
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 5RP
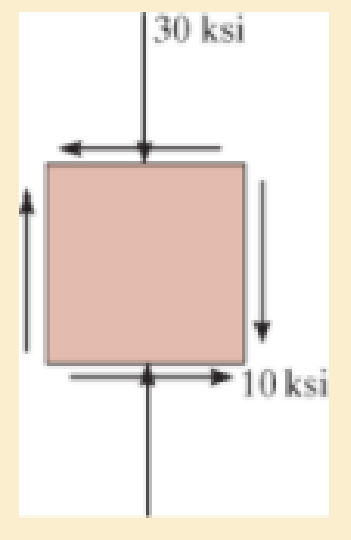
Determine the equivalent state of stress on an element which represents (a) the principal stresses, and (b) the maximum in-plane shear stress and the associated average normal stress. Also for each case determine the corresponding orientation of the element with respect to the element shown and sketch the results on the element.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
PROBLEM 3.23
3.23 Under normal operating condi-
tions a motor exerts a torque of
magnitude TF at F. The shafts
are made of a steel for which
the allowable shearing stress is
82 MPa and have diameters of
dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20
mm. Knowing that rp = 165
mm and rg114 mm, deter-
mine the largest torque TF
which may be exerted at F.
TF
F
rG-
rp
B
CH
TE
E
1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure
mode and describe the observed plane of failure.
(b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown
in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross
section.
M
M
Fig. 1
(c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis.
(d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.
using the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottom
Chapter 9 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.99 using the stress transformation...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...
Ch. 9.3 - The stress along two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point in a member is...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a section of the beam are...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point B. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point C. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - It is subjected to a torque of 12 kip in. and a...Ch. 9.3 - A paper tube is formed by rolling a cardboard...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.931 for the normal stress acting...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stresses in the...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the equivalent state of stress if an...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle trial describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - The solid shaft is subjected to a torque, bending...Ch. 9.5 - The frame is subjected to a horizontal force and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 1RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward
- 1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license