
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780073511191
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.68AP
Xylitol is a nontoxic compound as sweet as table sugar but with only one-third the calories, so it is often used as a sweetening agent in gum and hard candy.
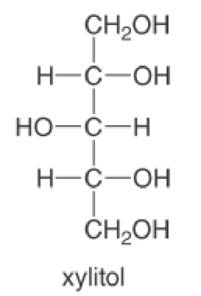
- a. Classify the OH groups as 1°, 2°, or 3°.
- b. What product is formed when only the 1° OH groups are oxidized?
- c. What product is formed when all of the OH groups are oxidized?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1. Classify the molecule shown according to the location of its carbonyl group and the
number of carbon atoms.
CH₂OH
C=O
PIL
a. Aldotriose
b. Aldotetrose
Aldopentose
d., Ketotriose
Ketotetrose
HO-C-H
L
CH₂OH
Determining Whether a Compound Is Oxidized or Reduced
Determine whether the organic compound is oxidized or reduced in each transformation.
Draw the products of each reaction.
OH
он
CH3
Cl2
FeCla
Cl2
a.
b.
С.
FeCl,
Chapter 12 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
Ch. 12.1 - a. Label the hydroxyl groups, thiols, halogens,...Ch. 12.1 - Draw out each compound to clearly show what groups...Ch. 12.2 - Classify each alcohol as 1, 2, or 3.Ch. 12.2 - Classify each hydroxyl group in sorbitol as 1, 2,...Ch. 12.2 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12.2 - Label each compound as water soluble or water...Ch. 12.2 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 12.2 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12.3 - Name each ether. a. CH3OCH2CH2CH2CH3 b....Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.10P
Ch. 12.3 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.12PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 12.13PCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.14PCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.6 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 12.17PCh. 12.8 - Give the IUPAC name for each aldehyde. a....Ch. 12.8 - Prob. 12.19PCh. 12.8 - Give the IUPAC name for each aldehyde depicted in...Ch. 12.8 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.8 - Prob. 12.22PCh. 12.8 - Acetone and progesterone are two ketones that...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 12.24PCh. 12.10 - Prob. 12.25PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.26PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.27PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.31PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.32PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.33UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.34UKCCh. 12 - Consider the following ball-and-stick model of an...Ch. 12 - Consider the following ball-and-stick model. a....Ch. 12 - Name each compound. a. CH3CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3Ch. 12 - Name each compound. a. CH3OCH2CH2CH3 b....Ch. 12 - Answer the following questions about alcohol A. a....Ch. 12 - Answer the following questions about alcohol B. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.41UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.42UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.43UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.44UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.45APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.46APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.47APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.48APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.49APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.50APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.51APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.52APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.53APCh. 12 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.55APCh. 12 - Draw structures for the four constitutional...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.57APCh. 12 - Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 12 - Explain why two four-carbon organic molecules have...Ch. 12 - Explain why the boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH...Ch. 12 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12 - Which compound in each pair is more water soluble?...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.63APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.64APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.65APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.66APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.67APCh. 12 - Xylitol is a nontoxic compound as sweet as table...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.69APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.70APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.71APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.72APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.73APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.74APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.75APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.76APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.77APCh. 12 - Draw the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.79APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.80APCh. 12 - What product is formed when each compound is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.82APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.83APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.84APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.85APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.86APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.87APCh. 12 - Label each of the following objects as chiral or...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.89APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.90APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.91APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.92APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.93APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.94APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.95APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.96APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.97APCh. 12 - How are the compounds in each pair related? Are...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.99APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.100APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.101APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.102APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.103APCh. 12 - Lactic acid [CH3CH(OH)CO2H] gives sour milk its...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.105APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.106APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.107CPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.108CPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.109BTCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.110BTC
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- List the products of each alcohol reaction. CH3 a. CH,-C-OH CH, NazCrO b. CH3-CH-CH;-CH2-OH c. CH-CH-OH +HCI -arrow_forwardA B 9 What is the missing reactant? CHF-d-OCH MgCl i. LDA 78°C THF [?] с D. La ---OCHarrow_forwardAmino acids such as glycine are the building blocks of large molecules called proteins that give structure to muscle, tendon, hair, and nails. a. Explain why glycine does not actually exist in the form with all atoms uncharged, but actually exists as a salt called a zwitterion. b. What product is formed when glycine is treated with concentrated HCl? c. What product is formed when glycine is treated with NaOH?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
GCSE Chemistry - Differences Between Compounds, Molecules & Mixtures #3; Author: Cognito;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jBDr0mHyc5M;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY