
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The Lewis diagram for
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure shows the connectivity between atoms by identifying the lone pairs of electrons in a compound. Lewis structures are also known as Lewis dot structures. The valence electrons around an atom are shown by dots. Bonds between atoms are shown by lines and the lone pair of electrons is shown by a pair of dots.
Answer to Problem 10E
The Lewis diagram for
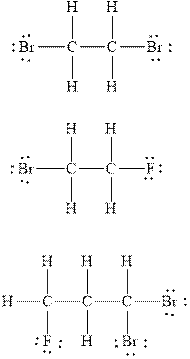
Explanation of Solution
The number of valence electrons in the carbon atom is
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
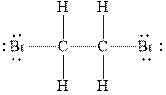
Figure 1
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
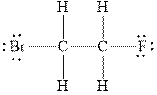
Figure 2
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bond between the carbon atoms surrounded by other atoms through single bonds is drawn. Each bond contains
Figure 3
The Lewis diagram for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- If I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when acetophenone reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile with a sulfonitric mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained in the reaction of p-Toluidine with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-methylbenzonitrile with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 2-nitrophenol with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


