
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
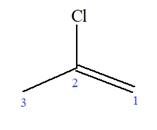
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
In this molecule, the root is propene. Thus, the longest carbon chain must have three carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the chain. The position of the double bond in the chain is between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
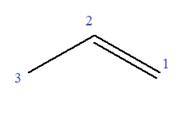
At C2 carbon atom of the root, one chlorine is attached. Thus, the structure of
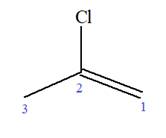
The structure of
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
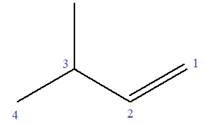
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
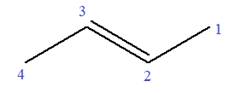
In this molecule, the root is butene. Thus, the longest carbon chain must have four carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the chain. The position of the double bond in the chain is between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
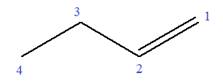
At C3 carbon atom of the root, a methyl substituent is attached.
Thus, the structure of

The structure of
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
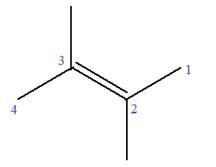
In this molecule, the root is butene. Thus, the longest carbon chain must have four carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the chain. The position of the double bond in the chain is between carbon atoms C2 and C3.
The root can be shown as:
At C2 and C3 carbon atoms of the root, two methyl substituents are attached.
Thus, the structure of
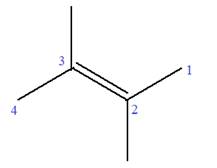
The structure of
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents, are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
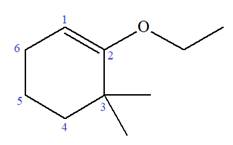
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
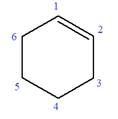
In this molecule, the root is cyclohexene. Thus, the largest carbon ring must have six carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the ring. The position of the double bond in the ring is always between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
At C2 and C3 carbon atoms of the ring, one ethoxy and two methyl substituents are attached respectively. Thus, the structure of

The structure of
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
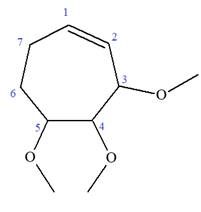
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
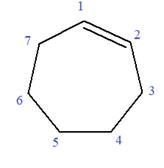
In this molecule, the root is cyclohexene. Thus, the largest carbon ring must have seven carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the ring. The position of the double bond in the ring is always between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
At C2, C3, and C4 carbon atoms of this ring, three methoxy substituents are attached.
Thus, the structure of
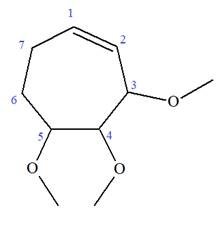
The structure of
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
Explanation of Solution
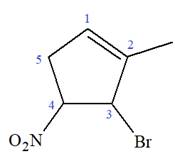
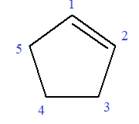
The given molecule is
In this molecule, the root is cyclohexene. Thus, the largest carbon ring must have six carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the ring. The position of the double bond in the ring is always between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
At C2, C3, and C4 carbon atoms, bromine, methyl, and nitro group are attached.
Thus, the structure of
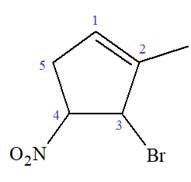
The structure of
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
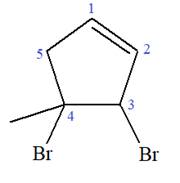
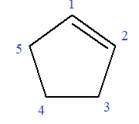
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
In this molecule, the root is cyclopentene. Thus, the largest carbon ring must have five carbon atoms. The suffix ‘ene’ indicates that there is a double bond in the ring. The position of the double bond in the ring is always between carbon atoms C1 and C2.
The root can be shown as:
At C3 and C4 carbon atoms of the ring, two bromine atoms and one methyl group are attached.
Thus, the structure of
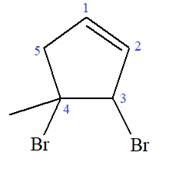
The structure of
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure for
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.26P
The structure for
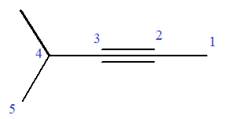
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
In this molecule, the root is pentyne. Thus, the longest carbon chain must have five carbon atoms. The suffix ‘yne’ indicates that there is a triple bond in the chain. The position of the triple bond in the chain is always between carbon atoms C2 and C3.
The root can be shown as:
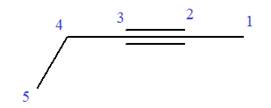
At C4 carbon atom of the root, a methyl group is attached.
Thus, the structure of
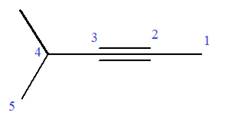
The structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter B Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- 6. In an experiment the following replicate set of volume measurements (cm3) was recorded: (25.35, 25.80, 25.28, 25.50, 25.45, 25.43) A. Calculate the mean of the raw data. B. Using the rejection quotient (Q-test) reject any questionable results. C. Recalculate the mean and compare it with the value obtained in 2(a).arrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T G OH де OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardMacmillan Leaming Draw the major organic product of the reaction. 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H+ - G Select Draw Templates More H о QQarrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 3-hydroxy-2-butanone. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardGive the expected major product of reaction of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane with each of the following reagents. 2. Reaction with dilute H₂SO, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More CHC Erase QQQ c. Reaction with dilute aqueous HBr. Select Drew Templates More Era c QQQ b. Reaction with NaOCH, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More d. Reaction with concentrated HBr. Select Draw Templates More En a QQQ e. Reaction with CH, Mg1, then H*, H₂O 1. Reaction with CH,Li, then H', H₂Oarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure O OH OH name X ☐arrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning One of the molecules shown can be made using the Williamson ether synthesis. Identify the ether and draw the starting materials. А со C Strategy: Review the reagents, mechanism and steps of the Williamson ether synthesis. Determine which of the molecules can be made using the steps. Then analyze the two possible disconnection strategies and deduce the starting materials. Identify the superior route. Step 6: Put it all together. Complete the two-step synthesis by selecting the reagents and starting materials. C 1. 2. Answer Bank NaH NaOH NaOCH, снен, сен, он Сиси, Сне (СН), СОН (Сн, Свarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 O CH3-CH-CH-C-CH3 OH HV. CH3-C-CH-CH2-CH3 OH CH3 O HO—CH, CH–CH—C CH3 OH 오-오 name X G ☐arrow_forwardHI Organic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? HO OH H +回 + H₂O 60013 Naomi V Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 1 2 #3 $ 4 2025 % ala5 'a :☐ G & 67 8 Ar K enter Accessible 9 Q W E R TY U 1 tab , S H J Karrow_forward
- Please help me with number 5 using my data and graph. I think I might have number 3 and 4 but if possible please check me. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwarddict the major products of this organic reaction. C Explanation Check 90 + 1.0₂ 3 2. (CH3)2S Click and drag f drawing a stru © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. • 22 4 5 7 8 Y W E R S F H Bilarrow_forwardcan someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all the curly arrows and 2. Draw the GPNA molecule and identify the phenylalanine portion. 3. Draw L-phenylalanine with the correct stereochemistryarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





