
Concept explainers
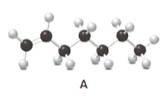
Answer the following questions about compound A, represent in the given ball-and-stick model.
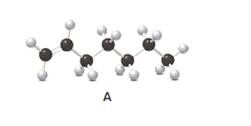
- Convert A to a condensed structure and give its IUPAC name.
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2 in the presence of metal catalyst?
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2O in the presence of H2SO4?
- What
polymer is formed when A ispolymerized ?
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the molecule A should be converted to a condensed structure and IUPAC name of the molecule should be given.
 = (
= (
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
In alkene nomenclature, the longest C chain will be considered as the parent/ main C chain. At the end of the alkane suffix -ene is added. The longest chain which includes the carbon-carbon double bond will be considered as the main carbon chain. The numbering of the main C chain is starting from the first substituent by giving the lower number to that substituent and as well as the double bond should get the lower number. All the substituents should be numbered and named. Two or more identical substituents should be indicated by using appropriate prefixes as di-. Names of the substituents should be alphabetized. Each substituent should have a position number which is mentioned in the main C chain.
Answer to Problem 13.103P
Condensed structure −
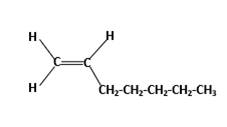
IUPAC name −Heptene
Explanation of Solution
In alkenes, there is a carbon-carbon double bond and different groups are connected to the two carbons. In most of the alkenes; out of four binding positions of carbon-carbon double bond, two of them are bind with two hydrogen atoms and the other two binding positions bind with two different alkyl groups. In this molecule, carbon atoms are represented in black and hydrogen atoms are represented in white color. The structure of a chemical compound is the arrangement of atoms and bonds in the space.
Condensed structure −
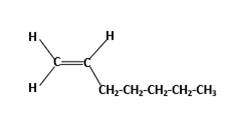
In this molecule, the main carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon double bond is a seven-membered chain and there are no substituents in this molecule. According to the numbering of the main chain double bond gets the lowest number and it is number 1. Hence, the IUPAC name of the molecule is heptene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 13.103P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.103P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction;
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting polymer should be identified after polymerization of
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond inside a molecule.
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules.
Answer to Problem 13.103P
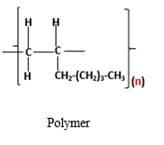
Explanation of Solution
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules. When forming polymers from alkene monomers, the weak bond which is in the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and new strong bond will form to connect the monomer molecules together. Hence; weak bond of the carbon-carbon double bond of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- In a Pt electrode, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density of an electrode is 0.79 mA cm-2. ¿Qué corriente flow across the electrode of área 5 cm2 when the difference in potential of the interface is +5 mV?.arrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V, indicate which of the 2 voltage formulas of the ley of Tafel must be applied i a a) == exp (1-B). xp[(1 - ß³): Fn Fn a b) == exp B RT RTarrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forward
- Topic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTwo cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forwardWith the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning


