
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron-pair geometry for the molecules,
Concept introduction:
The electron pairs in Lewis diagrams repel each other in real molecule and therefore, they distribute themselves in positions around the central atoms that are as far away from one another. This arrangement of electron pairs is known as electron-pair geometry. The electron pairs may be shared in covalent bond, or they may be lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 19E
The Lewis diagrams for
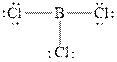

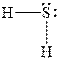
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for

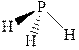
![]()
The electron pair geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule,
In the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In
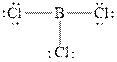
Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In
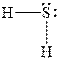
Figure 3
The electron-pair geometry depends on the number of electron pairs around the central atoms. In the molecule
In the molecule
In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule

Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
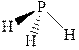
Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
![]()
Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry predicted by the valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory for the molecules
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the precise term that is used to describe the shape of molecules and arrangement of atoms around the central atom. The molecular geometry of a molecule is predicted by valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory or in short VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory applies to substances in which a second period element is bonded to two, three, four, or other atoms.
Answer to Problem 19E
The Lewis diagrams for
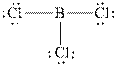

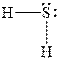
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for

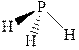
![]()
The molecular geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule,
In the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In

Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In
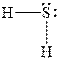
Figure 3
The molecular geometry depends on the number of electron pairs as well as number of unpaired electron on the central atoms. In the molecule
In the molecule
In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule

Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule
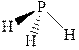
Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecule
![]()
Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forwardIdentify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forwardH- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forward
- Why doesn't this carry on to form a ring by deprotonating the alpha carbon and the negatively-charged carbon attacking the C=O?arrow_forward6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward7. Describe the expected 31P and 19F (where applicable) NMR spectral patterns for the following compounds (indicate number of signals and their splitting patterns). a) tetraphenyldiphosphine Ph Ph P-P Ph Ph Ph Ph ' b) tetraphenyldiphosphine monoxide P-P-Ph Ph (2 points) (2 points c) tetrafluorophosphonium hexafluorophosphate [PF4]*[PF6]¯ (4 points)arrow_forward3. For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ Which (if any) of these complexes would be expected to display Jahn-Teller distortion? (2 points)arrow_forward
- What is Instrumental Neutron Activation and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications? (I'm doing an in class assignment and need better understanding of what the instrument can be used for) Please include references so that I can better understand the application of how the instrument works!arrow_forwardWhat is Isotope Analysis and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications and instrumentalization? Please include references so that I can better understand how the instrument works!arrow_forward5. Count the electrons on the following complexes and state whether they follow the 18- electron rule: (3 points) Fe(CO)5 Ni(PMe3)4 PMe3 is trimethylphosphine Mn(CO)5Brarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


