
Concept explainers
Classify each example of molecular art as a pure element, a pure compound, or a mixture.

(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular art has to be classified as a pure element, a pure compound or a mixture.
The given molecular art is,
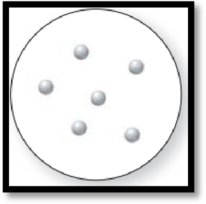
Figure 1
Concept Introduction:
Matter can be classified into two type’s namely pure substance and mixture.
Pure substance: A single component that has a constant composition, irrespective of the sample size and the sample origin is called as pure substance. A pure substance could not be broken down to other pure substances by any physical change.
Example: Water, sugar etc.
Element: A pure substance, which cannot be broken down into smaller substances by a chemical reaction is called as an element.
Example: Hydrogen gas, Magnesium ribbon and copper wire etc.
Mixture: A mixture consists of more than one substance and the composition of a mixture is dependent on the sample. The separation of mixture into its components can be done by physical changes.
Compound: A pure substance that is formed by combination of two or more elements by chemical process is called as a compound. Example: Sodium chloride is a compound because it is formed from elements sodium and chlorine.
Answer to Problem 1.31UKC
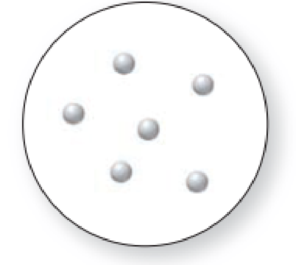
The given molecular art is a pure element.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular art is,
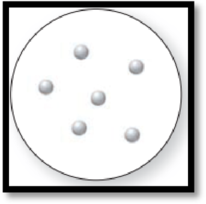
Figure 1
The molecular art shown above is a pure element because it comprises of only single entity.
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular art has to be classified as a pure element, a pure compound or a mixture.
The given molecular art is,
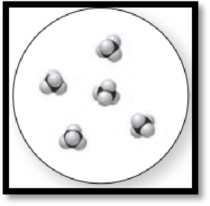
Figure 2
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Answer to Problem 1.31UKC
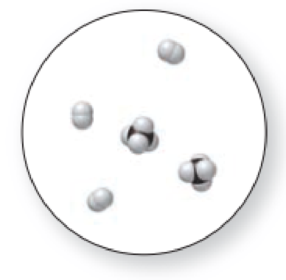
The given molecular art is a pure compound.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular art is,
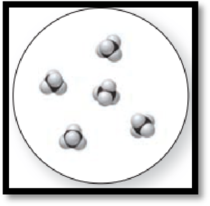
Figure 2
The given molecular art is a pure compound because it comprises of combination of two elements (one type of molecules).
(c)
Interpretation:
The molecular art has to be classified as a pure element, a pure compound or a mixture.
The given molecular art is,
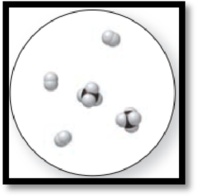
Figure 3
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Answer to Problem 1.31UKC
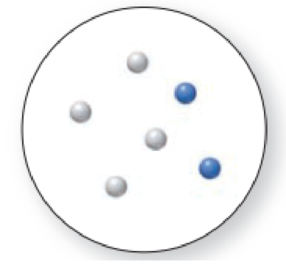
The given molecular is a mixture.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular art is,
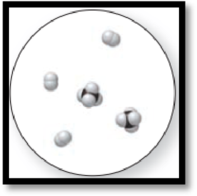
Figure 3
The molecular art shown above is a mixture because it comprises of more than one component (different types of molecules).
(d)
Interpretation:
The molecular art has to be classified as a pure element, a pure compound or a mixture.
The given molecular art is,

Figure 4
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Answer to Problem 1.31UKC
The given molecular art is a mixture.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular art is,

Figure 4
The molecular art shown above is a mixture because it consists of more than a single component (different types of atoms).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





