
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.4.15P
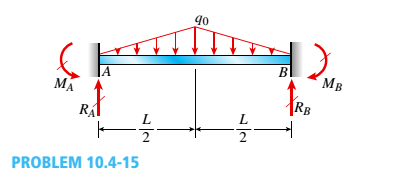
Determine the fixed-end moments (MAand MB) and fixed-end forces (R4and Rs) for a beam of length L supporting a triangular load of maximum intensity q0(see figure). Then draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams, labeling all critical ordinates.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
please solve and show work
Water is boiling in a 25 cm diameter aluminum pan (k=237 W/mK) at 95 degrees C. Heat is transferred steadily to the boiling water in the pan through its .5 cm thick flat bottom at a rate of 800 W. if the inner surface temp of the bottom of the pan is 108 degrees C determine the boiling heat transfer coefficent on the inner surface of the pan and the outer surface temp of the bottom of the pan.
please solve and show work
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever steel beam is constructed...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn is subjected to a point load at...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L is...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L supports a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam AB of a length L has a fixed...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam of a length L and loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam has a length L and is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by a...
Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn of a length L is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A counterclockwise moment M0acts at the midpoint...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to uniform...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.3-15 using L = 3.5 m, max = 3...Ch. 10 - A two-span, continuous wood girder (E = 1700 ksi)...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB carries point load P acting at...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 10 - -4-4 A cantilever beam is supported at B by cable...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L carries...Ch. 10 - A beam with a sliding support at B is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L with a...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at /l,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at A,...Ch. 10 - Beam AB has a pin support at A and a roller...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABCD has a pin support at B:...Ch. 10 - Two flat beams AB and CD, lying in horizontal...Ch. 10 - -4-13 A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is loaded...Ch. 10 - Determine the fixed-end moments (MAand MB) and...Ch. 10 - A continuous beam ABC wit h two unequal spans, one...Ch. 10 - Beam ABC is fixed at support A and rests (at point...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam has flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 10 - A triangularly distributed 1oad with a maximum...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam is loaded by a uniform load q =...Ch. 10 - Uniform load q = 10 lb/ft acts over part of the...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam with a length L = 4 m is...Ch. 10 - A cant i levé r b ea m i s supported by a tie rod...Ch. 10 - The figure shows a nonprismatic, propped...Ch. 10 - A beam ABC is fixed at end A and supported by beam...Ch. 10 - A three-span continuous beam A BCD with three...Ch. 10 - A beam rests on supports at A and B and is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to two...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A temporary wood flume serving as a channel for...Ch. 10 - Two identical, simply supported beams AB and CD...Ch. 10 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure is an...Ch. 10 - The beam AB shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a fixed support at A,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pinned support at...Ch. 10 - A wide-flange beam ABC rests on three identical...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A beam supporting a uniform load of intensity q...Ch. 10 - A thin steel beam AB used in conjunction with an...Ch. 10 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.4-41 for the loading shown in...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by two...Ch. 10 - A cable CD of a length H is attached to the third...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam, fixed at the left-hand...Ch. 10 - Solve t he preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - A two-span beam with spans of lengths L and L/3 is...Ch. 10 - Solve the preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - Assume that the deflected shape of a beam AB with...Ch. 10 - (a) A simple beam AB with length L and height h...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please solve and show workarrow_forwardA thin plastic membrane separates hydrogen from air. The molar concentrations of hydrogen in the membrane at the innner and outer surfaces are determined to be 0.045 and 0.002 kmol/m^3 respectiveley. The binary diffusion coefficent of hydrogen in plastic at the operation temp is 5.3*10^-10 m^2/s. Determine the mass flow rate of hydrogen by diffusion through the membrane under steady conditions if the thickeness of the membrane is 2mm and 0.5 mm.arrow_forwardCalculate the vertical cross section moment of inertia for Orientations 1 and 2. State which number is the higher moment of inertia using equation 1. Given: b1=1 in, h1=1.5 in, b2=1.5 in, h2=1 in, t=0.0625 in. Then calculate the maximum deflection for a point load of 8 lb on the free end of the beam using equation 2. Given: E=10.1*10^6 psi. 1. ((bh^3)/12) - (((b-2t)(h-2t)^3))/12) 2. S = (PL^3)/(3EI)arrow_forward
- 1-69E The pressure in a natural gas pipeline is measured by the manometer shown in Fig. P1-69E with one of the arms open to the atmosphere where the local atmospheric pressure is 14.2 psia. Determine the absolute pressure in the pipeline. Natural Gas 10 in 6 in FIGURE P1-69E Mercury SG= 13.6 Air 2 in + 25 in Waterarrow_forwardB 150 mm 120 mm PROBLEM 15.193 The L-shaped arm BCD rotates about the z axis with a constant angular velocity @₁ of 5 rad/s. Knowing that the 150-mm- radius disk rotates about BC with a constant angular velocity @2 of 4 rad/s, determine (a) the velocity of Point A, (b) the acceleration of Point A. Answers: V₁ =-(0.600 m/s)i + (0.750 m/s)j - (0.600 m/s)k a=-(6.15 m/s²)i- (3.00 m/s²)jarrow_forward3 Answer: 002 PROBLEM 15.188 The rotor of an electric motor rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 1800 rpm. Determine the angular acceleration of the rotor as the motor is rotated about the y axis with a constant angular velocity 2 x of 6 rpm counterclockwise when viewed from the positive y axis. α = (118.4 rad/s²)iarrow_forward
- 12 in.. 10 in. PROBLEM 15.187 At the instant considered the radar antenna shown rotates about the origin of coordinates with an angular velocity @ = ai + @j+wk Knowing that (VA) = 15 in./s, (VB), 9 in./s, and (VB), = 18 in./s, determine (a) the angular velocity of the antenna, (b) the velocity of point A. B 10 in. Answers: = (0.600 rad/s)i - (2.00 rad/s) j + (0.750 rad/s)k V₁ = (20.0 in./s)i + (15.00 in./s) j + (24.0 in./s)karrow_forward3. An engine has three cylinders spaced at 120° to each other. The crank torque diagram can be simplified to a triangle having the following values: Angle 0° Torque (Nm) 0 (a) What is the mean torque? 60° 4500 180° 180° to 360° 0 0 (b) What moment of inertia of flywheel is required to keep the speed to within 180 ± 3 rpm? (c) If one cylinder of the engine is made inoperative and it is assumed that the torque for this cylinder is zero for all crank angles, determine the fluctuation in speed at 180rpm for the same flywheel. (a) 3375 Nm (b) 50kgm (c) ±21 rpmarrow_forwardProb 5. Determine the largest load P that can be applied to the frame without causing either the average normal stress or the average shear stress at section a-a to exceed o-150 MPa and 1-60 MPa, respectively. Member CB has a square cross section of 25 mm on each side. 2 m FAC 1.5 m Facarrow_forward
- Derive the component transformation equations for tensors shown below where [C] = [BA] is the DCM (direction cosine matrix) from frame A to B. ^B [T] = [C]^A [T] [C]^Tarrow_forwardCalculate for the vertical cross section moment of inertia for both Orientations 1 and 2 of a 1 x 1.5 in. horizontal hollow rectangular beam with wall thickness of t = 0.0625 in. Use the equation: I = ((bh^3)/12) - (((b-2t)(h-2t)^3)/12)arrow_forwardPlease answer 'yes' or 'no' and 'is' or 'is not' for the following:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C-FEVzI8oe8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bending Stress; Author: moodlemech;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QIqewkE6xM;License: Standard Youtube License