
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.4.27P
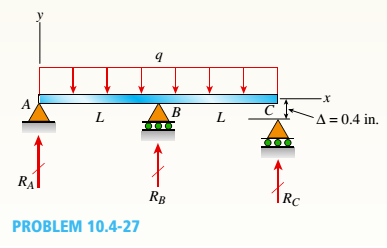
A beam rests on supports at A and B and is loaded by a distributed load with intensity q as shown. A small gap
Hint: See Example 9-9 for guidance on computing the deflection at C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Part A
The man pulls on the rope with a force of F = 30 N as shown in (Figure 1).
Figure
1.5 m
3 m.
4m
10.5 m
1 of 1
Determine the position vector from O to A.
Express the x, y, and z components of the position vector in meters to three significant figures separated by commas.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
vec
(TOA). (TOA)y. (TOA)==
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
m
Determine the position vector from O to B.
Express the x, y, and z components of the position vector in meters to three significant figures separated by commas.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
↓↑ vec
(TOB)x, (TOB)y, (TOB) =
Submit
Request Answer
Part C Complete previous part(s)
Provide Feedback
?
m
4
Part A
The tool is used to shut off gas valves that are difficult to access (Figure 1).
Figure
0.25 m
30
0,4 m
<
1 of 1
If the force F= {-60i+40j+15k} N is applied to the handle, determine the component of the moment created about the z axis of the valve.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Mz
=
Value
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
| ?
Units
3. A steam power plant has an average monthly net power delivery of 740 MW over the course of
a year. This power delivery is accomplished by burning coal in the boiler. The coal has a heating
value of 9150 Btu/lbm. The cost of the coal is $14.20/ton. The overall thermal efficiency of the
plant is,
nth
Wnet
Qboiler
0.26 = 26%
Determine the annual cost of the coal required to deliver the given average monthly power.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever steel beam is constructed...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn is subjected to a point load at...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L is...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L supports a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam AB of a length L has a fixed...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam of a length L and loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A cantilever beam has a length L and is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by a...
Ch. 10 - A fixed-end b earn of a length L is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam of a length L is loaded by...Ch. 10 - A counterclockwise moment M0acts at the midpoint...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length L is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to uniform...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.3-15 using L = 3.5 m, max = 3...Ch. 10 - A two-span, continuous wood girder (E = 1700 ksi)...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB carries point load P acting at...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 10 - -4-4 A cantilever beam is supported at B by cable...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam AB of a length L carries...Ch. 10 - A beam with a sliding support at B is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L with a...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at /l,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pin support at A,...Ch. 10 - Beam AB has a pin support at A and a roller...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABCD has a pin support at B:...Ch. 10 - Two flat beams AB and CD, lying in horizontal...Ch. 10 - -4-13 A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam of a length 2L is loaded...Ch. 10 - Determine the fixed-end moments (MAand MB) and...Ch. 10 - A continuous beam ABC wit h two unequal spans, one...Ch. 10 - Beam ABC is fixed at support A and rests (at point...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam has flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 10 - A triangularly distributed 1oad with a maximum...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam is loaded by a uniform load q =...Ch. 10 - Uniform load q = 10 lb/ft acts over part of the...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam with a length L = 4 m is...Ch. 10 - A cant i levé r b ea m i s supported by a tie rod...Ch. 10 - The figure shows a nonprismatic, propped...Ch. 10 - A beam ABC is fixed at end A and supported by beam...Ch. 10 - A three-span continuous beam A BCD with three...Ch. 10 - A beam rests on supports at A and B and is loaded...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is subjected to two...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by a...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A temporary wood flume serving as a channel for...Ch. 10 - Two identical, simply supported beams AB and CD...Ch. 10 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure is an...Ch. 10 - The beam AB shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a fixed support at A,...Ch. 10 - The continuous frame ABC has a pinned support at...Ch. 10 - A wide-flange beam ABC rests on three identical...Ch. 10 - A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A beam supporting a uniform load of intensity q...Ch. 10 - A thin steel beam AB used in conjunction with an...Ch. 10 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.4-41 for the loading shown in...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam is loaded by two...Ch. 10 - A cable CD of a length H is attached to the third...Ch. 10 - A propped cantilever beam, fixed at the left-hand...Ch. 10 - Solve t he preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - A two-span beam with spans of lengths L and L/3 is...Ch. 10 - Solve the preceding problem by integrating the...Ch. 10 - Assume that the deflected shape of a beam AB with...Ch. 10 - (a) A simple beam AB with length L and height h...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cable exerts a force of P = 4 kN at the end of the 8-m-long crane boom. A P 8 m B -x- I'm En ▾ Part A If 0 = 30°, determine the placement x of the boom at B so that this force creates a maximum moment about point O. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. x = 9.81 m Submit Previous Answers ✓ Correct ▾ Part B What is this moment? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is counterclockwise. (Mo) max 43.7 = E ? N Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 28 attempts remaining Enter your answer with a different unit type. Review a list of acceptable units.arrow_forwardFind highest and lowest temperature.arrow_forwardExplained step by step.arrow_forward
- The bevel gear shown in is subjected to the force F which is caused from contact with another gear. Part A F (201+8j 15k) N 40 mm Determine the moment of this force about the y axis of the gear shaft. Express your answer with the appropriate units. My = Value Submit Request Answer ? Units 30 mmarrow_forwardConsider the beam in. Part A 1.5 ft 200 lb 200lb 2 ft 30° 1.25 ft 30° If F 90 lb, determine the resultant couple moment. = Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures. Assume the positive direction is counterclockwise. ΑΣΦ vec MR = Submit Request Answer ? lb.ftarrow_forward4. An operating parameter often used by power plant engineers is the heat rate. The heat rate is defined as, HR Qbioler Wnet where Qbioler is the heat transfer rate (Btu/h) to the water in the boiler due to the combustion of a fuel and Wnet is the net power (kW) delivered by the plant. In comparison, the thermal efficiency of the power plant is defined as, nth Wnet Qbioler where the numerator and denominator have the same units. Consider a power plant that is delivering 1000 MW of power while utilizing a heat transfer rate of 3570 MW at the boiler. Determine the heat rate and thermal efficiency of this power plant.arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the sketch is subjected to tensile torsional and bending loads Determine the principal stresses at the location of stress concentration ✓ D=45MR F=3MM 1000-M 1000N チ d=30mm 500N 150 мм MM- 120 MA-arrow_forwardcalculate moment of inertia of this tapered beam structurearrow_forwardThe system shown below is in statics equilibrium. Cable OB lies in the xy plane and makes a 30° angle with the positive x-axis. Cable OA lies along the negative y-axis. If the weight of the load being supported is 100 lb, determine the magnitude of the forces in all four cables: OA, OB, OC, and OD.arrow_forward
- This is a mechanics/statics problem involving finding internal reactions, V(x) and M(x). Please refer to image for details. I'm not sure about where to take cuts and how to formulate the equations as a function of x. For my support Reactions I got Ay = 1008.33 lb, By = 1416.67 lb and Cy = 175 lb. and for the first cut V(x) = 1008.33 -250(x) and M(x) = 1008.33x - 125x^2. I'm struggling with the equations for the 2nd and 3rd cut.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, a ring is used to suspend a load and is supported by Cable OA and Spring OB. Given that the tension in Cable OA is 400 N, what is the weight of the load being supported? Assume the system is in static equilibrium.arrow_forward4. (a) State the conditions that must be met to ensure dynamic balance is achieved for long rotors. (b) A rotor carries three out-of-balance discs in planes A, B and C as shown in Figure 4. The out-of- balance mass x radius products of the rotor discs are tabulated in Table 4. The shaft is to be dynamically balanced by adding balancing masses in planes P and Q, spaced along the shaft at a distance da = 800 mm. Determine the magnitude mara and angular position of the balancing mass x radius product that must be added to plane Q. MBB Ов θε mdc Мага End View on Plane P P MBB MATA dA dB dc do Figure 4 moc Table 4 MATA = 0.6 kg mm 6A = 0° d₁ = 200 mm mers = 0.2 kg mm 6g = 45° dB = 400 mm mcrc = 0.4 kg mm Bc=240° dc = 600 mm Ans. (b) = 110.5°, moro = 0.2 kg mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY