
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The reason for the bromination to be much more regioselective than chlorination needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction : Hess's law states that when the reactants are converted to products the change of enthalpy (i.e. the heat of reaction at constant pressure) does not dependent on the pathway between the initial and final states.
Hess’s law states that enthalpy changes are additive. Thus, for a single reaction,
(a)
Answer to Problem 10E
The radical construction depends on the statistical factor and bromination reaction the reaction is endothermic and hence the transition state is nearer to the radical generated than the
The formation of radical depends on the stability of the radical and more selectivity is attained .
Explanation of Solution
Considering the bromination and chlorination of an alkane to check the
In the propagation process, the free radical of the reagent in step by step reacts with the
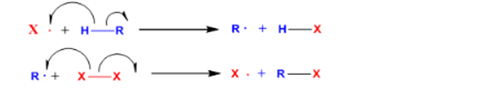
The initial stage controls the generation of a specific kind of radical.
The reaction enthalpy of this stage of bromination is measured as
The reaction enthalpy of this stage of chlorination is measured as follows:
Hence, the chlorination reaction is exothermic whereas the stage for bromination reaction is endothermic.
Hammond’s postulate the transition state of a reaction and would be nearer to the reactant in case of an exothermic reaction.
In chlorination reaction, the reaction is exothermic and thus the transition state is closer to the alkane than the radical generated.
The radical construction depends on the statistical factor.
In bromination reaction the reaction is endothermic and hence the transition state is nearer to the radical generated than the alkane.
The radical formation depends on the stability of the radical and more selectivity is attained.
(b)
Interpretation: The reason behind the dangerousness of fluorination needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction : Hess's law states that when the reactants are converted to products the change of enthalpy (i.e. the heat of reaction at constant pressure) does not dependent on the pathway between the initial and final states.
Hess’s law states that enthalpy changes are additive. Thus, for a single reaction,
(b)
Answer to Problem 10E
High exothermic nature of the bond formation, a huge amount of heat is liberated during fluorination hence the fluorination is dangerous.
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation enthalpy of carbon fluorine bond formation is as follows:
Due to this high exothermic nature of the bond formation, huge amount of heat is liberated during fluorination. Thus, the process is dangerous.
(C)
Interpretation: The reason behind the difficulty in the generation of an alkyl iodide by free radical chain halogenations needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction : Hess's law states that when the reactants are converted to products the change of enthalpy (i.e. the heat of reaction at constant pressure) does not dependent on the pathway between the initial and final states.
Hess’s law states that enthalpy changes are additive. Thus, for a single reaction,
(C)
Explanation of Solution
The iodination reaction of an alkane can be expressed as follows
The enthalpy change in this reaction is calculated as
As the reaction is endothermic in nature the reaction is difficult to carry out at room temperature.
The reverse reaction can also occur which further decreases the yield of the reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale & Microscale Approach (Cengage Learning Laboratory Series for Organic Chemistry)
- Steps on how to solve. Thank you!arrow_forward3. Name this ether correctly. H₁C H3C CH3 CH3 4. Show the best way to make the ether in #3 by a Williamson Ether Synthesis. Start from an alcohol or phenol. 5. Draw the structure of an example of a sulfide.arrow_forward1. Which one(s) of these can be oxidized with CrO3 ? (could be more than one) a) triphenylmethanol b) 2-pentanol c) Ethyl alcohol d) CH3 2. Write in all the product(s) of this reaction. Label them as "major" or "minor". 2-methyl-2-hexanol H2SO4, heatarrow_forward
- 3) Determine if the pairs are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or mesocompounds. (4 points)arrow_forwardIn the decomposition reaction in solution B → C, only species C absorbs UV radiation, but neither B nor the solvent absorbs. If we call At the absorbance measured at any time, A0 the absorbance at the beginning of the reaction, and A∞ the absorbance at the end of the reaction, which of the expressions is valid? We assume that Beer's law is fulfilled.arrow_forward> You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: 1. ☑ CI 2. H3O+ O Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check ? DO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardConsider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forward
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





