
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Solid are the chemical substance which are characterized by definite shape and volume, rigidity, density low compressibility. The constituent particles (atoms molecules or ions) are closely packed and held together by strong antiparticle forces.
Type of solid:
The solid are of two types crystalline solid and amorphous solids.
Unit cell:
The smallest geometrical portion of the crystal lattice which can be used as repetitive unit to build up the whole crystal is called unit cell.
Concept introduction:
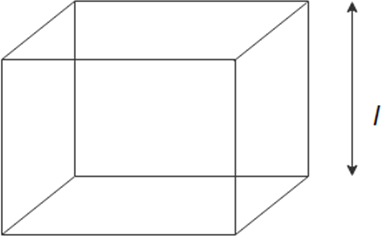
Side length , body diagonal
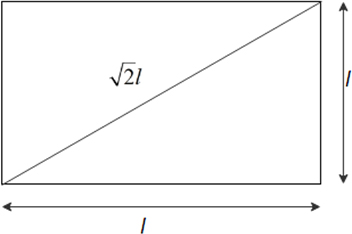
Diagonal of face of cube
To determine:
A tetrahedral site in a closed packed lattice is formed by four spheres at the corners of a regular tetrahedron. This is equivalent to placing the spheres at alternate corners of a cube. In such a closed packed arrangement the spheres are in contact and if the spheres have a radius , the diagonal hole is inside the middle of the cube. Find the length of the body diagonal of this cube and the radius of the tetrahedral hole.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties Custom Edition for Rutgers University General Chemistry
- You're competing on a Great British television game show, and you need to bake a cake. The quantity for each ingredient is given in grams, but you haven't been given a kitchen scale. Which of these properties would correlate with the mass of a baking ingredient like eggs or milk? Check all that apply. depth of color viscosity volume densityarrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for each of the following species. Again, assign charges where appropriate. a. H-H¯ b. CH3-CH3 c. CH3+CH3 d. CH3 CH3 e. CH3NH3+CH3NH3 f. CH30-CH3O¯ g. CH2CH2 - h. HC2-(HCC) HC2 (HCC) i. H202×(HOOH) H₂O₂ (HOOH) Nortonarrow_forwardIs molecule 6 an enantiomer?arrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forwardUse the vapor-liquid equilibrium data at 1.0 atm. for methanol-water (Table 2-8 ) for the following: If the methanol vapor mole fraction is 0.600, what is the methanol liquid mole fraction? Is there an azeotrope in the methanol-water system at a pressure of 1.0 atmospheres? If water liquid mole fraction is 0.350, what is the water vapor mole fraction? What are the K values of methanol and of water at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200? What is the relative volatility αM-W at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200?arrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. || |II***** Molecule 1 | Molecule 4 none of the above Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Х mm... C ---||| *** Molecule 5 Molecule 6arrow_forward
- is SiBr4 Silicon (IV) tetra Bromine? is KClO2 potassium dihypochlorite ?arrow_forward"יוון HO" Br CI Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Br Br Br HO OH H CI OH ✓ Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 CI Br יייון H Br OH OH CI Br ☐ none of the above × Garrow_forwardUS2 Would this be Uranium (II) diSulfide?arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





