
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.3, Problem 25P
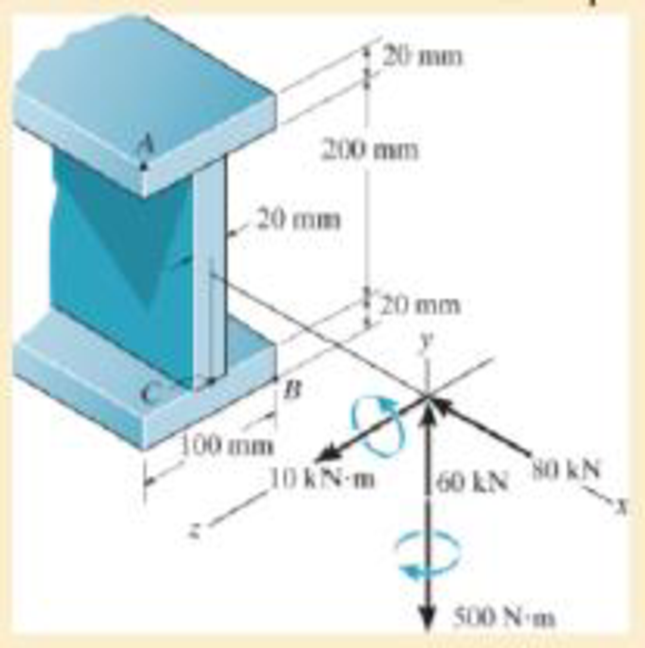
The internal loadings at a section of the beam are shown. Determine the in-plane principal stresses at point A. Also compute the maximum in-plane shear stress at this point.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(Read image) (Answer given)
Problem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a
mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and
(y2), respectively.
Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s].
Givens:
y1 = 4.112 m
y2 =
0.387 m
b = 0.942 m
Answers:
( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s
( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s
( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s
( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/s
Problem (14): A pump is being used to lift water from an underground
tank through a pipe of diameter (d) at discharge (Q). The total head
loss until the pump entrance can be calculated as (h₁ = K[V²/2g]), h
where (V) is the flow velocity in the pipe. The elevation difference
between the pump and tank surface is (h).
Given the values of h [cm], d [cm], and K [-], calculate the maximum
discharge Q [Lit/s] beyond which cavitation would take place at the
pump entrance. Assume Turbulent flow conditions.
Givens:
h = 120.31 cm
d = 14.455 cm
K = 8.976
Q
Answers:
(1) 94.917 lit/s
(2) 49.048 lit/s
( 3 ) 80.722 lit/s
68.588 lit/s
4
Chapter 9 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.99 using the stress transformation...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...
Ch. 9.3 - The stress along two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point in a member is...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a section of the beam are...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point B. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point C. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - It is subjected to a torque of 12 kip in. and a...Ch. 9.3 - A paper tube is formed by rolling a cardboard...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.931 for the normal stress acting...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stresses in the...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the equivalent state of stress if an...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle trial describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - The solid shaft is subjected to a torque, bending...Ch. 9.5 - The frame is subjected to a horizontal force and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 1RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem (13): A pump is being used to lift water from the bottom tank to the top tank in a galvanized iron pipe at a discharge (Q). The length and diameter of the pipe section from the bottom tank to the pump are (L₁) and (d₁), respectively. The length and diameter of the pipe section from the pump to the top tank are (L2) and (d2), respectively. Given the values of Q [L/s], L₁ [m], d₁ [m], L₂ [m], d₂ [m], calculate total head loss due to friction (i.e., major loss) in the pipe (hmajor-loss) in [cm]. Givens: L₁,d₁ Pump L₂,d2 오 0.533 lit/s L1 = 6920.729 m d1 = 1.065 m L2 = 70.946 m d2 0.072 m Answers: (1) 3.069 cm (2) 3.914 cm ( 3 ) 2.519 cm ( 4 ) 1.855 cm TABLE 8.1 Equivalent Roughness for New Pipes Pipe Riveted steel Concrete Wood stave Cast iron Galvanized iron Equivalent Roughness, & Feet Millimeters 0.003-0.03 0.9-9.0 0.001-0.01 0.3-3.0 0.0006-0.003 0.18-0.9 0.00085 0.26 0.0005 0.15 0.045 0.000005 0.0015 0.0 (smooth) 0.0 (smooth) Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.00015 Drawn…arrow_forwardThe flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (20): Given the value of APm/Lm [kPa/m], and assuming pressure coefficient similitude, calculate the drop in the pressure per unit length of the water main (APP/Lp) in [Pa/m]. Givens: AP M/L m = 590.637 kPa/m meen Answers: ( 1 ) 59.369 Pa/m ( 2 ) 73.83 Pa/m (3) 95.443 Pa/m ( 4 ) 44.444 Pa/m *******arrow_forward
- Find the reaction force in y if Ain = 0.169 m^2, Aout = 0.143 m^2, p_in = 0.552 atm, Q = 0.367 m^3/s, α = 31.72 degrees. The pipe is flat on the ground so do not factor in weight of the pipe and fluid.arrow_forwardFind the reaction force in x if Ain = 0.301 m^2, Aout = 0.177 m^2, p_in = 1.338 atm, Q = 0.669 m^3/s, and α = 37.183 degreesarrow_forwardProblem 5: Three-Force Equilibrium A structural connection at point O is in equilibrium under the action of three forces. • • . Member A applies a force of 9 kN vertically upward along the y-axis. Member B applies an unknown force F at the angle shown. Member C applies an unknown force T along its length at an angle shown. Determine the magnitudes of forces F and T required for equilibrium, assuming 0 = 90° y 9 kN Aarrow_forward
- Problem 19: Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression. 4 ft K J I H G B C D E F -3 ft -3 ft 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft- 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lbarrow_forwardProblem 14: Determine the reactions at the pin A, and the tension in cord. Neglect the thickness of the beam. F1=26kN F2 13 12 80° -2m 3marrow_forwardProblem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forward
- Problem 20: Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG. After the truss is sectioned use a single equation of equilibrium for the calculation of each force. State if the members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B D E F 3 m -5 m- -5 m- 5 m 5 m-arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (19): Given the value of Qp [m³/s], and assuming Reynolds number similitude between the water main and experimental tube, calculate the flow rate in the model tube (Qm) in [lit/s]. = 30.015 m^3/sarrow_forwardProblem 11: The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by the six cords connected together as shown. Determine the tension in each cord and the angle 0 for equilibrium. Cord BC is horizontal. E 30° B 60° Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license