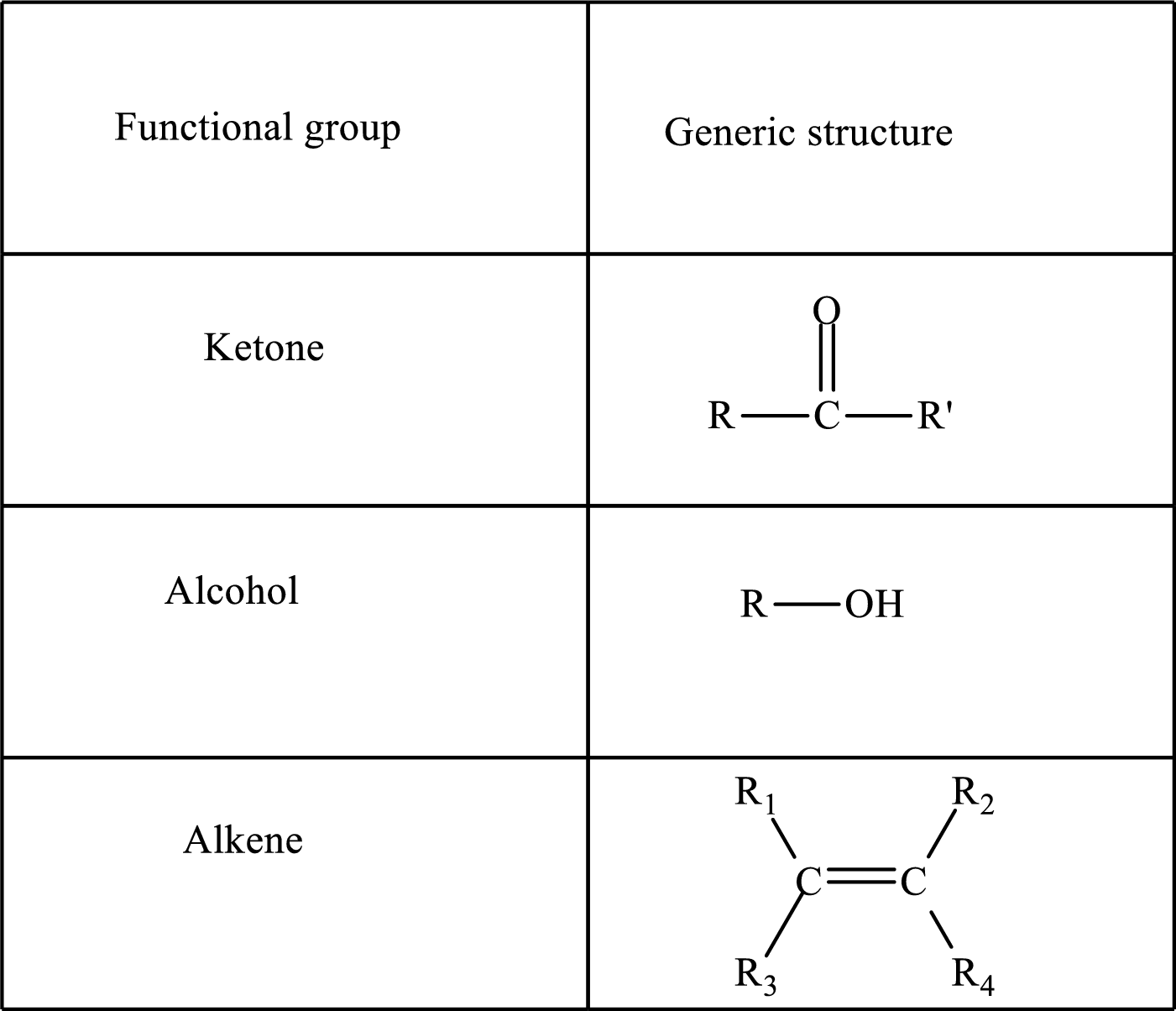
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether malate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
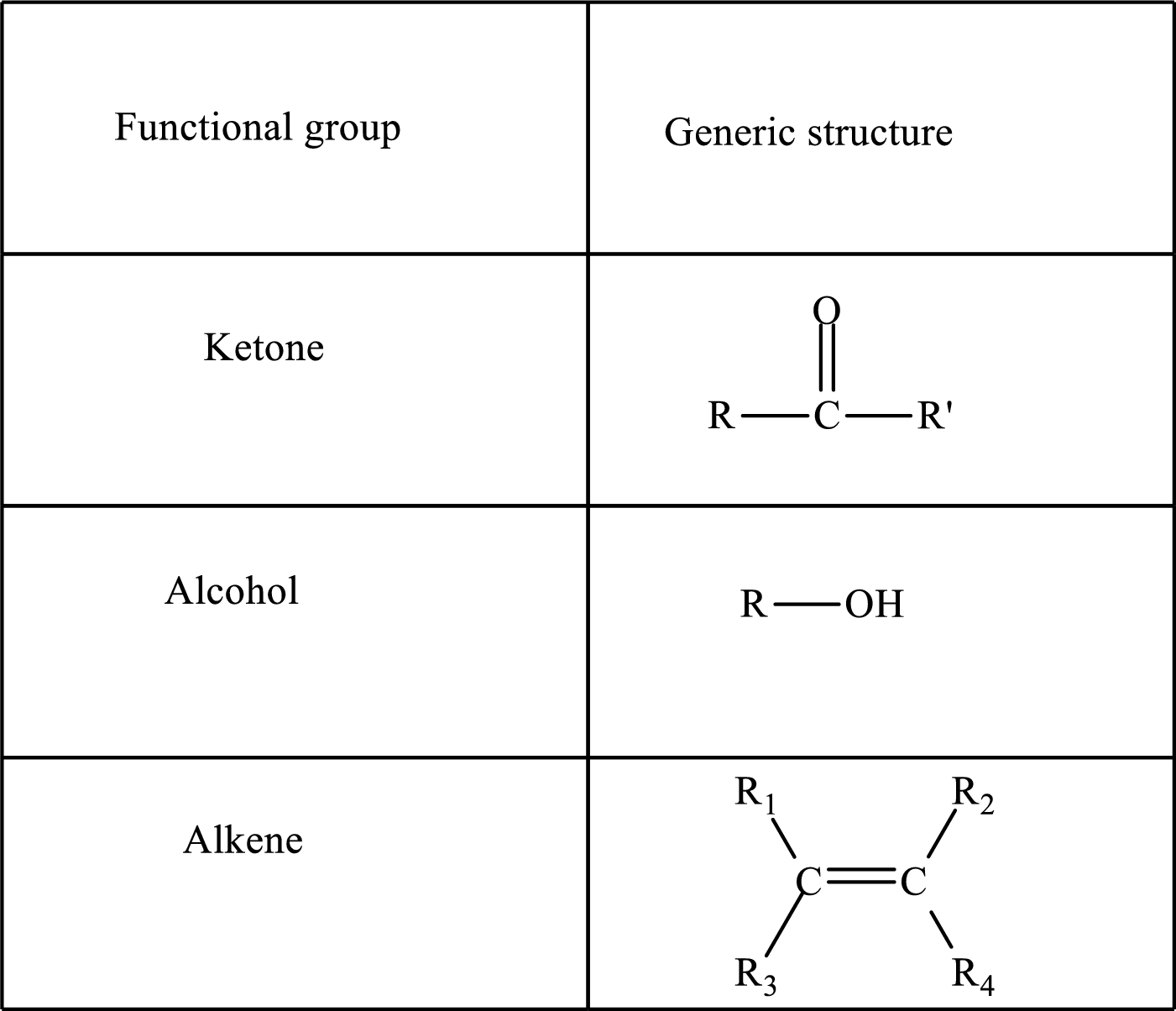
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- Would Si(CH3)3F react with AgCl? If so, write out the balanced chemical equation. If not,explain why no reaction would take place.arrow_forwardNH3 reacts with boron halides (BX3 where X = F, Cl, Br, or I) to form H3N-BX3 complexes.Which of these complexes will have the strongest N-B bond? Justify your answerarrow_forward3Helparrow_forward
- Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? Temperature of cold water (°C) 4.0 Temperature of hot water ("C) 87.0 Volume of cold water (mL) 94.0 Volume of hot water (mL) 78.0 Final temperature after mixing ("C) 41.0 Mass of cold water (g) 94.0 Mass of hot water (g) 78.0 Calorimeter constant (J/°C) 12.44 How to calculate the calorimeter constantarrow_forwardplease draw the arrowsarrow_forwardwhere should i draw arrows, please indicate clearly or draw itarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





