
(a)
Interpretation: Using the figure
Concept Introduction: The particles of a crystal are organized in an ordered, repeating, three-dimensional structure. The crystal system is a way of categorizing crystalline compounds based on the unit cell of the substance. There are seven different crystal systems.
(a)
Answer to Problem 78A
The three unequal edges intersect at right angles in the orthorhombic crystal system.
Explanation of Solution
The given figures are as follows:
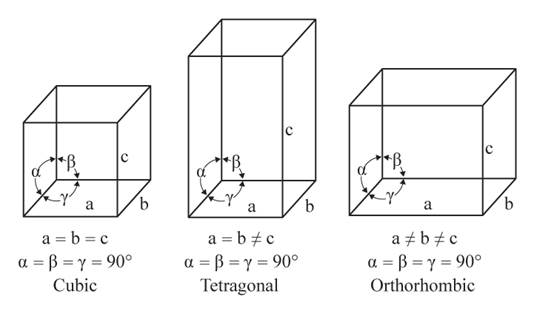
From the figure, the cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic crystal systems have edges that meet at right angles. Only the orthorhombic crystal system has unequal edges
(b)
Interpretation: Using the figure
Concept Introduction: The particles of a crystal are organized in an ordered, repeating, three-dimensional structure. The crystal system is a way of categorizing crystalline compounds based on the unit cell of the substance. There are seven different crystal systems.
(b)
Answer to Problem 78A
No crystal system has three equal edges and three equal but not right angles.
Explanation of Solution
The given figures are as follows:
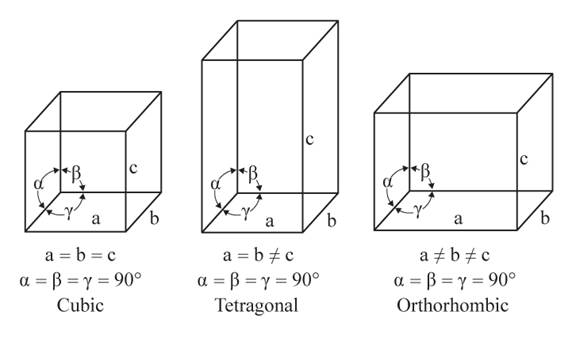
From the figure, the cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic crystal systems have edges that meet at right angles. Thus, no crystal system which shows three equal edges and three equal but not right angles.
(c)
Interpretation: Using the figure
Concept Introduction: The particles of a crystal are organized in an ordered, repeating, three-dimensional structure. The crystal system is a way of categorizing crystalline compounds based on the unit cell of the substance. There are seven different crystal systems.
(c)
Answer to Problem 78A
In the tetragonal crystal system, three edges, two equal and one unequal meet at right angles.
Explanation of Solution
The given figures are as follows:
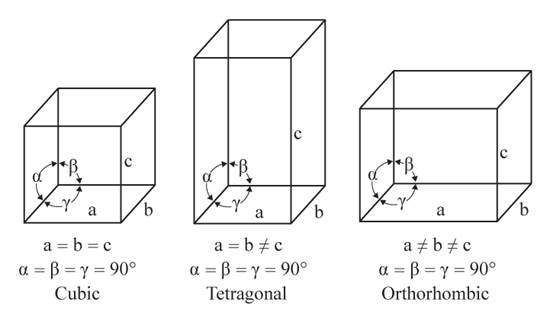
From the figure, the cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic crystal systems have edges that meet at right angles. Only the tetragonal crystal system has two equal edges, and one unequal edge
(d)
Interpretation: Using the figure
Concept Introduction: The particles of a crystal are organized in an ordered, repeating, three-dimensional structure. The crystal system is a way of categorizing crystalline compounds based on the unit cell of the substance. There are seven different crystal systems.
(d)
Answer to Problem 78A
No crystal system has three unequal edges that do not intersect at right angles.
Explanation of Solution
The given figures are as follows:
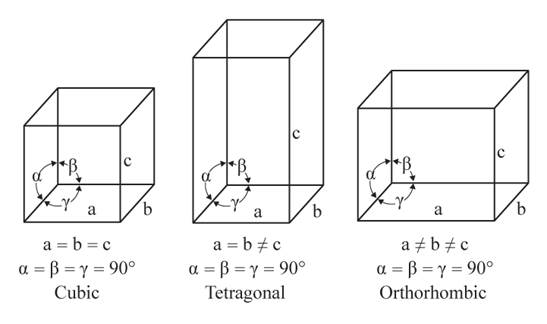
From the figure, the cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic crystal systems have edges that meet at right angles. Thus, no crystal system shows three uneven edges that do not meet at right angles.
(e)
Interpretation: Using the figure
Concept Introduction: The particles of a crystal are organized in an ordered, repeating, three-dimensional structure. The crystal system is a way of categorizing crystalline compounds based on the unit cell of the substance. There are seven different crystal systems.
(e)
Answer to Problem 78A
Three equal edges in the cubic crystal system meet at the right angles.
Explanation of Solution
The given figures are as follows:
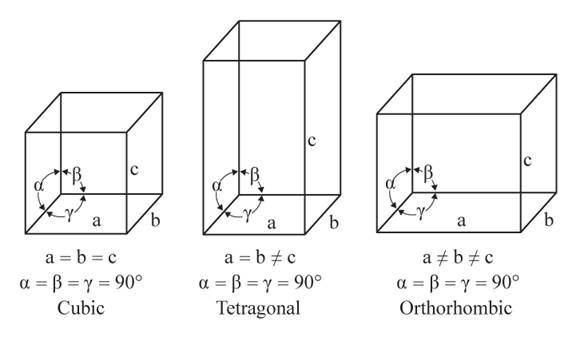
From the figure, the cubic, tetragonal, and orthorhombic crystal systems have edges that meet at right angles. Only the cubic crystal system has equal edges
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- Draw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPlease help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forward
- Can I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph, if you could show exactly where it needs to pass through please.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





