
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
Concept introduction:
The linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO) states that two atomic orbitals combine together to form a new orbital which is known as bonding molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital theory also states that two atoms combines together to form a molecule. During the formation of a molecule, the electrons are shared between two atoms to form a
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
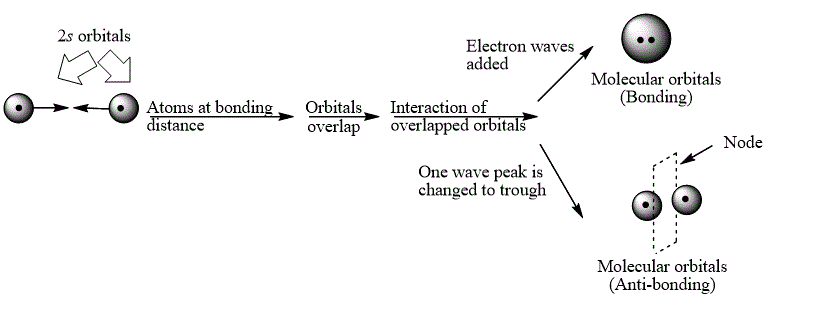
Explanation of Solution
The bond electrons which on addition form a molecular orbital are known as bonding electrons.
The bond electrons which on subtraction form a molecular orbital are known as anti-bonding electrons.
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations for the interaction of two

Figure 1
The bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital are obtained by the overlapping of two
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
(b)
Interpretation:
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
Concept introduction:
The linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO) states that two atomic orbitals combine together to form a new orbital which is known as bonding molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital theory also states that two atoms combines together to form a molecule. During the formation of a molecule, the electrons are shared between two atoms to form a chemical bond.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
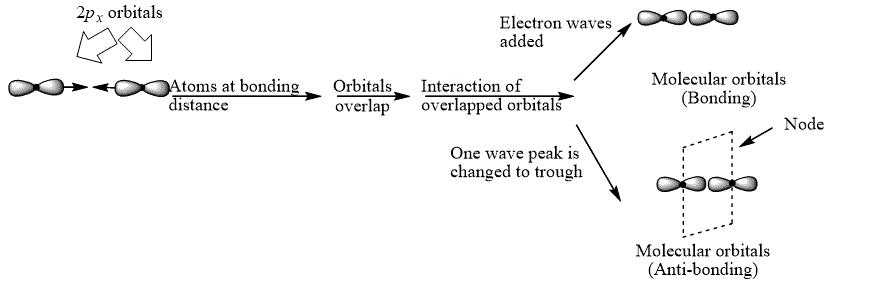
Explanation of Solution
The bond electrons which on addition form a molecular orbital are known as bonding electrons.
The bond electrons which on subtraction form a molecular orbital are known as anti-bonding electrons.
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations for the interaction of two
 Figure 2
Figure 2
The bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital are obtained by the overlapping of two
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
(c)
Interpretation:
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
Concept introduction:
The linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO) states that two atomic orbitals combine together to form a new orbital which is known as bonding molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital theory also states that two atoms combines together to form a molecule. During the formation of a molecule, the electrons are shared between two atoms to form a chemical bond.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
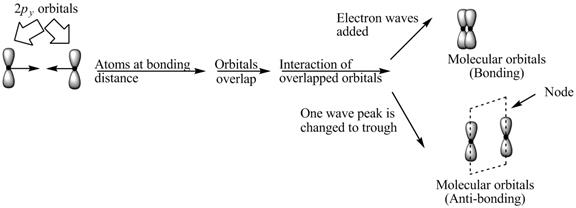
Explanation of Solution
The bond electrons which on addition form a molecular orbital are known as bonding electrons.
The bond electrons which on subtraction form a molecular orbital are known as anti-bonding electrons.
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations for the interaction of two
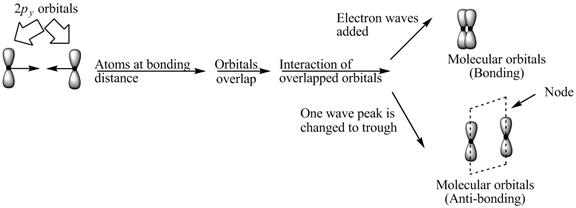
Figure 3
The bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital are obtained by the overlapping of two
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
(d)
Interpretation:
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
Concept introduction:
The linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO) states that two atomic orbitals combine together to form a new orbital which is known as bonding molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital theory also states that two atoms combines together to form a molecule. During the formation of a molecule, the electrons are shared between two atoms to form a chemical bond.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
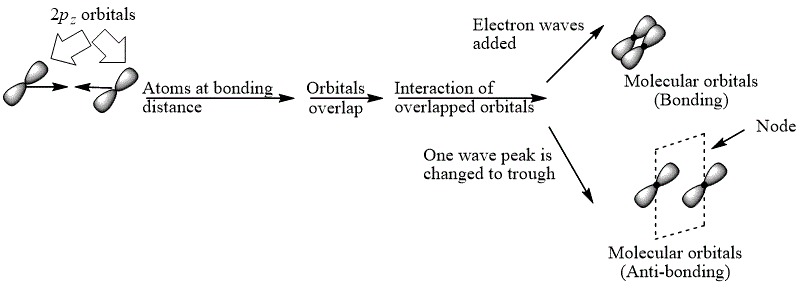
Explanation of Solution
The bond electrons which on addition form a molecular orbital are known as bonding electrons.
The bond electrons which on subtraction form a molecular orbital are known as anti-bonding electrons.
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations for the interaction of two

Figure 4
The bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital are obtained by the overlapping of two
The bonding and anti-bonding combinations
(e)
Interpretation:
The orbital interaction energy diagram showing the energy levels of the atomic orbitals along with the energies of the given MOs is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO) states that two atomic orbitals combine together to form a new orbital which is known as bonding molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital theory also states that two atoms combines together to form a molecule. During the formation of a molecule, the electrons are shared between two atoms to form a chemical bond.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The orbital interaction energy diagram showing the energy levels of the atomic orbitals along with the energies of the given MOs is represented below.
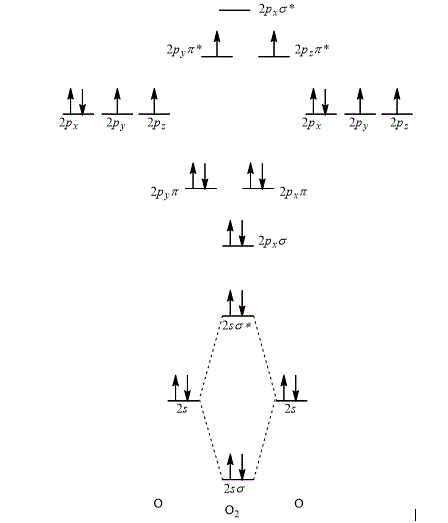
Explanation of Solution
According to the rules for filling the electrons in the molecular orbital, first of all the lower energy molecular orbital is filled followed by the filling of increasing energy order of the molecular orbital.
Thus, the orbital interaction energy diagram showing the energy levels of the atomic orbitals along with the energies of the given MOs of oxygen atom is shown as,

Figure 5
The energy of sigma,
The orbital interaction energy diagram showing the energy level of the atomic orbitals along with the energies of the given MOs is shown Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reason corresponding to the fact that liquid
Concept introduction:
The atoms which contain no unpaired electron in their orbital and have total spin equals to zero are known as diamagnetic atoms. The atoms which contain one or more unpaired electron in their orbital are known as paramagnetic atoms.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The liquid
Explanation of Solution
In oxygen molecule, two unpaired electrons are present in the anti-bonding molecular orbital. Thus, oxygen molecule is paramagnetic in nature due to which it gets attracted towards the magnetic field.
In comparison to liquid oxygen, the movement of the oxygen gas molecules is faster. Therefore, liquid oxygen molecules are not attracted by the magnetic field.
Hence, liquid
The reason corresponding to the fact that liquid
(g)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure that best describes the covalent bond(s) in
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure shows the connectivity between atoms by identifying the lone pairs of electrons in a compound. Lewis structures are also called Lewis dot structures. The valence electrons around an atom are shown by dots. Bonds between atoms are shown by lines and the lone pair of electrons is shown by a pair of dots.
Answer to Problem 1.47AP
The Lewis structure that best describes the covalent bond(s) in
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structures of
The reason corresponding to the fact that liquid
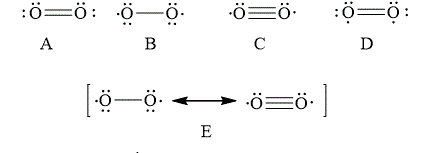
Figure 6
The total number of bonding electrons in
The total number of anti-bonding electrons in
The bond order of
Substitute the number of bonding molecular orbital and anti-bonding molecular orbital electrons in the above expression.
Thus, the bond order of oxygen molecule is
Therefore, the Lewis structures of
In option D, the Lewis structures of
In option A, the Lewis structures of
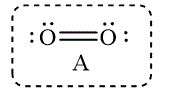
Figure 7
The Lewis structure that best describes the covalent bond(s) in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Name the following carbohydrates give both the systematic and common names. Don't forget to identify the Isomer.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction of XeF4 with H2O? Group of answer choices H2XeF2 H2XeF4 XeO3 H2XeOarrow_forwardWhile noble gas exerts the strongest London (dispersion) forces on neighboring atoms? Group of answer choices Xe Ar Kr Nearrow_forward
- Which of the following elements is corrosive to your skin due to that element breaking down C=C bonds? Group of answer choices fluorine iodine bromine chlorinearrow_forwardWhat the best source of sulfide to use on a small scale in the lab? Group of answer choices thiourea H2S NaHS Na2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about sulfur is FALSE? Group of answer choices H2S is the product of an oxygen-depleted ecosystem. In the acid mine drainage reaction, FeS2 is a product. One allotrope of sulfur has the formula S20. In the environment, bacterial oxidation can convert S2− to elemental S or SO42−.arrow_forward
- Of the following choices, which is the best reason that most materials DON'T spontaneously combust even though our atmosphere is about 21% oxygen? Group of answer choices The reduction of O2 in the gas phase (O2 + e− → O2−) is spontaneous. The reduction of O2 in acid solution (O2 + H+ + e− → HO2(aq)) is spontaneous. O2 is not a reactant in combustion. The O2 bond dissociation energy is 494 kJ/mol, leading to a high activation energy for combustion.arrow_forwardplease answer in the scope of the SCH4U course, I am having a hard time understanding, may you show all steps please and thank you! can you also put the final answers in the table so its understandablearrow_forwardPlan the synthesis of the following compound using the starting material provided and any other reagents needed as long as carbon based reagents have 3 carbons or less. Either the retrosynthesis or the forward synthesis (mechanisms are not required but will be graded if provided) will be accepted if all necessary reagents and intermediates are shown (solvents and temperature requirements are not needed unless specifically involved in the reaction, i.e. DMSO in the Swem oxidation or heat in the KMnO4 oxidation). There may be more than one correct answer, and chemically correct steps will be accepted. Extra points will be given if correct names are provided. The points earned here will be applied to your lowest exam score! H Harrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





