
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “A single bond between carbon and nitrogen is polar” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The polar bond is a type of covalent bond. It is a bond in which the electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms because of which one atom becomes partially negative and the other becomes partially positive.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “A single bond between carbon and nitrogen is polar” is true.
Explanation of Solution
In the molecule of
Therefore, the
The given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “A bond between phosphorus and sulfur will be less polar than a bond between phosphorus and chlorine” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The polar bond is a type of covalent bond. It is a bond in which the electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms because of which one atom becomes partially negative and the other becomes partially positive.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “A bond between phosphorus and sulfur will be less polar than a bond between phosphorus and chlorine” is true.
Explanation of Solution
The strength of the polarity between bonds is based on the electronegativity of the bond. The difference in electronegativity between the atoms of phosphorus and chlorine is
On the other hand, the difference in electronegativity between the atoms of phosphorus and sulfur is
Therefore,
The given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “The electronegativity of calcium is less than the electronegativity of aluminum” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Electronegativity is defined as the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards it. Polarized bonds are a result of the electronegativity difference between bonding atoms. If the electronegativity difference is
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “The electronegativity of calcium is less than the electronegativity of aluminum” is true.
Explanation of Solution
Electronegativity is the capability of an atom to attract the shared pair of electron towards itself.
On moving left to right in a period, the electronegativity increases.
Since, calcium is a
Therefore, aluminum is more electronegative than calcium.
The given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Strontium
Concept introduction:
The ions or atoms which possess the same electron configuration are known as the isoelectronic species. The meaning of isoelectronic species is the species which contains the equal charge. The isoelectronic species shows the similar chemical properties.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “Strontium
Explanation of Solution
The isoelectronic species are those in which the number of electrons are same.
The electronic configuration of
The electronic configuration of
Since the number of electrons in
Therefore,
The given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “The monoatomic ion formed by selenium
Concept introduction:
The ions or atoms which possess the same electron configuration are known as the isoelectronic species. The meaning of isoelectronic species is the species which contains the equal charge. The isoelectronic species shows the similar chemical properties.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “The monoatomic ion formed by selenium
Explanation of Solution
The isoelectronic species are those in which the number of electrons are same.
The
Therefore, the statement “The monoatomic ion formed by selenium
The given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Most elements in Group
Concept introduction:
The monoatomic ion is one that is formed by a single atom. In a montoatomic ion, the number of protons and electrons are different. The difference in the number of protons and electrons gives the charge to the atom. When the number of proton is more then the atom attains a positive charge. When the number of electrons is more then the atom acquires a negative charge.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “Most elements in Group
Explanation of Solution
The elements of group
So, the statement “Most elements in Group
The given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Multiple bonds can form only between atoms of the same element” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The forces that holds various constituents such as atoms, ions or elements together and forms a chemical compound is known as chemical bonding.
The
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “Multiple bonds can form only between atoms of the same element” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The bonds between the different elements can be more than one. The example to this is the molecule of
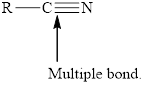
Figure 1
The Figure 1 shows
Therefore, the statement “Multiple bonds can form only between atoms of the same element” is false.
The given statement is false.
(h)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “If an atom is triple-bonded to another atom, it may still form a bond with one additional atom” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The forces that hold various constituents such as atoms, ions or elements together and forms a chemical compound is known as chemical bonding.
The chemical bonds hold together the atoms in the molecules.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “If an atom is triple-bonded to another atom, it may still form a bond with one additional atom” is true.
Explanation of Solution
In order to complete the octet, the triple bonded atoms can form bond with the other atom. The example to this is the molecule of
![]()
Figure. 2
In Figure 2, the carbon atom is triply bonded with nitrogen atom but still its octet is not complete. Therefore, to complete its octet, it forms a bond with the hydrogen atom.
So, the statement “If an atom is triple-bonded to another atom, it may still form a bond with one additional atom” is true.
The given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “An atom that conforms to the octet rule can bond to no more than three other atoms if one bond is a double bond” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The forces that hold various constituents such as atoms, ions or elements together and forms a chemical compound is known as chemical bonding.
The chemical bonds hold together the atoms in the molecules.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “An atom that conforms to the octet rule can bond to no more than three other atoms if one bond is a double bond” is true.
Explanation of Solution
When an atom attains eight electrons in its outermost shell then it is known to have a complete octet.
When the atom is bonded with the other atom with a double bond then it can form single bonds with only two other atoms and therefore, its octet will be completed.
So, the statement “An atom that conforms to the octet rule can bond to no more than three other atoms if one bond is a double bond” is true.
The given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Electrons are localized between atoms in a metal” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The substance that has high electrical conductivity and that readily donates electrons in order to attain a positive charge is defined as a metal. Most of the metals react with oxygen to produce oxides.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “Electrons are localized between atoms in a metal” is false.
Explanation of Solution
The electrons are present inside the atoms and not between the atoms. So, the localization of electrons between the atom is not possible.
Therefore, the statement “Electrons are localized between atoms in a metal” is false.
The given statement is false.
(k)
Interpretation:
Whether the statement “Alloys are pure substances” is true or false is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The fusion of two or more metals that chemically combines together is known as an alloy. The fusion of metal with a non-metal is also possible. An alloy is a homogenous mixture, so, it retains the properties of metal even when it is made up of a non-metal or metalloid.
Answer to Problem 42E
The statement “Alloys are pure substances” is false.
Explanation of Solution
An alloy is formed by a mixture of two or more metals or one metal and other non-metal. So, an alloy can not be pure, rather it is a mixture.
Therefore, the statement “Alloys are pure substances” is false.
The given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Iarrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forwardBe sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H :0: CH3 O: OH Q CH3OH2+ Draw Intermediate protonation CH3OH CH3OH nucleophilic addition H Draw Intermediate deprotonation :0: H3C CH3OH2* protonation H 0: H CH3 H.arrow_forwardPredicting the reactants or products of hemiacetal and acetal formation uentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X+Y OH H+ за Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ? olo 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardcan someone please answer thisarrow_forward
- Please, please help me figure out the the moles, molarity and Ksp column. Step by step details because I've came up with about three different number and have no idea what I'm doing wrong.arrow_forwardwhat reagents are used to get this product from this reactant? Br OCH3arrow_forwardcan someone answer this pleasearrow_forward
- can someone do the reaction mechanism for this reaction and draw the molecules for Q2 and q3arrow_forwardIn this question, the product of the aldol condensation is shown. What would be the reactants for this product? Please provide a detailed explanation, as well as a drawing showing how the reactants will react to produce the product.arrow_forward7. Propene undergoes a hydration reaction with water in the presence of an acid. a. There are two possible products for this reaction, both with the formula C,H,O. Show their structural formulas and names. (A1, B2) SCH4UR Name: (answer for part a. here!) VER 3 2021-2022 b. Which of the two products do you predict will form. Explain your choice using details from your learning. (B3)arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





