
The decomposition of sulfuryl chloride,
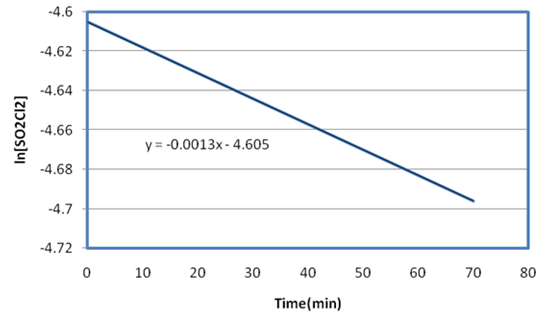
(a) Plot the data to show that the reaction is first-order.
(b) From the graph, determine k.
(c) What is the half-life of the decomposition?
(d) Using k from (b), find the time it takes to decrease the concentration to 0.00427 M.
(e) What is the rate of decomposition
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- 2. 200 LOD For an unknown compound with a molecular ion of 101 m/z: a. Use the molecular ion to propose at least two molecular formulas. (show your work) b. What is the DU for each of your possible formulas? (show your work) C. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 4 2 (ppm) 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI-11arrow_forwardComplete the spectroscopy with structurearrow_forwardComplete the spectroscopy with structurearrow_forward
- Given the following concentrations for a system, calculate the value for the reaction quotient: Cl2(g)+ CS2(g) ⇌ CCl4(g)+ S2Cl2(g) Cl2 = 31.1 atm CS2 = 91.2 atm CCl4 = 2.12 atm S2Cl2 = 10.4 atmarrow_forwardMatch each chemical or item with the proper disposal or cleanup mwthod, Not all disposal and cleanup methods will be labeled. Metal sheets C, calcium, choroide solutions part A, damp metal pieces Part B, volumetric flask part A. a.Return to correct lables”drying out breaker. Place used items in the drawer.: Rinse with deionized water, dry as best you can, return to instructor. Return used material to the instructor.: Pour down the sink with planty of running water.: f.Pour into aqueous waste container. g.Places used items in garbage.arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction: HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + NO2-(aq)arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





