
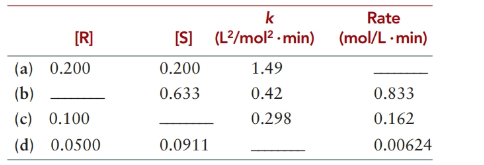
Complete the following table for the reaction
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 17QAP
Rate of reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Here the given chemical reaction is:
It is given that reaction is first order with respect to R and second order with respect with S. Thus, rate law for above reaction will be:
Here we have:
Concentration of R=0.200 M
Concentration of S = 0.200 M
Rate constant =1.49 L2/mol2.min
Rate of reaction = let it ‘r’
Plugging value in rate law expression:
(b)
Interpretation:
To determine the concentration of R in given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 17QAP
Concentration of R is
Explanation of Solution
Here the given chemical reaction is:
It is given that reaction is first order with respect to R and second order with respect with S. Thus, rate law for above reaction will be:
Here we have:
Concentration of R= let it ‘[R]’ mol/L
Concentration of S = 0.633 mol/L
Rate constant =0.42 L2/mol2.min
Rate of reaction = 0.833 mol/L.min
Plugging value in rate law expression:
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the concentration of S in given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 17QAP
Concentration of S is
Explanation of Solution
Here the given chemical reaction is:
It is given that reaction is first order with respect to R and second order with respect with S. Thus, rate law for above reaction will be:
Here we have:
Concentration of R= 0.100 mol/L
Concentration of S = let it ‘[S]’ mol/L
Rate constant = 0.298 L2/mol2.min
Rate of reaction = 0.162 mol/L.min
Plugging value in rate law expression:
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate constant in the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 17QAP
Rate constant is
Explanation of Solution
Here the given chemical reaction is:
It is given that reaction is first order with respect to R and second order with respect with S. Thus, rate law for above reaction will be:
Here we have:
Concentration of R= 0.0500 mol/L
Concentration of S = 0.0911 mol/L
Rate constant = let it ‘k’ L2/mol2.min
Rate of reaction = 0.00624 mol/L.min
Plugging value in rate law expression:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- When two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forwardCalculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forward
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
- Using Luther's rule, determine the reference potentials of the electrodes corresponding to the low stability systems Co³+/Co and Cr²+/Cr from the data in the table. Electrodo ΕΝ Co²+/Co Co3+/Co²+ -0,28 +1,808 Cr³+ / Cr -0,508 Cr3+ / Cr²+ -0,41arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6tt electrons and is there pore aromuntre and is Assigned the Following structure contenus Since aromatk moleculey undergo electrophilic allomatic substitution, Pyridine should undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this roaction Based upon the reaction the reaction mechanism determine which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materia Show how each of the Following molecules could Ve synthesked 9. CHI d. 10450 b 0 -50311 ८ City -5034 1-0-650 e NO2arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





