
Interpretation:
The reaction when hydrogen chloride reacts with 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene to form 1-chloro-3-methyl-2-butene as a major product via 1,4-addition mechanism and no product formed by 1,2-additon, is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Free radical is an atom, molecule or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of hydrogen molecule is called hydrogenation reaction.
舧
舧 Hydrogenation with platinum as a catalyst is used to convert unsaturated carbohydrates to saturated hydrocarbons
舧 Oxidation of
舧 Ozonolysis helps convert the carbon–carbon double bonds to carbon–oxygen double bond (carbonyl compounds).
舧 Dimethyl sulfide is used as a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed into the carbonyl group.
舧 NBS (nitro-bromo succinimide) is a special reagent used for bromination of allylic carbocations.
舧 Bromine replaces the hydrogen attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbon bearing double bond.
舧 This method of using NBS can produce allylic bromides without bromine reacting with the double bond.
舧 Dehydration of a primary alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid like concentrated sulfuric acid results in the formation of alkene via E2 elimination.
舧 The stability of carbocation:
舧 The 1,2 – addition to a diene is the addition of an electrophile to the carbon designated as 1 and a nucleophile to the carbon designated as 2. The positions of carbons as 1 and 2 are not according to the IUPAC numbering of the molecule, but as a conjugated diene molecule. 1,4-addition results in addition of hydrogen to thee carbon designated as 1 and a halogen to the carbon designated as 4.
舧 The mechanism of 1,2 addition and 1,4-addition of hydro halogenation is given below:
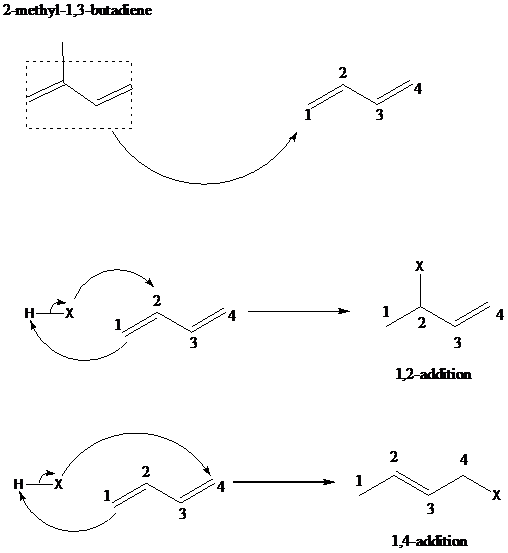
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 7. Use Pauling's electronegativity values (Table 1.7) and Ketelaar triangle (Fig. 2.28) to classify bonding in: (3 points) a) CIF3 b) ZnCl2 c) PbSarrow_forward7. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A) (R)-1-oxo-2-butanol C) (R)-2-hydroxybutanal E) (S)-1-formyl-1-propanol B) (S)-1-oxo-2-butanol D) (S)-2-hydroxybutanal OH Harrow_forwardCual es la formula semidesarrollada del 3-metil-1-butino?arrow_forward
- 2. A graph shown below shows first ionization energies for elements from H to Ne. First ionization energy/kJ mol 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 T T T T 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 Atomic number a) Using arguments of electronic structure, explain why ionization energy of Li is much lower than that of H. (2 points) then dips at O. b) Using the same arguments, explain why ionization energy increases from B to N, and (3 points)arrow_forwardGive the name of this compound, including stereochemistry if relevant: CICH2 CH3 Br CH₂CH=CH2 Write in the product, including stereochemistry where relevant, for these reactions. See end of ch. 8, p. 301-303. 1. 03 a) 2-methyl-2-pentene -> 2. Zn, H* Br2 b) 1-ethylcyclopentene -->arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- 3. You may want to read paragraph 1.5 in your textbook before answering this question. Give electron configuration (short-hand notation is fine) for: (5 points) 3+ a) Manganese atom and Mn³+ b) Se atom c) Cu atom and Cu+arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardHowever, why are intermolecular forces in metallic and ionic compounds not discussed as extensively? Additionally, what specific types of intermolecular attractions exist in metals and ionic compoundsarrow_forwardWhat is the preparation of 1 Liter of 0.1M NH4Cl buffer at pH 9.0 with solid NH4Cl and 0.1M NaOH. How would I calculate the math to describe this preparation? How would I use Henderson-Hasselbach equation?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





