
Interpretation:
Matter
(Physical substance in general which occupies space and possesses rest mass)
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| (1) A solid is a sample of matter that retains its shape and density when not confined. (2) Strong molecular force of attraction exist between atoms ions molecules. |
(1) A liquid is a sample of matter that conforms to shape of container in which it is held and which acquires a defined surface in the presence of gravity. (2) Weak molecular force of attraction exists between atoms/ions/molecule. |
(1) A gas is a sample of matter that conforms to the shape of container in which it is placed and acquire whole volume of container. (2) Negligible force of attraction exists between atoms/ion/molecules. |
Concept Introduction:
Physical change: physical change occurs when a substance alters its state , but does not change its chemical composition.
State of matter depends upon temperature and pressure. As temperature or pressure or both change then state of matter may also change.
Phase change: transition of a substance from one state to another state
Phase: it is defined as a homogenous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristic.
Draw initial temperature and pressure on phase diagram identify the initial phase similarly draw final temperature and pressure on phase diagram identify the final phase. After that you can decide which phase transition occurs.
To determine:
A sample of the substance in this phase diagram is initially at and . Which phase transition occurs when the pressure is decreased to at constant temperature?
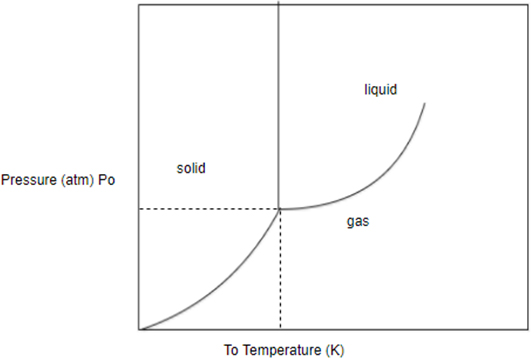
Solid to liquid.
Liquid to gas.
Solid to gas.
Liquid to solid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties Custom Edition for Rutgers University General Chemistry
- Briefly indicate the structure and bonding of silicates.arrow_forward4 Part C Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma.arrow_forwardTry: Draw possible resonance contributing structures for the following organic species: CH3CH2NO2 [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHCHO] [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHNH2]arrow_forward
- Complete the following synthesis. (d). H+ ง сarrow_forwardCan the target compound be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the substituted benzene of the starting material? If yes, draw the synthesis. Include all steps and all reactants.arrow_forwardThis is a synthesis question. Why is this method wrong or worse than the "correct" method? You could do it thiss way, couldn't you?arrow_forward
- Try: Draw the best Lewis structure showing all non-bonding electrons and all formal charges if any: (CH3)3CCNO NCO- HN3 [CH3OH2]*arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Draw all the major products. If there are no major products, then there is no reaction that will take place. Use wedge and dash bonds when necessary.arrow_forwardZeolites. State their composition and structure. Give an example.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and show all reactionsarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIX) By writing the appropriate electron configurations and orbital box diagrams briefly EXPLAIN in your own words each one of the following questions: a) The bond length of the Br2 molecule is 2.28 Å, while the bond length of the compound KBr is 3.34 Å. The radius of K✶ is 1.52 Å. Determine the atomic radius in Å of the bromine atom and of the bromide ion. Br = Br b) Explain why there is a large difference in the atomic sizes or radius of the two (Br and Br). Tarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





