
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337705028
Author: Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.13P
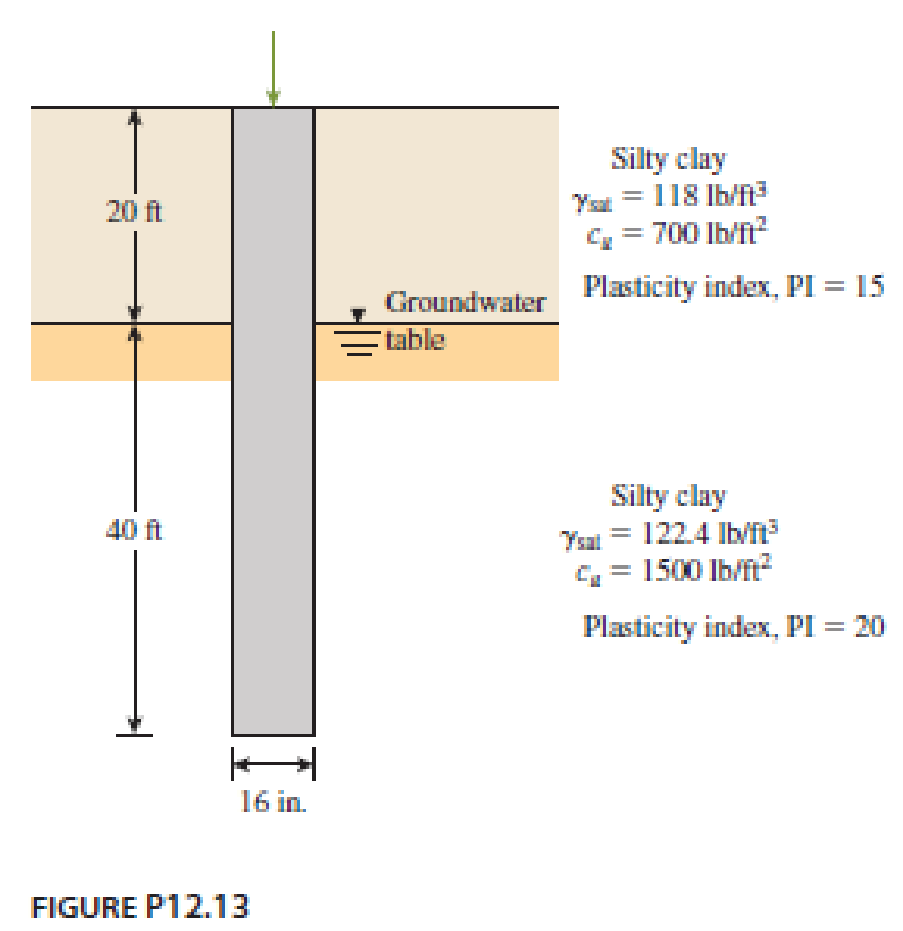
A concrete pile 16 in. × 16 in. in cross section is shown in Figure P12.13. Calculate the ultimate skin friction resistance by using the
- a. α method [use Eq. (12.61) and Table 12.11]
- b. λ method
- c. β method
Use
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Ex 11: Design inlet system for the road in figure below with
catchment area=86 m*239 m. C=0.8, i=100 mm/hr, Gutter data: y
max.=8cm, n=0.018, k=0.38, slope=%1, Z=25, %25 clogging,
(space=bar=2 cm). Inlet type used (consists of tow part curb and
Q grad inlet =0.6Qgutter max.
grade inlet) Q curb inlet =0.4Qgutter max.
0.8*100
3600*1000
Solution: (Qs) Total=CIA=
Qgutter (Max.)=k²√√s y8/3 = 0.38-
25
0.018
*(86*239)=0.457 m³/s
√0.01 0.088/3= 0.0627 m³/s
30 m
12 m
2mL
12 m
30 m
Residence
30 m
Streat
12 m
Bof
2 m
ㅈ
239 m
A2
A1
(20
02 A concrete beam of rectangular cross-section (300 x 400) mm is Prestressed with
wires located at (30) mm from the top of the beam .The wires are initially tensioned to
0-6 mm) diameter wires at (100) mm from the soffit of the beam and (5-6 mm)
a stress of (900 N/mm²). Compute the percentage loss of stress in steel after transfer due
to elastic deformation of concrete.
Given: Es=200 x 103 N/mm², Ec = 25 x 10³ N/mm².
300
за
60000
400
100
546
2046
Reinforced Concrete Design
First Monthly Exam
24/02/2
Q1. A simply supported rectangular beam (300 x 400) mm and span (12) m with live load of
from the soffit of the beam. Compute the stresses at mid-span of beam for the following
(5 kN/m). At the centre of the beam the prestressing force of (120) kN is located at (50 mm)
conditions:
(a) Prestress + self- weight of beam (initial stage).
(b) Prestress + self- weight of beam + Live Load (service stage).
3:00
400
120
K
*
12m
5kN/m.
120 KN
Chapter 12 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12 - A 20 m long concrete pile is shown in Figure...Ch. 12 - A 500 mm diameter are 20 m long concrete pile is...Ch. 12 - Redo Problem 12.3 using Coyle and Castellos...Ch. 12 - A 400 mm 400 mm square precast concrete pile of...Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum load that can be allowed on...Ch. 12 - A driven closed-ended pile, circular in cross...Ch. 12 - Consider a 500 mm diameter pile having a length of...Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum load that can be allowed on...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.10P
Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.11PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.12PCh. 12 - A concrete pile 16 in. 16 in. in cross section is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.14PCh. 12 - Solve Problem 12.13 using Eqs. (12.59) and...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.17PCh. 12 - A steel pile (H-section; HP 310 125; see Table...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.19PCh. 12 - A 600 mm diameter and 25 m long driven concrete...Ch. 12 - Redo Problem 12.20 using Vesics method, assuming...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.22PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.23PCh. 12 - Solve Problem 12.23 using the method of Broms....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.25PCh. 12 - Solve Problem 12.25 using the modified EN formula....Ch. 12 - Solve Problem 12.25 using the modified Danish...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12 - Figure 12.49a shows a pile. Let L = 15 m, D (pile...Ch. 12 - Redo Problem 12.30 assuming that the water table...Ch. 12 - Refer to Figure 12.49b. Let L = 18 m, fill = 17...Ch. 12 - Estimate the group efficiency of a 4 6 pile...Ch. 12 - The plan of a group pile is shown in Figure...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.35PCh. 12 - Figure P12.36 shows a 3 5 pile group consisting...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.37P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A driven pipe pile in clay is shown in Figure (1). The pipe has outside diameter of 406 mm, and wall thickness is 6.35 mm. a. calculate the net point bearing capacity. b. calculate the skin resistance (1) by using a method, (2) by using A method. e. Estimate the net allowable pile capacity. Use FS-4. Figure (1) 5 m Saturated clay 30 kN/m² Groundwater table y= 18 kN/m 5 m Clay C-30 kN/m2 y= 18 kN/m 20 m C Clay -100 kN/m² 19.6 kN/marrow_forwardA fully embeded precast, prestressed concrete pile is 12 m long and is driven into homogeneous layer of sand. The pile is square in cross section, with sides measuring 305 mm. The dry unit weight of sand is 16.8 kN/m, and the average effective soil friction angle is 35°. The allowable working load is 338 kN. If 240 kN is contributed by the frictional resistance and 98 kN is from the point load, determine the elastic settlement of the pile. Use Ep 21 x 10 kN/m², E, 30000 kN/m², and μ-0.3.arrow_forwardA 15 in. x 26 in. rectangular RC beam (shown in figure below) supports a service uniform deadload of 1.3 kip/ft and a service uniform live load of 1.6 kip/ft. The dead load includes the beam’sself-weight. Design the reinforcement required for maximum moments and show the design insketches. Use f c ’ = 4,000 psi and f y = 60,000 psi. The beam is used in an open parking garage andis exposed to weather.a. Find factored maximum bending moments.b. Design for max. negative moment.c. Design for max. positive moment.Hint: Assume an initial beam shape (b, d), then solve for the needed reinforcements at the maximumnegative and positive factored bending momearrow_forward
- A structure is an intersecting hip roof with the main hip roof outside dimensions being 73 ft long and the width being 30 ft wide. The intersection portion extends 20 ft beyond the 30-ft side, and the intersecting portion is 20 ft wide. The overhang is 2 ft 6 in. and the slope is 5:12. The rafters are 16 in. on center. Based on the information provided, what is the total length of the common rafters in linear feet?arrow_forwardHow many board feet is 200 lnft of 2 in. × 6 in wood studs.arrow_forwardExample: Determine the minimum slope in the upper reach of a chute section of 30 m width. The range of discharge is 150 to 2000 m³/sec. n = 0.015.arrow_forward
- 1. Zinc is an important trace nutrient for photosynthetic organisms (e.g., phytoplankton) in sea water. Calculate the speciation of zinc (Zn(II)) in seawater assuming Zn(II) TOT = 5 x 10-8 M. Provide a list of the metal-ligand complexes and their corresponding stability Constants that you will include in your calculation. If you decide to exclude any of the complexes for which stability constants are provided in Table 9.4, please list these separately and explain your rationale. b. Compute the concentrations of the metal-ligand complexes identified in part a. c. Compute the activities of the metal-ligand complexes using the concentrations calculated in part b and using the data in Table 9.6B to calculate the activity coefficients. (Note—you likely already have a spreadsheet where you calculated activity coefficients from week 3!)arrow_forwardQ.2 The required design span for the beam given in Q.1 is increased to 18 ft. The design loads are the same as given in Q.1 Check the adequacy of a 10"x16" 10 Caribbean Pitch Pine – (Select Structural) for this these design conditions.arrow_forwardThe timber floor framing for a building comprise floor joists using 2" wide nominal lumber is to be constructed as shown in Fig. 1. The Dead load (D) = 26 lbs./ft² (inclusive of joists and flooring) and the live load L= 40 lbs./ft². Lateral torsional buckling is prevented for all members and normal service conditions and temperatures are expected. (i) Design the floor joists using 2" wide nominal lumber using Southern Pine No. 1 (ii) Design the floor beams using Caribbean Pitch Pine (Select Structural). (Assume a 8" x 14” trial section to estimate beam self-weight for your initial design). Density of Caribbean Pitch Pine = 50 lbs/ft³ (800 kN/m³).arrow_forward
- P12.38 WP At a point on the free surface of a stressed body, a normal stress of 64 MPa (C) and an unknown positive shear stress exist on a horizontal plane. One principal stress at the point is 8 MPa (C). The absolute maximum shear stress at the point has a magnitude of 95 MPa. Determine the unknown stresses on the horizontal and vertical planes and the unknown principal stress at the point.arrow_forwardA pile group of 25 piles has to be proportioned in a uniform pattern in soft clay with equal spacing in all directions. Assuming the value of cu to be constant throughout the depth of the piles, determine the optimum value of spacing of piles in the group. Assume a = 0.7. Neglect point bearing effect, and assume the piles to be circular.arrow_forwardExample 5 By using the yield line theory, determine the moment (m) for an isotropic reinforced concrete two-way slab (supports on two S.S sides shown in figure under the load (P) (all dimensions are in mm). Solve by using equilibrium method m m 3000 2000 2000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Concrete Slab Calculations 006; Author: Jerry Howard;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R19jILyBxio;License: Standard Youtube License