
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The possible resonance structures for the following skeleton structure have to be determined. Also, the most important resonance structure has to be identified.
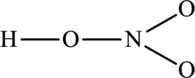
Concept Introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound that has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Estimate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
The formula to calculate formal charge of the atom is as follows:
Some molecules and ions do not have one unique Lewis structure. The Lewis structures that differ only in the placement of multiple bonds are called resonance structures.
Resonance structures are defined as a set of two or more Lewis structures that collectively describe the electronic bonding. The actual bonding is an average of the bonding in the resonance structures. Also, not all resonance structures contribute equally in every case. Resonance structures that have high formal charges or that place charges of the same sign on adjacent atoms do not contribute to the bonding.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.74QE
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
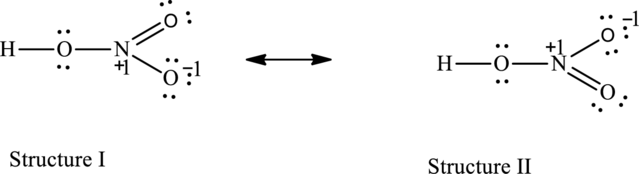
All resonance structures are equally important.
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
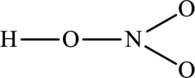
The resonance structures are as follows:
For structure I:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 2for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
For structure II:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pair of electrons and 2for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pair of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
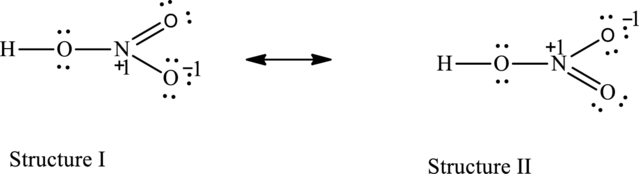
All the structures have same formal charge. Also, the atoms that have charge are same in each structure. Therefore, all structures are equally important.
(b)
Interpretation:
The possible resonance structures for the following skeleton structure have to be determined. Also, the most important resonance structure has to be identified.
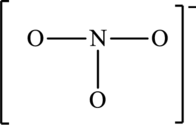
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.74QE
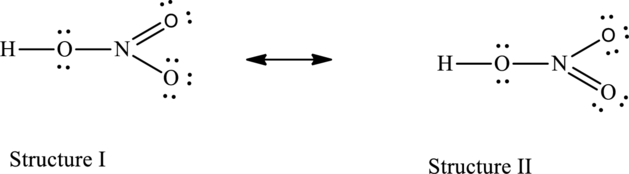
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
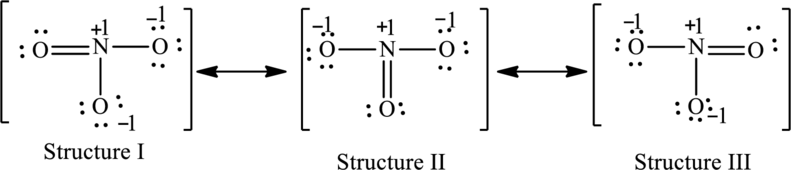
All the structures are equally important.
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is,
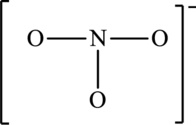
The resonance structures are as follows:
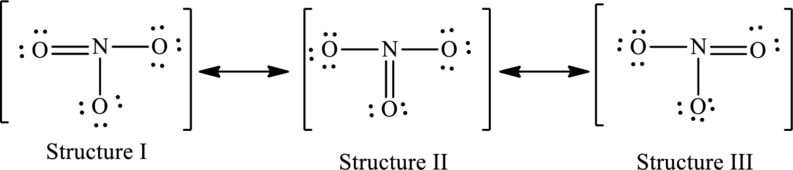
For structure I:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure III:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
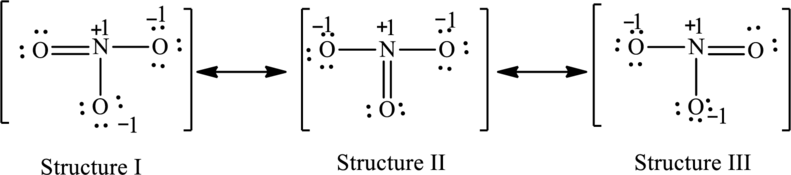
All the structures have the same formal charge. Also, the atoms that have charge are same in each structure. Therefore, all structures are equally important.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry Principles And Practice
- no Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- 3. Synthesize the following synthon from the indicated starting material. i HO.arrow_forwardIdentifying the stereochemistry of natural Write the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below. Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is. molecule H O-C-CH2 H3N. HN N H C=O common name (not the IUPAC name) NH3 ☐ H3N H ☐ CH2 Xarrow_forward> Draw the structure of alanine at pH 1.2. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





