
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.5, Problem 83P
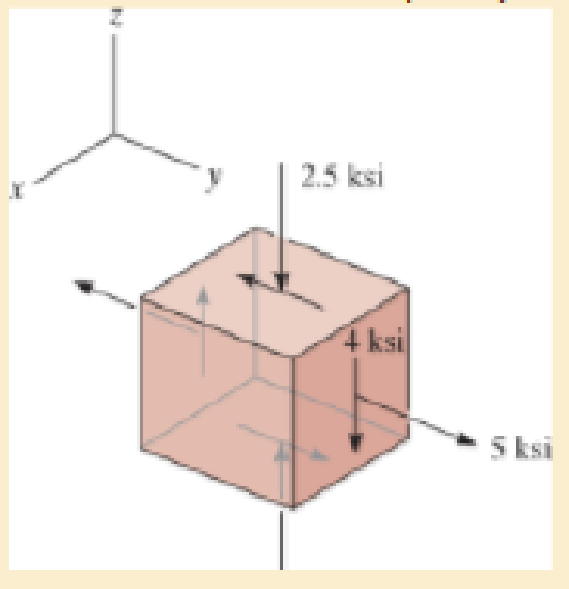
Determine the principal stresses and the absolute maximum shear stress.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A 4-m × 5-m × 6-m room is to be heated by a baseboard resistance heater. It is desired that the resistance heater be able to raise the air temperature in the room from 5 to 25°C within 10 min. Assuming no heat losses from the room and an atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa, determine the required power of the resistance heater. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. The properties of air are R = 0.287 kJ/kg·K and cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2a).
The required power of the resistance heater is kW.
I need solve without AI and chatgpt
An ordinary egg can be approximated as a 5.5-cm-diameter sphere. The egg is initially at a uniform temperature of 8°C and is dropped into boiling water at 97°C. Taking the properties of the egg to be ρ = 1020 kg/m3 and cp = 3.32 kJ/kg·°C, determine how much heat is transferred to the egg by the time the average temperature of the egg rises to 82°C.
The heat transferred to the egg in this case is kJ.
Chapter 9 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.99 using the stress transformation...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...
Ch. 9.3 - The stress along two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point in a member is...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a section of the beam are...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point B. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point C. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - It is subjected to a torque of 12 kip in. and a...Ch. 9.3 - A paper tube is formed by rolling a cardboard...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.931 for the normal stress acting...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stresses in the...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the equivalent state of stress if an...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle trial describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - The solid shaft is subjected to a torque, bending...Ch. 9.5 - The frame is subjected to a horizontal force and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 1RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I don't want an AI solution please.arrow_forward1.7 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.23 using two beam elements. A. E. I constant M₂ T + FIGURE 1.23 A fixed-pinned beam subjected to a momentarrow_forward42 PART 1 Introduction A. E. I constant FIGURE 1.22 A fixed-pinned beam. 1.6 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.22 using two beam elements.arrow_forward
- 1.4 Using a one-beam element idealization, find the stress distribution under a load of P for the uniform cantilever beam shown in Fig. 1.20. A, E, I constant L FIGURE 1.20 A uniform cantilever beamarrow_forwardMechanical engineering,FBD required.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Please Please use MATLAB with codes and graph. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure is attached below.arrow_forwardPlease only step 6 (last time I asked it was cut off at that point)arrow_forwardPlease Please use a MATLAB with codes and grap. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure attached below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license