
(a)
Interpretation:
Given chemical equation has to be balanced and also the oxidizing agent and reducing agent has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
In
In redox reactions, reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized by causing reduction. These agents can be ions, elements, or even compounds. In reduction, the oxidation number decreases due to gain of electrons.
(a)
Answer to Problem K.18E
Balanced chemical equation is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is written as follows;
The above chemical equation has the same number of atoms of elements equal on both sides. Hence, this itself is a balanced equation.
Oxidation number of the atoms present in the above equation is indicated as follows;
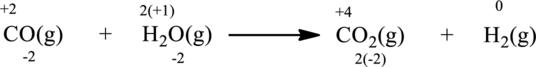
From the above equation, it is found that the oxidation state of carbon is increased from
The oxidation state of hydrogen decreases from
(b)
Interpretation:
Given chemical equation has to be balanced and also the oxidizing agent and reducing agent has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem K.18E
Balanced chemical equation is;
Oxidizing agent is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is written as follows;
Balancing Chlorine atoms: In the left side of the equation there is one chlorine atom while on the product side there are two chlorine atoms. Adding coefficient
Balancing Oxygen atoms: In the left side of the equation there are seven oxygen atoms while on the product side there are eight oxygen atoms. Adding coefficient
Oxidation number of the atoms present in the above equation is indicated as follows;
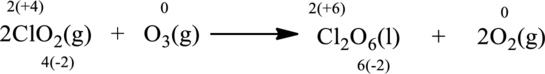
From the above equation, it is found that the oxidation state of chlorine is increased from
The oxidation state of oxygen decreases from
(c)
Interpretation:
Given chemical equation has to be balanced and also the oxidizing agent and reducing agent has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem K.18E
Balanced chemical equation is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is written as follows;
Balancing chlorine atom: In the reactant side, there are two chlorine atoms while on the product side, there is one chlorine atom. Adding coefficient
Balancing fluorine atom: In the reactant side, there are two fluorine atoms while on the product side, there are six fluorine atoms. Adding coefficient
Oxidation number of the atoms present in the above equation is indicated as follows;
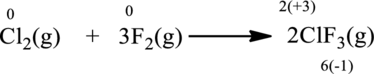
From the above equation, it is found that the oxidation state of chlorine is increased from
The oxidation state of fluorine decreases from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (LL) W/ACCESS
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





