
The exergy destruction associated with each of the processes of the Brayton cycle.
Answer to Problem 142P
The exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 of the given Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 2-3 of the given Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 of the given Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 4-1 of the given Brayton cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Show the simple Brayton cycle, and with air as the working fluid on
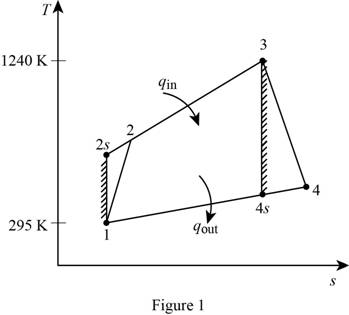
For the given simple Brayton cycle with air as the working fluid, let
Write the expression of pressure ratio relation for the process 1-2.
Write the relation of pressure ratio and pressure for the process 3-4.
Write the expression of efficiency of the compressor
Write the expression of efficiency of the turbine
Write the expression of heat input to the Brayton cycle
Write the expression of heat rejected by the Brayton cycle
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 1-2 of the given Brayton cycle
Here, temperature of the surroundings is
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 2-3 of the given Brayton cycle
Here, temperature of the heat source is
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 3-4 of the given Brayton cycle
Here, entropy of air at state 3 as a function of temperature is
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 4-1 of the given Brayton cycle
Here, temperature of the sink is
Conclusion:
Refer Table A-17E given in the textbook to find the properties of air at 295 K
Substitute 10 for
Refer Table A-17E given in the textbook to find the properties of air at 13.07
Refer Table A-17E given in the textbook to find the properties of air at 1,240 K
Substitute
Refer Table A-17 given in the textbook to find the properties of air at 27.23
Rearrange Equation (III) and substitute
Refer Table A-17E given in the textbook to find the properties of air at
Rearrange Equation (IV) and substitute
Refer Table A-17 given in the textbook, to find the properties of air at
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute 295 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 of the given Brayton cycle is
Substitute 295 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 2-3 of the given Brayton cycle is
Substitute 295 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 of the given Brayton cycle is
Substitute 295 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 4-1 of the given Brayton cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





