
A gas turbine operates with a regenerator and two stages of reheating and intercooling. Air enters this engine at 14 psia and 60°F, the pressure ratio for each stage of compression is 3, the air temperature when entering a turbine is 940°F, the engine produces 1000 hp, and the regenerator operates perfectly. The isentropic efficiency of each compressor is 88 percent and that of each turbine is 93 percent. Which process of the cycle loses the greatest amount of work potential? The temperature of the heat source is the same as the maximum cycle temperature, and the temperature of the heat sink is the same as the minimum cycle temperature. Use constant specific heats at room temperature.
Which process of the cycle loses the greatest amount of work potential.
Answer to Problem 151P
The exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 and 3-4 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 5-6 and 7-8 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 6-7 and 8-9 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 10-1 and 2-3 is
The exergy destruction associated at regenerator is
During the heat rejection process the highest energy destruction occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Draw the
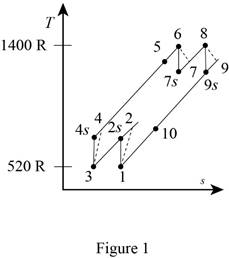
Write the expression for the temperature and pressure relation for the isentropic process 1-2s.
Here, the pressure ratio is
Write the expression for the efficiency of the compressor
Here, the specific heat at constant pressure is
Write the expression for the temperature and pressure relation ratio for the expansion process 6-7s.
Here, temperature at state 7s for isentropic process is
Write the expression for the efficiency of the turbine
Here, temperature at state 7 is
Write the expression to calculate the heat input for the two-stage gas turbine
Here, the specific heat of air at constant pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the heat output for the two-stage gas turbine
Write the expression for the exergy destruction during the process of as steam from an inlet to exit state.
Here, entropy generation is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 1-2
Here, pressure at state 2 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 5-6
Here, pressure at state 5 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 6-7
Here, pressure at state 7 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 10-1
Here, pressure at state 10 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for regenerator
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The regenerator is ideal, the effectiveness is 100% and therefore,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 and 3-4 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 5-6 and 7-8 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 6-7 and 8-9 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 10-1 and 2-3 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated at regenerator is
During the heat rejection process the highest energy destruction occurs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS LLF W/ CONNECT ACCESS
- The airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. 0 a.) If 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces = required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. 20. YAAY' Farag Ө Fthrust CC + BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to 101,855 ☑ lbs. The lift force is equal to 141,282 ☑ lbs. Part (b) The trajectory angle 0 is equal to 7.31 ✓ deg. The lift force is equal to 143,005 ☑ lbs.arrow_forwardsimply supported beam has a concentrated moment M, applied at the left support and a concentrated force F applied at the free end of the overhang on the right. Using superposition, determine the deflection equations in regions AB and BC.arrow_forwardwhat is heat exchanger, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of heat exchanger, and how did values end up in that number. based on standards . what is dshellarrow_forward
- FIGURE P1.37 1.38 WP As shown in Figure P1.38, an inclined manometer is used to measure the pressure of the gas within the reservoir, (a) Using data on the figure, determine the gas pressure, in lbf/in.² (b) Express the pressure as a gage or a vacuum pressure, as appropriate, in lbf/in.² (c) What advantage does an inclined manometer have over the U-tube manometer shown in Figure 1.7? Patm = 14.7 lbf/in.² L I C i Gas a Oil (p = 54.2 lb/ft³) 140° 8=32.2 ft/s² 15 in.arrow_forwardwhat is an low pressure Heater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forwardwhat is an air preheater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forward
- Qf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC. a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D P = 4 kip Ma = 5 kip-ft w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft a = 3 ftarrow_forwardFrom the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





