
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.4.22P
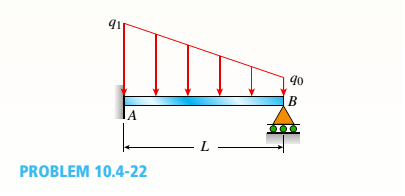
A propped cantilever beam with a length L = 4 m is subjected to a trapezoidal load with intensities q0= 10 kN/m and q1 = 15 kN/m. Find the reactions at A and B. Hint: The loading is the sum of uniform and triangular loads.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
cutting
Instructions:
Do not copy the drawing.
Draw In third-angle orthographic projection, and to scale 1:1,
the following views of the hinge:
A sectional front view on A-A
A top view
⚫ A right view (Show all hidden detail)
Show the cutting plane in the top view
. Label the sectioned view
Note:
All views must comply with the SABS 0111 Code of Practice for
Engineering Drawing.
Galaxy A05s
Assessment criteria:
⚫ Sectional front view
026
12
042
66
[30]
11
10
1. Plot the moment (M), axial (N), and shear (S) diagrams as functions of z.
a)
b)
F₁ = 1250 N
F₁ = 600 N
M₁ = 350 000 N mm
F2 = 500 N
200 N
a = 600 mm
b=1000 mm
a=750 mm
b = 1000 mm
d)
M₁ = 350 000 N mm
F₁ = 600 N
F₂ =200 N
a = 600 mm
b = 1000 mm
M₁ 175 000 Nmm
F = 900 N
a-250 mm
b-1000 mm
-250 mm.
Figure 1: Schematics problem 1.
Given the following cross-sections (with units in mm):
b)
t=2
b=25
h=25
t = 1.5
b=20
b=25
t=2
I
t = 1.5
a=10
b=15
h-25
b=15
t=3
T
h=25
Figure 3: Cross-sections for problem 2.
1. For each of them, calculate the position of the centroid of area with respect to the given coordinate system
and report them in the table below.
2. For each of them, calculate the second moments of inertia I...
and I, around their respective centroid
of area and report them in the table below. Note: use the parallel axes theorem as much as possible to
minimize the need to solve integrals.
Centroid position
x
y
box
Moment of inertia
lyy
by
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever steel beam is constructed...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn is subjected to a point load at...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L is...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L supports a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam AB of a length L has a fixed...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam of a length L and loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam has a length L and is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by a...
Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn of a length L is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A counterclockwise moment M0acts at the midpoint...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to uniform...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.3-15 using L = 3.5 m, max = 3...Ch. 10 - A two-span, continuous wood girder (E = 1700 ksi)...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB carries point load P acting at...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 10 - -4-4 A cantilever beam is supported at B by cable...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L carries...Ch. 10 - A beam with a sliding support at B is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L with a...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at /l,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at A,...Ch. 10 - Beam AB has a pin support at A and a roller...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABCD has a pin support at B:...Ch. 10 - Two flat beams AB and CD, lying in horizontal...Ch. 10 - -4-13 A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is loaded...Ch. 10 - Determine the fixed-end moments (MAand MB) and...Ch. 10 - A continuous beam ABC wit h two unequal spans, one...Ch. 10 - Beam ABC is fixed at support A and rests (at point...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam has flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 10 - A triangularly distributed 1oad with a maximum...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam is loaded by a uniform load q =...Ch. 10 - Uniform load q = 10 lb/ft acts over part of the...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam with a length L = 4 m is...Ch. 10 - A cant i levé r b ea m i s supported by a tie rod...Ch. 10 - The figure shows a nonprismatic, propped...Ch. 10 - A beam ABC is fixed at end A and supported by beam...Ch. 10 - A three-span continuous beam A BCD with three...Ch. 10 - A beam rests on supports at A and B and is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to two...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A temporary wood flume serving as a channel for...Ch. 10 - Two identical, simply supported beams AB and CD...Ch. 10 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure is an...Ch. 10 - The beam AB shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a fixed support at A,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pinned support at...Ch. 10 - A wide-flange beam ABC rests on three identical...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A beam supporting a uniform load of intensity q...Ch. 10 - A thin steel beam AB used in conjunction with an...Ch. 10 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.4-41 for the loading shown in...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by two...Ch. 10 - A cable CD of a length H is attached to the third...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam, fixed at the left-hand...Ch. 10 - Solve t he preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - A two-span beam with spans of lengths L and L/3 is...Ch. 10 - Solve the preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - Assume that the deflected shape of a beam AB with...Ch. 10 - (a) A simple beam AB with length L and height h...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1: Analyze the canard-wing combination shown in Fig. 1. The canard and wing are made of the same airfoil section and have AR AR, S = 0.25, and = 0.45% 1. Develop an expression for the moment coefficient about the center of gravity in terms of the shown parameters (, and zg) and the three-dimensional aerodynamic characteristics of the used wing/canard (CL C and CM). 2. What is the range of the cg location for this configuration to be statically stable? You may simplify the problem by neglecting the upwash (downwash) effects between the lifting surfaces and the drag contribution to the moment. You may also assume small angle approximation. Figure 1: Canard-Wing Configuration.arrow_forwardProblem 2: Consider the Boeing 747 jet transport, whose layout is shown in Fig. 2 and has the following characteristics: xoa 0.25, 8 5500/2, b 195.68ft, 27.31ft, AR, 3.57, V = 0.887 Determine the wing and tail contributions to the CM-a curve. You may want to assume CM, reasonable assumptions (e.g., -0.09, 0, -4°. i=0.0°, and i = -2.0°. Make any other 0.9).arrow_forwardZ Fy = 100 N Fx = 100 N F₂ = 500 N a = 500 mm b = 1000 mm Figure 2: Schematics for problem 3. 1. Draw the moment (M), axial (N), and shear (S) diagrams. Please note that this is a 3D problem and you will have moment (M) and shear (S) along two different axes. That means that you will have a total of 5 diagrams.arrow_forward
- An ideal gas with MW of 29 g/mol, cp = 1.044 kJ/kgK and c₁ = 0.745 kJ/kgK contained in a cylinder-piston assembly initially has a pressure of 175 kPa, a temperature of 22°C, and a volume of 0.30 m³. It is heated slowly at constant volume (process 1-2) until the pressure is doubled. It is then expanded slowly at constant pressure (process 2-3) until the volume is doubled. Draw a figure of the system and the PV diagram showing each state and the path each process takes. Determine the total work done by the system and total heat added (J) in the combined process.arrow_forwardplease explain each method used, thank youarrow_forwardDetermine the resultant loadings acting on the cross sections at points D and E of the frame.arrow_forward
- please read everything properly... Take 3 4 5 hrs but solve full accurate drawing on bond paper don't use chat gpt etc okk.... Not old solutions just new solvearrow_forwardplease box out or highlight all the answersarrow_forwardWhat are some ways Historical Data can be used and applied to an estimate?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY