
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
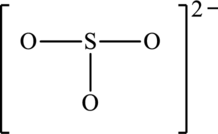
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is a bond that is formed from the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structures are representations of the covalent bond. In this, Lewis symbols show how the valence electrons are present in the molecule.
Steps to write Lewis structures are as follows:
1. The skeleton structure with single bonds between all bonded atoms has to be written
2. Sum the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule.
(a) For cations, one electron is subtracted for each positive charge.
(b) For anions, one electron is added for each negative charge.
3. Subtract two electrons from total number of valence electrons for each bond in the skeleton structure.
4. Count the number of electrons required to satisfy the octet rule for each atom in the structure. If the number of electrons needed is less than the number remaining, add one bond for every two electrons needed between atoms to attain an octet.
5. The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on atoms that need them to satisfy the octet rule.
The formula to calculate formal charge of atom is,
Some molecules do not have only one Lewis structure. The Lewis structures that differ only in the arrangement of multiple bonds are called resonance structures.
Resonance structure comprises of two or more Lewis Structures that describes the arrangement of bond of a single species and include fractional bonds and fractional charges.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.82QE
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
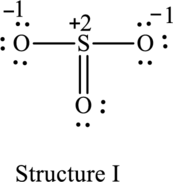
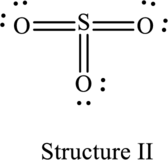
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
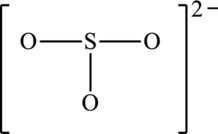
The resonance structures are as follows:
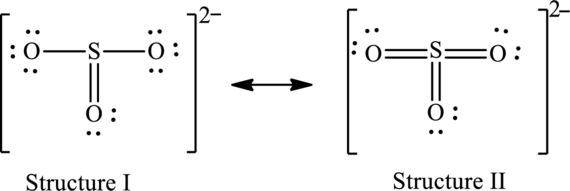
For structure I:
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 12 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
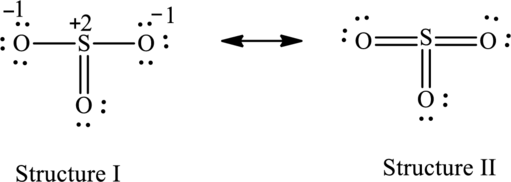
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
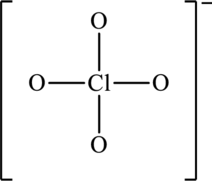
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.82QE
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
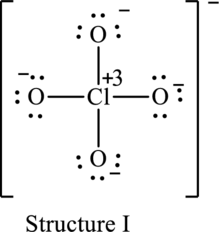
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
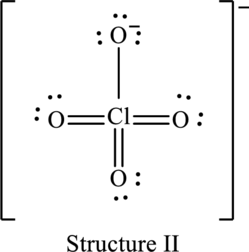
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
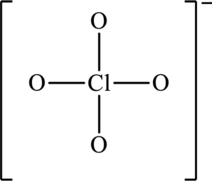
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
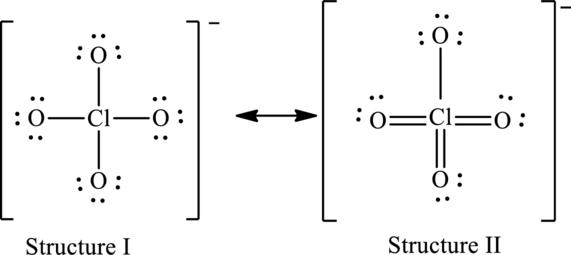
For structure I:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 4 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
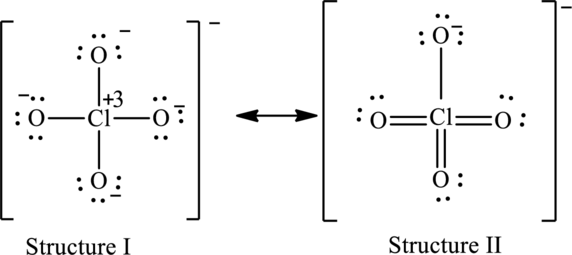
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry Principles And Practice
- How to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forward
- a. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forwardhelp draw any straightchain moleculearrow_forward
- How to do the mechanism drawn for the reactionarrow_forwardPlease provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forward

 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning


