
The schematic of a single-flash geothermal power plant with state numbers is given in Fig. P10–69. Geothermal resource exists as saturated liquid at 230°C. The geothermal liquid is withdrawn from the production well at a rate of 230 kg/s and is flashed to a pressure of 500 kPa by an essentially isenthalpic flashing process where the resulting vapor is separated from the liquid in a separator and is directed to the turbine. The steam leaves the turbine at 10 kPa with a moisture content of 5 percent and enters the condenser where it is condensed; it is routed to a reinjection well along with the liquid coming off the separator. Determine (a) the power output of the turbine and the thermal efficiency of the plant, (b) the exergy of the geothermal liquid at the exit of the flash chamber, and the exergy destructions and the second-law efficiencies for (c) the turbine and (d) the entire plant.
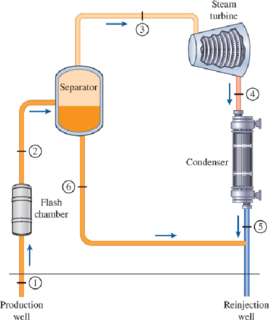
FIGURE P10–69
(a)
The temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of flash chamber is
Answer to Problem 69P
The power output turbine is
The thermal efficiency of the plant is
Explanation of Solution
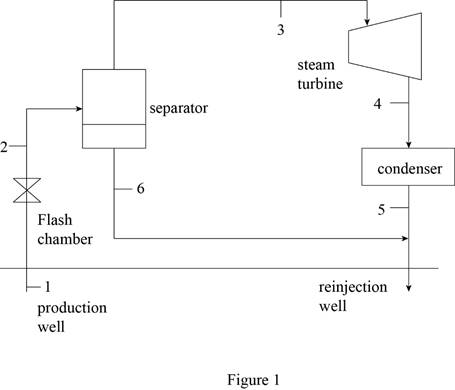
Draw schematic diagram of single flash geothermal power plant as shown in Figure 1.
Write the general energy rate balance equation.
Here, the rate of total energy in is
Consider the system operates at steady state. Hence, the rate of change in net energy of the system becomes zero.
The Equation (I) is reduced as follows.
Refer Figure 1.
The flash chamber is nothing but the expansion valve. At expansion valve, the enthalpy kept constant.
Express the energy balance equation for the flash chamber.
Express the energy balance equation for the separator.
Express the energy balance equation for the turbine.
At state 1:
The geothermal water is extracted at the state of saturated liquid at the temperature of
The enthalpy and entropy at state 1 is as follows.
Refer Table A-4, “Saturated water-Temperature table”
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-1, “Molar mass, gas constant, and critical-point properties”.
At state 2:
The exit pressure of the flash chamber is
The geothermal steam is flashed at constant enthalpy. The exit steam of the flash chamber is at the quality of
Here, the fluid enthalpy is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
The entropy
Write the formula for mass flow rate of vapor at entering the turbine.
Here, the mass flow rate is
At state 3:
There is no pressure drop in the separator. The separator separates vapor and liquid form the flashed steam, and the separated vapor alone sent to the turbine.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 4:
The steam is at the state of saturated mixture at the pressure of
The quality at state 4 is as follows.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
At state 6:
The saturated water only exits at the bottom of the separator. The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
Write the formula for net energy input of the plant.
Write the formula for thermal efficiency.
Consider, the surrounding temperature is
The surrounding enthalpy
Refer Table A-4, “Saturated water-Temperature table”.
The enthalpy
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (VII).
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (III).
Thus, the power output turbine is
Substitute
Equation (IX).
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of the plant is
(b)
The exergy of the geothermal liquid at the exit of the flash chamber, and the exergy destructions.
Answer to Problem 69P
The exergy of the geothermal liquid at the exit of the flash chamber, and the exergy destruction is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for exergy of the steam at their respective process state.
Here, the enthalpy is
Write the formula for rate of exergy destruction at the exit of flash chamber (state 6).
Here, the rate of exergy destruction at state 6 is
Conclusion:
For process state 1:
Substitute
For process state 2:
Substitute
For process state 3:
Substitute
For process state 4:
Substitute
For process state 6:
Substitute
The mass flow rate of water at the bottom exit of separator (state 6) is expressed as follows.
Substitute
Thus, the exergy of the geothermal liquid at the exit of the flash chamber, and the exergy destruction is
(c)
The exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the turbine.
Answer to Problem 69P
The exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the turbine is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for rate of exergy destruction of the turbine.
Write the formula for second law of efficiency of the turbine.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the turbine is
(d)
The exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the entire plant.
Answer to Problem 69P
The exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the plant is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for rate of exergy input of the plant.
Write the formula for rate of exergy destruction of the plant.
Write the formula for second law of efficiency of the plant.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction and second law of efficiency for the plant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS (LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- I don't know how to solve thisarrow_forwardQuestion 2 (40 Points) Consider the following double pendulum-like system with links ₁ and 12. The angles 0 and & could have angular velocities ėêk and êk, respectively, where ②k is a unit vector that points out of the page and is perpendicular to x and y. They could also have angular accelerations Ök and êk. The angle is defined relative to the angle 0. The link 12 is a spring and can extend or compress at a rate of 12. It can also have a rate of extension or compression Ï2. li y êr1 êe 12 χ 3 еф er2 ده لج 1) Express the velocity of the mass in terms of the unit vectors ê0, êr1, êø, and êr2, and any extension/contraction of the links (e.g.,. i; and Ï¿) (12 Points) 2) Express the acceleration of the mass in terms of the unit vectors ê¤, ê×1, êp, and êÃ2, and any extension/contraction of the links (e.g.,. İ; and Ï¿) (12 Points) 3) Express the velocity of the mass in terms of unit vectors î and ĵ that point in the x and y directions, respectively. Also include the appropriate,…arrow_forwardprovide step by step solutions for angles teta 3 and teta 4 by the vector loopmethod. Show work in: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure.arrow_forward
- (Manometer) A tank is constructed of a series of cylinders having diameters of 0.35, 0.30, and 0.20 m as shown in the figure below. The tank contains oil, water, and glycerin and a mercury manometer is attached to the bottom as illustrated. Calculate the manometer reading, h. 0.11 m + SAE 30 Oil 0.13 m + Water 0.10 m Glycerin + 0.10 m Mercury h = marrow_forwardP = A piston having a cross-sectional area of 0.40 m² is located in a cylinder containing water as shown in the figure below. An open U-tube manometer is connected to the cylinder as shown. For h₁ = 83 mm and h = 111 mm what is the value of the applied force, P, acting on the piston? The weight of the piston is negligible. Hi 5597.97 N P Piston Water Mercuryarrow_forwardStudent Name: Student Id: College of Applied Engineering Al-Muzahmiyah Branch Statics (AGE 1330) Section-1483 Quiz-2 Time: 20 minutes Date: 16/02/2025 Q.1. A swinging door that weighs w=400.0N is supported by hinges A and B so that the door can swing about a vertical' axis passing through the hinges (as shown in below figure). The door has a width of b=1.00m and the door slab has a uniform mass density. The hinges are placed symmetrically at the door's edge in such a way that the door's weight is evenly distributed between them. The hinges are separated by distance a=2.00m. Find the forces on the hinges when the door rests half-open. Draw Free body diagram also. [5 marks] [CLO 1.2] Mool b ర a 2.0 m B 1.0 marrow_forward
- For the walking-beam mechanism shown in Figure 3, find and plot the x and y coordinates of the position of the coupler point P for one complete revolution of the crank O2A. Use the coordinate system shown in Figure 3. Hint: Calculate them first with respect to the ground link 0204 and then transform them into the global XY coordinate system. y -1.75 Ꮎ Ꮎ 4 = 2.33 0242.22 L4 x AP = 3.06 L2 = 1.0 W2 31° B 03 L3 = 2.06 P 1 8 5 .06 6 7 P'arrow_forwardThe link lengths, gear ratio (2), phase angle (Ø), and the value of 02 for some geared five bar linkages are defined in Table 2. The linkage configuration and terminology are shown in Figure 2. For the rows assigned, find all possible solutions for angles 03 and 04 by the vector loop method. Show your work in details: vector loop, vector equations, solution procedure. Table 2 Row Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 Link 4 Link 5 λ Φ Ө a 6 1 7 9 4 2 30° 60° P y 4 YA B b R4 R3 YA A Gear ratio: a 02 d 05 r5 R5 R2 Phase angle: = 0₂-202 R1 05 02 r2 Figure 2. 04 Xarrow_forwardProblem 4 A .025 lb bullet C is fired at end B of the 15-lb slender bar AB. The bar is initially at rest, and the initial velocity of the bullet is 1500 ft/s as shown. Assuming that the bullet becomes embedded in the bar, find (a) the angular velocity @2 of the bar immediately after impact, and (b) the percentage loss of kinetic energy as a result of the impact. (c) After the impact, does the bar swing up 90° and reach the horizontal? If it does, what is its angular velocity at this point? Answers: (a). @2=1.6 rad/s; (b). 99.6% loss = (c). Ah2 0.212 ft. The bar does not reach horizontal. y X 4 ft 15 lb V₁ 1500 ft/s 0.025 lb C 30°7 B Aarrow_forward
- subject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. In a joule cycle, intake of the compressor is 40,000 cfm at 0.3 psig and 90 deg F. The compression ratio is 6.0 and the inlet temperature at the turbine portion is 1900R while at the exit, it is 15 psi. Calculate for the back work ratio in percent.arrow_forwardsubject: combustion please include complete solution, no rounding off, with diagram/explanation etc. A gasoline engine, utilizing cold air, recorded a work of 431 BTU/lb at a maximum temperature of 3,273 K and 1112 deg F temperature at the beginning of constant volume heat addition. What is the compression ratio?arrow_forwardsubject: combustion please do step by step solution and no rounding off, complete solution with diagram/explanation if needed etc. thank you! Air enters the compressor at 101,320 Pascals, 305.15K, and leaves at a pressure of 0.808MPa. The air is heated to 990.15K in the combustion chamber. For a net output of 2,125,000 Watts, find the rate of flow of air per second.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
