
Concept explainers
The angle of refraction when light passes from air to glass with help of given figure
Answer to Problem 5P
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
This is figure 9.34.
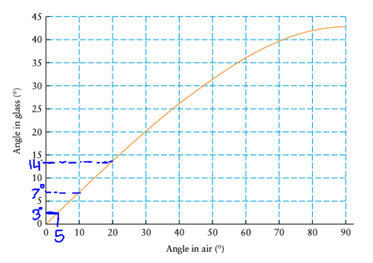
When we closely observe the figure, we can estimate the angle of refraction. So, we can see the following estimation as
Here, we can observe that as the angle of incidence increases, angle of refraction also increases. So, we can see that if we do the angle of incidence double, then, angle of refraction also be double.
Similarly, if we angle of incidence is
When we see the figure, we can also get angle of refraction as
Conclusion:
Thus, angle of incident changes as the angle of refraction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Inquiry into Physics
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer.. Find amplitude?arrow_forwardkerjakanarrow_forwardAn object is placed 37.4cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 18.1 cm. Please provide your answers in units of cm if necessary. bookmark_border1.0p3a Find the image distance. Answer Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3b Is the image real or virtual? Real Virtual Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3c Suppose the object is brought to a distance of 10.3 cm in front of the lens. Where is the image now with respect to its previous location? (Note: Ensure the sign convention you use is consistent by treating all image distances on the object side of the lens as negative.) Answer Updated 7 minutes ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3d How has the height of the image changed if the object is 84.2 cm tall? Answerarrow_forward
- n object is placed 37.4cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 18.1 cm. Please provide your answers in units of cm if necessary. bookmark_border1.0p3a Find the image distance. Answer Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3b Is the image real or virtual? Real Virtual Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3c Suppose the object is brought to a distance of 10.3 cm in front of the lens. Where is the image now with respect to its previous location? (Note: Ensure the sign convention you use is consistent by treating all image distances on the object side of the lens as negative.) Answer Updated just now Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3d How has the height of the image changed if the object is 84.2 cm tall? Answerarrow_forwardCan you draw a FBD and KD please!arrow_forwardIf a 120- volt circuit feeds four 40-watt fluorescent lamps, what current (in amps) is drawn if the power factor is 0.912 0.33 0.68 1.21 3.3arrow_forward
- How do you draw a diagram of the ruler and mass system in equilibrium identifying the anti-clockwise torque and clockwise torque? How do I calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers, does it come from the data in table 2? Please help, thank you!arrow_forwardA long, narrow steel rod of length 2.5000 m at 33.5°C is oscillating as a pendulum about a horizontal axis through one end. If the temperature drops to 0°C, what will be the fractional change in its period?arrow_forwardHow long should a pendulum be in order to swing back and forth in 1.6 s?arrow_forward
- LECTURE HANDOUT: REFRACTION OF LIGHT I. Review Each of the diagrams at right shows a ray incident on a boundary between two media. Continue each of the rays into the second medium. Using a dashed line, also draw the path that the wave would have taken if it had continued without "bending." Does the ray representing a wave "bend" toward or away from the normal when: the wave speed is smaller in the second medium? ⚫the wave speed is larger in the second medium? Faster medium Slower medium Slower medium Faster medium II. Qualitative applications of refraction A. Place a coin at the bottom of an empty can or cup. Look into the cup at the coin while your partner slowly moves the can away from you until you no longer see the coin. Now, keep your head steady while your partner gently pours water into the cup. 1. Describe your observations. Switch roles with your partner so that you each have a turn. Shown below are cross-sectional diagrams of the cup for when it was empty and when it was…arrow_forwardProblem Six. A 70 kg student in the figure balances a 1200 kg elephant on a hydraulic lift with diameter 2.0 m that is filled with oil which has a density of 900 kg/m³. How many 80 kg students would have to stand on the first piston in order to raise the elephant by 2.55 m? 80 kg 1200 kg 17.) (A) 5 (D) 8 (B) 6 (E) 9 (C) 7 Oil 2.0 m 5arrow_forwardIn the accompanying figure, the rails, connecting end pieces, and rod all have a resistance per unit length of 4.52/cm. The rod moves to the left at v = 5 m/s. If B = 0.3 T everywhere in the region, what is the current in the circuit (a) when a = 6.5 cm? (b) when a = 4 cm?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





