
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
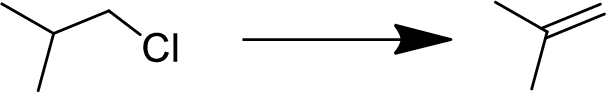
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
(b)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
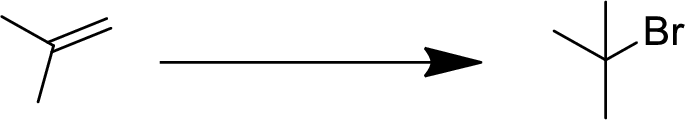
Concept Introduction:
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.

Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(d)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
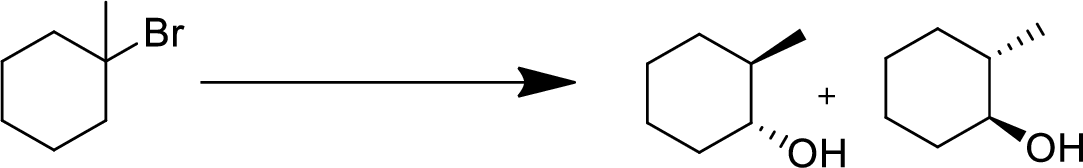
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(e)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
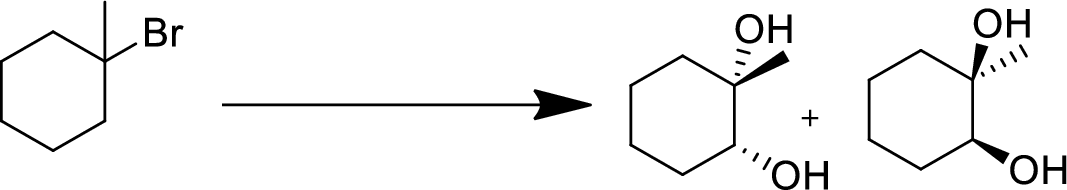
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(f)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
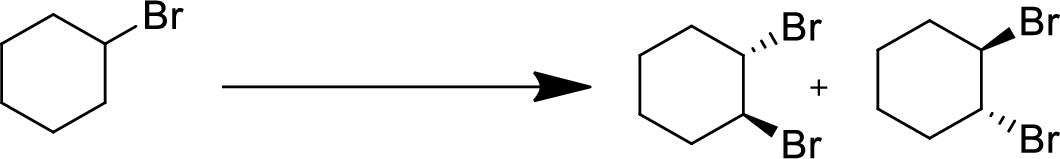
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(g)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
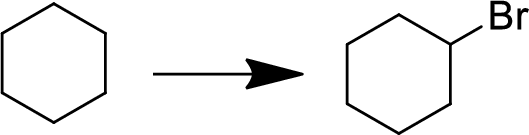
Concept Introduction:
(h)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
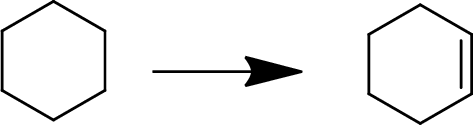
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
(i)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
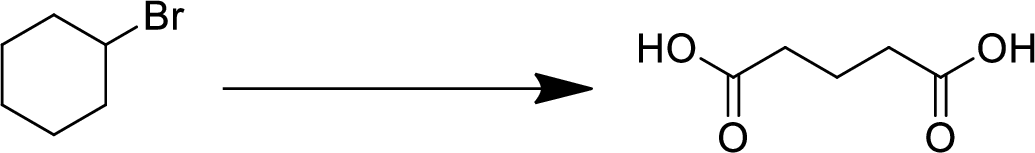
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
