
a.
Interpretation:
Amide given below has to be named.
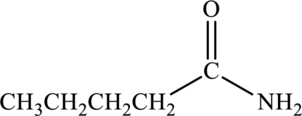
Concept Introduction:
Amides contain a nitrogen atom that is bonded to carbonyl group. The nitrogen atom that is bonded to the carbonyl group may be bonded to alkyl groups or hydrogen atoms. Depending on the number of carbon atoms that is attached to the nitrogen atom, the amide is classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Naming of amides are done using specific rules:
Primary amides are named by considering the parent
Secondary and tertiary amide contains two parts in its name. The alkyl groups that are bonded to the nitrogen atom is named using N- as the prefix for the alkyl group and this precedes the name. The
b.
Interpretation:
Amide given below has to be named.
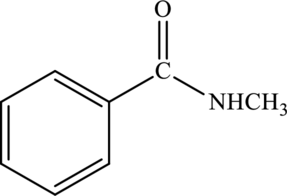
Concept Introduction:
Refer part “a.”.
c.
Interpretation:
Amide given below has to be named.
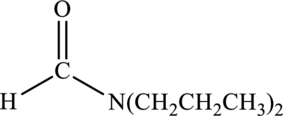
Concept Introduction:
Refer part “a.”.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardConsider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forward
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





