
Concept explainers
(a) Find both wattmeter readings in Fig. 12.39 if VA = 100∠0 ° V rms, VB = 50∠90° V rms, ZA = 10 − j10 Ω, ZB = 8 + j6 Ω, and ZC = 30 + j10 Ω. (b) Is the sum of these readings equal to the total power taken by the three loads? Verify your answer with an appropriate simulation.
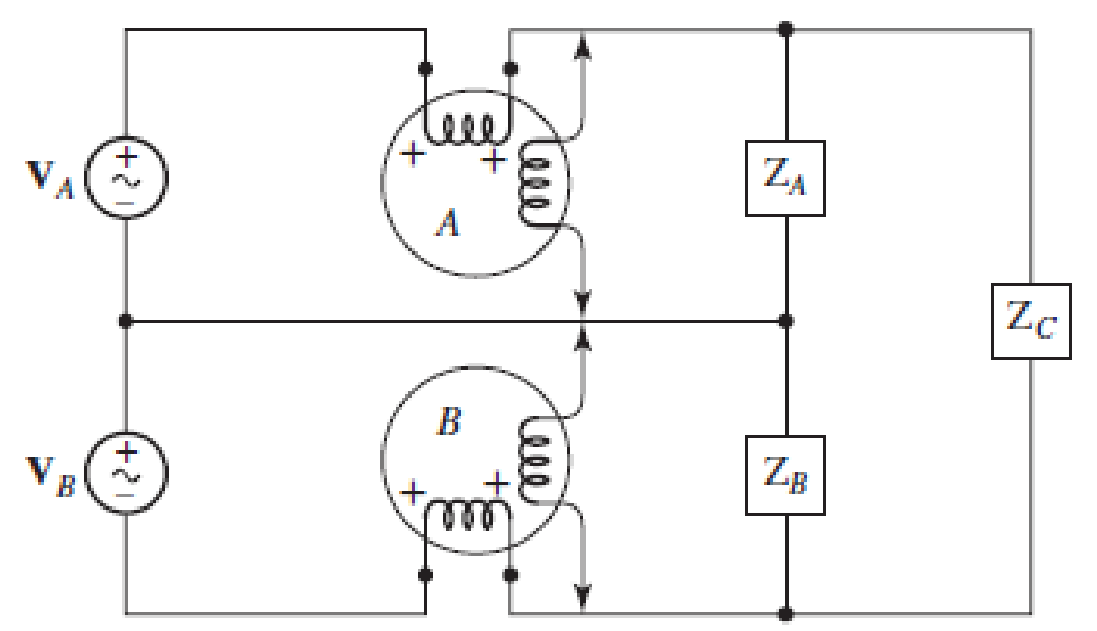
■ FIGURE 12.39
a.
Find the wattmeter readings in the circuit of Figure 12.39.
Answer to Problem 39E
The reading of wattmeter
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load impedance are
Calculation:
The given figure with mesh currents is shown in Figure 1.
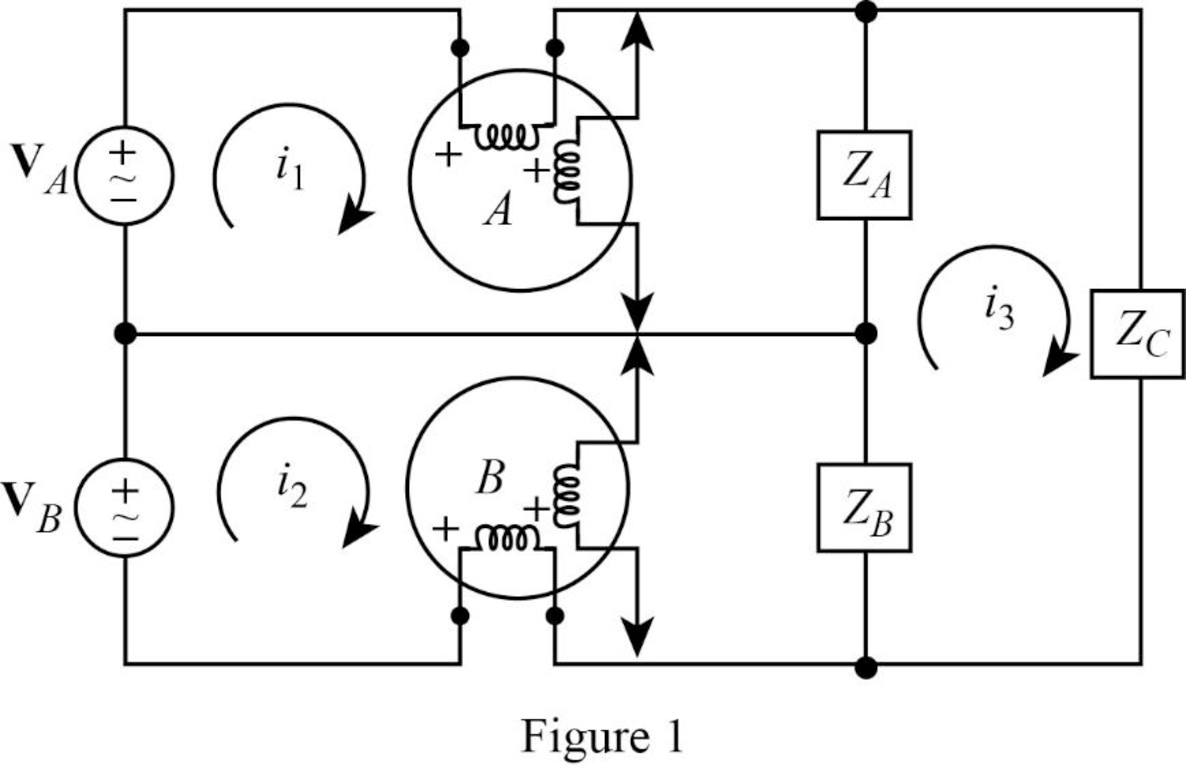
Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the loop with current
Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the loop with current
Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the loop with current
Rearrange equation (1).
Substitute equation (4) in (3).
Simplify the equation as follows.
Substitute equation (5) in (4).
Substitute equation (6) in (2).
Simplify the equation as follows.
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the power delivered by phase A as follows.
Calculate the power delivered by phase B as follows.
Conclusion:
Thus, the reading of wattmeter
b.
Verify that the sum of the wattmeter reading is equal to the total power taken by the three loads using LTspice.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Write the expression for inductive reactance.
Here,
Write the expression for capacitive reactance.
Here,
Calculation:
Let us assume that the angular frequency
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
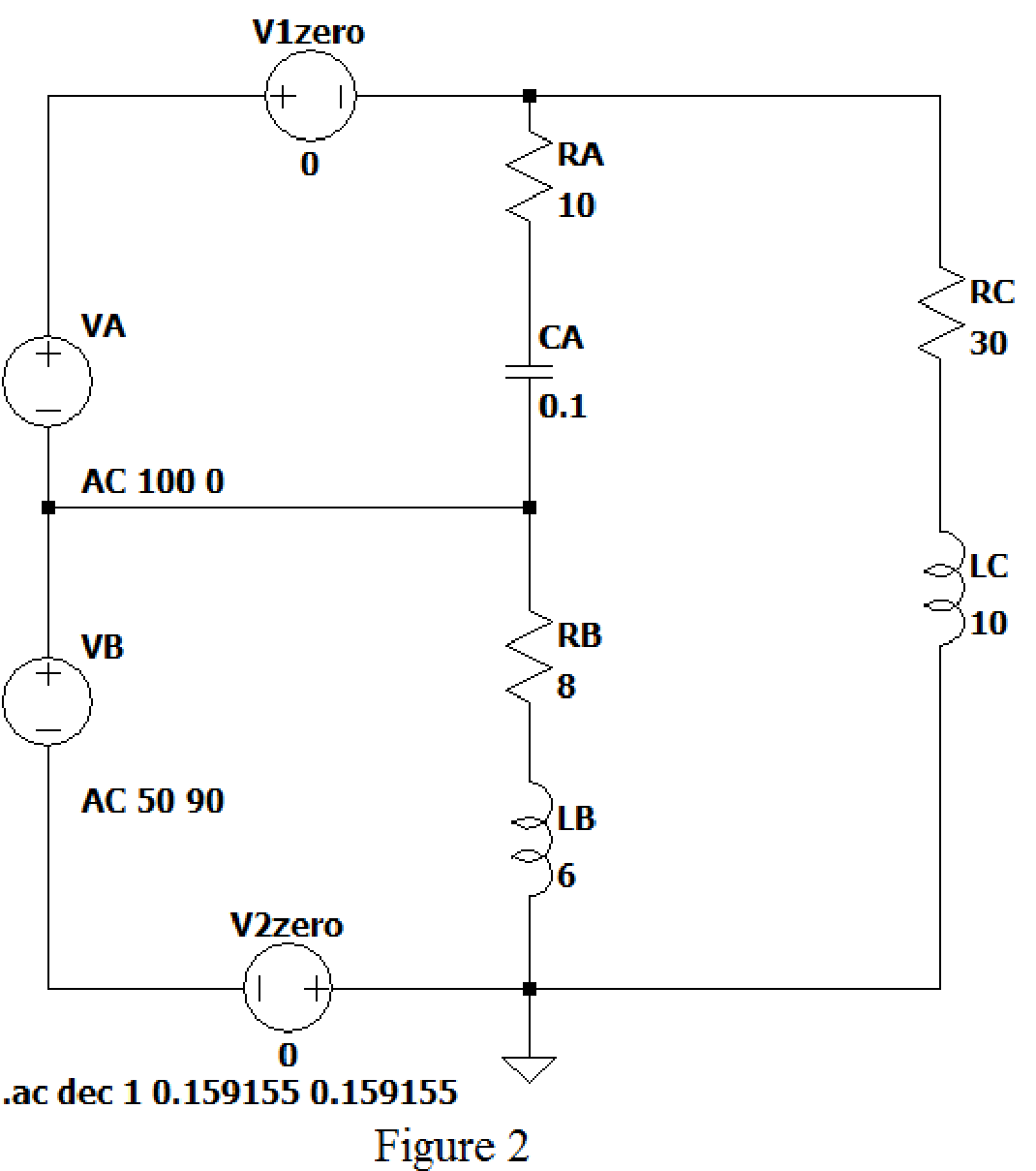
LTspice Simulation:
Draw the given figure in LTspice as shown in Figure 2. V1 zero and V2 zero connected in the circuit to find the current flows through it.
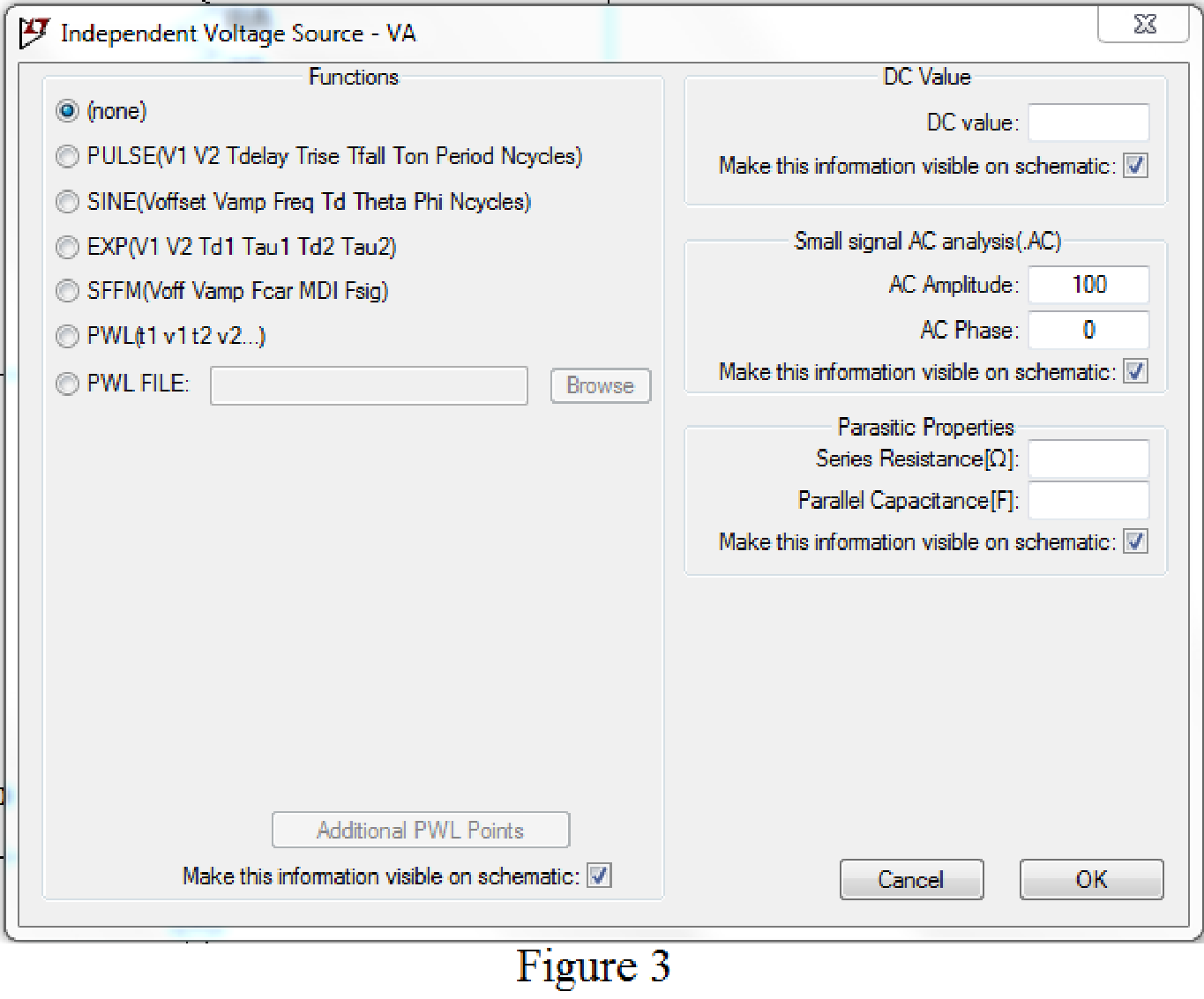
Set the values of voltages VA by right clicking on the voltage component, select none in “Functions” and enter the Small signal AC analysis parameters: AC amplitude as 100 for V1 as shown in Figure 3 for VA.
Now save the circuit, and open the “Edit Simulation command” choose AC analysis and select the sweep type as Decade, Number of points per decade 1, Start frequency and Stop frequency as 0.159155 Hz.
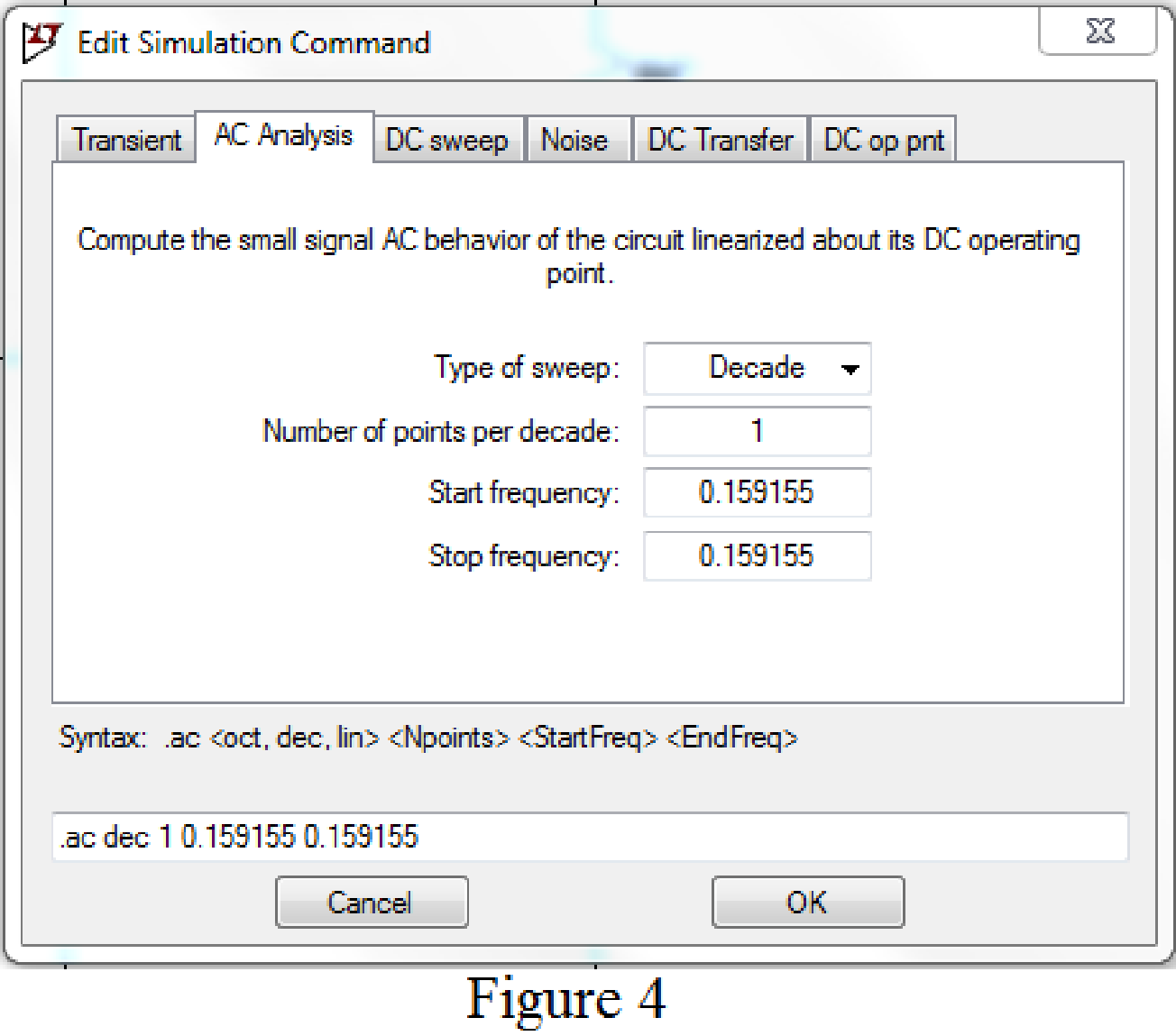
Now, run the simulation for the designed circuit. The output for the AC analysis will displays as shown in Figure 5.

From above simulation results, the current flows through the load resistance are given below.
Calculate the power delivered to load
Calculate the power delivered to load
Calculate the power delivered to load
The total power delivered to the load is
The sum of the wattmeter reading is
Conclusion:
Thus, it is verified that sum of the wattmeter reading is equal to the total power taken by the three loads using LTspice.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- A lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2. Answered now answer number 2. Repeat Q.1 but now assume the width of the pulse produced by the generator is 4 nS. Sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for 0 < t < 20 nS.arrow_forwardSolve this experiment with an accurate solution, please. Thank you.arrow_forwardA lossless uncharged transmission line of characteristic impedance Zo = 600 and length T = 1us is connected to a 180 load. If this transmission line is connected at t = 0 to a 90 V dc source with an internal resistance of 900, from a bounce diagram of this system sketch (a) the voltage at z=0, z=L, and z = L/2 for up to 7.25μs and (b) calculate the load voltage after an infinite amount of time.arrow_forward
- A lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2.arrow_forwardThe VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) is measured to be 2 on a transmission line. Find two values of the reflection coefficient with one corresponding to Z > Zo and the other to Zarrow_forwardA dc voltage of unknown value Vand internal resistance Reis connected through a switch to a lossless transmission line of Zo = 1000. If the first 5 μS of the voltages at z = 0 and z = L are observed to be as shown below, calculate Vo, RG, the load resistanceR,, and the transit time T. 100 + [V]:-0. V 90 [V]:-V 100 75 I, Տ 1,μs 2 4 6 0 2 4 6arrow_forwardA lossless open circuited transmission line behaves as an equivalent capacitance of Ceq = Tan (BL) Show for BL << 1 that Ceq = C'L where L is the length of the transmission line and wZo C' is the lumped parameter capacitance per unit length of the transmission line. Hint: For x small, Tan(x) = x.arrow_forward= A generator with VG 300V and R = 50 is connected to a load R = 750 through a 50 lossless transmission line of length L = 0.15 m. (a) Compute Zin, the input impedance of the line at the generator end. (b) Compute and V. (c) Compute the time-average power Pin delivered to the line. (d) Compute VL, IL, and the time-average power delivered to the load, PL (e) How does Pin compare to PL? Explain.arrow_forwardFor the regulated power supply circuit, assume regular diodes with 0.7V forward drop. Use a 15V (peak), 60Hz sine wave at the transformer secondary and assume a maximum ripple level of 1V. (a) Compute the unknown components needed to design 10V DC supply.Hint: find R first, and then C. What is the ripple level for C=22µF?Sketch the rectified, filtered, and regulated outputsarrow_forwardA) Find the solution of B) Find the convolution of Sewt (t-π)dt 8 e-atu(t)e-blu(t)arrow_forwardConsider the signal: f(t)= 0, ㅠ 1 Use the Fourier transform formula to find F(w). otherwisearrow_forwardA half-wave controlled rectifier is supplied by a 230 Vrms voltage source and has load resistance of 2502. Calculate the delay angle a that produces a load-absorbed power of 200W.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





