
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Whether the connectivity of
Concept Introduction:
Covalent bond is defined as a bond is formed from mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structures are representations of the covalent bond. In this, Lewis symbols show how the valence electrons are present in the molecule.
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound that has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Estimate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
The formula to calculate formal charge of the atom is as follows:
The different structures can be drawn for the same molecule. Structures that minimize the amount of formal charge found on each atom are more stable than structures that place large amounts of formal charge on atoms.
The structures that have adjacent atoms with formal charges of the same sign are less stable. Lewis structures that show the smallest formal charges are stable. The structure that has negative formal charges on the more electronegative atoms are favored.
Explanation of Solution
For structure
The given compound is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms.
The rules applied to obtain the Lewis structure of
1. Write the skeleton structure.
There are three hydrogen atom, one carbon atom and a nitrogen atom. Therefore, 4 bonds are formed.
2. Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
The valence electron of nitrogen is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of carbon is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of hydrogen is calculated as follows:
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as follows:
3. Calculate the remaining electrons that are not used in skeleton structure.
The skeleton structure has 4 bonds. Therefore 8 electrons are used in bonds.
The remaining electrons are calculated as follows:
4 To obey the octet rule, carbon atom needs 2 electrons and nitrogen atom needs 4 electrons.
5. Satisfy the octet rule.
There are 4 remaining electrons. Multiple bonds can be formed. In this compound, an additional bond is needed to complete the structure. Also, remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on atoms to satisfy octet.
The Lewis structure of
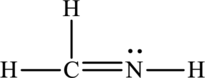
6. The Lewis structure is finished except for formal charges.
7. The formal charge on an atom in this Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
The formal charge on nitrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 5 for number of valence electrons, 2 for number of lone pairs and 6 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on first hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on second hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on third hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on carbon atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 4 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 8 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
In this Lewis structure, nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen atom has formal charge 0.
The Lewis structure made from
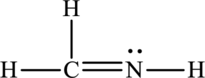
For structure
The given compound is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen molecule.
The rules applied to obtain the Lewis structure of
1. Write the skeleton structure.
There are three hydrogen atom, one carbon atom, and nitrogen atom. Therefore, 4 bonds are formed.
2. Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
The valence electron of nitrogen is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of carbon is calculated as follows:
The valence electron of hydrogen is calculated as follows:
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as follows:
3. Calculate the remaining electrons that are not used in skeleton structure.
The skeleton structure has 4 bonds. Therefore 8electrons are used in bonds.
The remaining electrons are calculated as follows:
4 To obey the octet rule, carbon atom needs 2 electrons and nitrogen atom needs 4 electrons.
5. Satisfy the octet rule.
There are 4 remaining electrons. Multiple bonds can be formed. In this compound, an additional bond is needed to complete the structure. Also, remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on atoms to satisfy octet.
The Lewis structure of
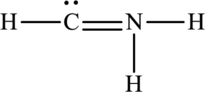
6. The Lewis structure is finished except for formal charges.
7. The formal charge on an atom in this Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
The formal charge on nitrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 5 for number of valence electrons, 2 for number of lone pairs and 6 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on first hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on second hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on third hydrogen atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 1 for number of valence electrons 0 for number of lone pairs and 2 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
The formal charge on carbon atom is calculated as follows:
Substitute 4 for number of valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs and 8 for number of shared electrons in equation (1).
In this Lewis structure, nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen atom has formal charge 0.
The Lewis structure made from
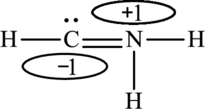
The
Hence,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry Principles And Practice
- The reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forward
- Draw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward
- 19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction OH OH CH3-CC- Ph + H2SO4 a 20°C | CH3 Pharrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





