
Concept explainers
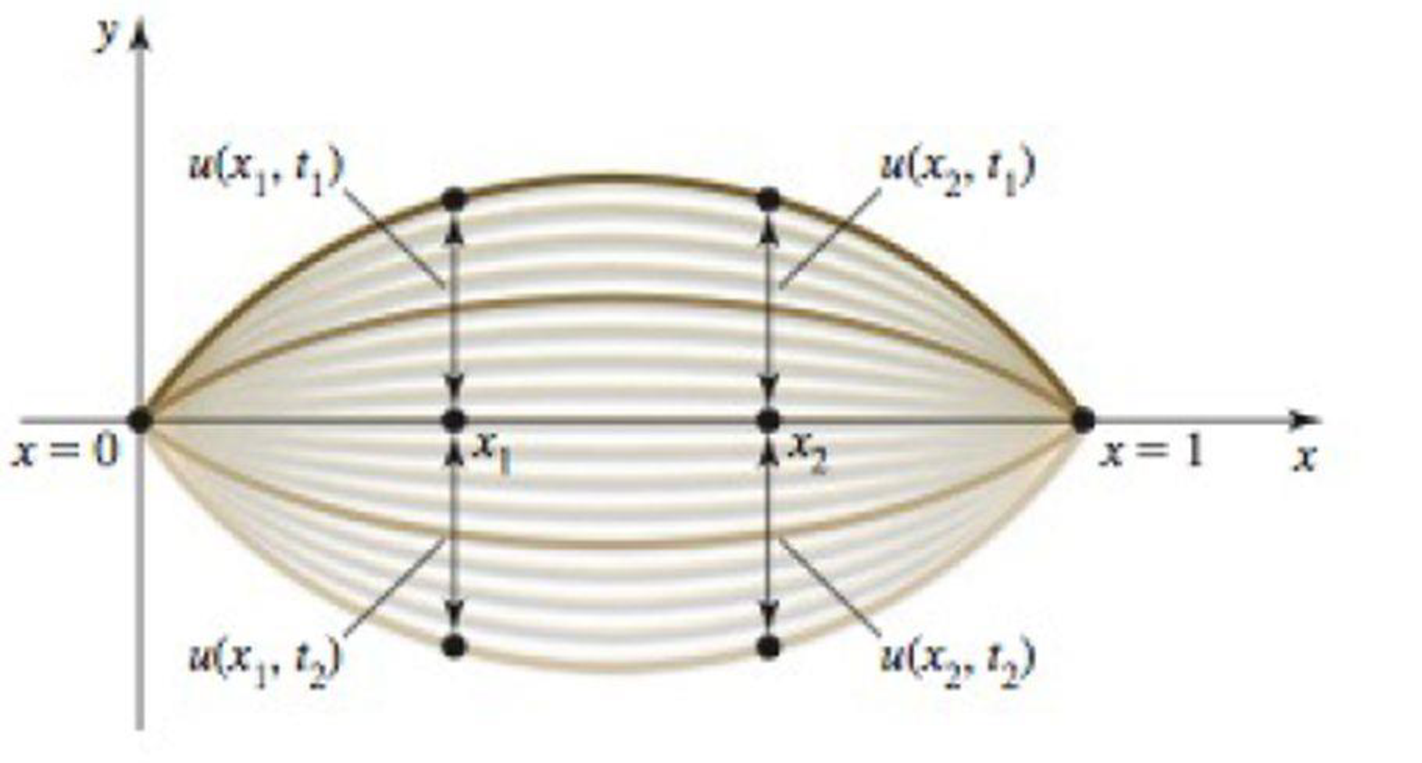
Wave on a string Imagine a string that is fixed at both ends (for example, a guitar string). When plucked, the string forms a standing wave. The displacement u of the string varies with position x and with time t. Suppose it is given by u = f(x, t) = 2 sin (πx) sin (πt/2), for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and t ≥ 0 (see figure). At a fixed point in time, the string forms a wave on [0, 1]. Alternatively, if you focus on a point on the string (fix a value of x), that point oscillates up and down in time.
a. What is the period of the motion in time?
b. Find the rate of change of the displacement with respect to time at a constant position (which is the vertical velocity of a point on the string).
c. At a fixed time, what point on the string is moving fastest?
d. At a fixed position on the string, when is the string moving fastest?
e. Find the rate of change of the displacement with respect to position at a constant time (which is the slope of the string).
f. At a fixed time, where is the slope of the string greatest?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 12 Solutions
CODE/CALC ET 3-HOLE
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Find the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 9.5%/year compounded monthly % (b) 9.5%/year compounded daily % Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER -/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.007. ASK YOUR TEACHE Find the present value of $90,000 due in 7 years at the given rate of interest. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) 9%/year compounded semiannually (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly LAarrow_forwardFind the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $160,000, r = 7%, t = 4, compounded daily A = $211113.60 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER --/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.005. Find the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 8%/year compounded semiannually % (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly %arrow_forwardFind the derivative of the function. g'(t) = 9t g(t) = In(t) (9ln(t) - 1) [In(t)] 2 × Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward
- Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $3800, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually A = $ 5645.60 × Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER [3.33/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES REVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER TANAPCALC10 5.3.001.EP. PRACTICE ANOTHER Consider the following where the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. P = $3,100, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually Determine m, the number of conversion periods per year. 2 Find the accumulated amount A (in dollars). (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) A = $ 4604.44arrow_forwardForce with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with a positive x axis, Draw the diagram representing this situationarrow_forwardI forgot to mention to you to solve question 1 and 2. Can you solve it using all data that given in the pict i given and can you teach me about that.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning

