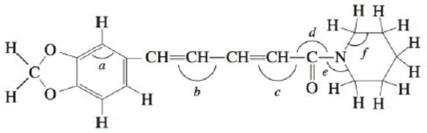
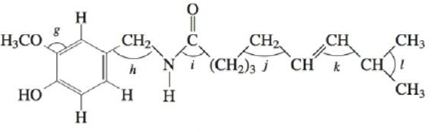
Problem 1RQ: Why do we hybtidize atomic orbitals to explain the bonding in covalent compounds? What type of bonds... Problem 2RQ: What hybridization is required for central atoms that have a tetrahedral arrangement of electron... Problem 3RQ: Describe the bonding in H2S, CH4, H2CO and HCN using the localized electron model. Problem 4RQ: What hybridization is required for central atoms exhibiting trigonal bipyramidal geometry?... Problem 5RQ: Electrons in bonding molecular orbitals are most likely to be found in the region between the two... Problem 1ALQ: What are molecular orbitals? How do they compare with atomic orbitals? Can you tell by the shape of... Problem 2ALQ: Explain the difference between the and MOs for homonuclear diatomic molecules. How are bonding and... Problem 3ALQ: Compare Figs. 4-47 and 4-49. Why are they different? Because B2 is known to be paramagnetic, the 2p... Problem 4ALQ: Which of the following would you expect to be more favorable energetically? Explain. a. an H2... Problem 5ALQ: Draw the Lewis structure for HCN. Indicate the hybrid orbitals, and draw a picture showing all the... Problem 6ALQ: Which is the more correct statement: The methane molecule (CH4) is a tetrahedral molecule because it... Problem 7ALQ: Compare and contrast the MO model with the local electron model. When is each useful? Problem 8ALQ: What are the relationships among bond order, bond energy, and bond length? Which of these quantities... Problem 9ALQ: The molecules N2 and CO are isoelectronic but their properties are quite different. Although as a... Problem 10ALQ: Do lone pairs about a central atom affect the hybridization of the central atom? If so, how? Problem 11Q: In the hybrid orbital model, compare and contrast bonds with bonds. What orbitals form the bonds... Problem 12Q: In the molecular orbital mode l, compare and contrast bonds with bonds. What orbitals form the ... Problem 13Q: Why are d orbitals sometimes used to form hybrid orbitals? Which period of elements does not used... Problem 14Q: The atoms in a single bond can rotate about the internuclear axis without breaking the bond. The... Problem 16Q: As compared with CO and O2, CS and S2 are very unstable molecules. Give an explanation based on the... Problem 17Q: Compare and contrast bonding molecular orbitals with antibonding molecular orbitals. Problem 18Q: What modification to the molecular orbital model was made from the experimental evidence that B2 is... Problem 19Q: Why does the molecular orbital model do a better job in explaining the bonding in NO and NO than the... Problem 20Q: The three NO bonds in NO3 are all equivalent in length and strength. How is this explained even... Problem 21E: Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in H2O. Problem 22E: Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in CCl4. Problem 23E: Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in H2CO (carbon is the central atom). Problem 24E: Use the localized electron model to describe the bonding in C2H2 (exists as HCCH). Problem 25E: The space-filling models of ethane and ethanol are shown below. Use the localized electron model to... Problem 26E: The space-filling models of hydrogen cyanide and phosgene are shown below. Use the localized... Problem 27E: Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the molecules or ions in Exercises 81 and 87... Problem 28E: Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the molecules or ions in Exercises 82 and 88... Problem 29E: Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the molecules in Exercises 21 and 22. Problem 30E: Give the expected hybridization of the central atom for the molecules in Exercises 27 and 28. Problem 33E: For each of the following molecules, write the Lewis structure(s), predict the molecular structure... Problem 34E: For each of the following molecules or ions that contain sulfur, write the Lewis structure(s),... Problem 35E Problem 36E: The allene molecule has the following Lewis structure: Must all hydrogen atoms lie the same plane?... Problem 37E: Indigo is the dye used in coloring blue jeans. The term navy blue is derived from the use of indigo... Problem 38E: Urea, a compound formed in the liver, is one of the ways humans excrete nitrogen. The Lewis... Problem 39E: Biacetyl and acetoin are added to margarine to make it taste more like butter. Biacetyl Acetion... Problem 40E: Many important compounds in the chemical industry are derivatives of ethylene (C2H4). two of them... Problem 41E: Two molecules used in the polymer industry are azodicarbonamide and methyl cyanoacrylate. Their... Problem 42E: Hot and spicy foods contain molecules that stimulate paindetecting nerve endings. Two such molecules... Problem 43E: One of the first drugs to be approved for use in treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome... Problem 44E: Minoxidil (C9H15N15O) is a compound produced by the Pharmacia Upjohn Company that has been approved... Problem 45E: Consider the following molecular orbitals formed from the combination of two hydrogen 1s orbitals:... Problem 46E: Sketch the molecular orbital and label its type ( or , bonding or antibonding) that would be formed... Problem 47E: Which of the following are predicted by the molecular orbital model to be stable diatomic species?... Problem 48E: Which of the following are predicted by the molecular orbital model to be stable diatomic species?... Problem 49E: Using the molecular orbital model, write electron configurations for the following diatomic species... Problem 50E: Consider the following electron configuration: (3s)2(3s)2(3p)2(3p)4(3p)4 Give four species that, in... Problem 52E: Using the molecular orbital model to describe the bonding in F2+, F2, and F2, predict the bond... Problem 54E: A Lewis structure obeying the octet rule can be drawn for O2 as follows: Use the molecular orbital... Problem 55E: Using the molecular orbital model, write electron configurations for the following diatomic species... Problem 56E: Using the molecular orbital model, write electron configurations for the following diatomic species... Problem 57E: In which of the following diatomic molecules would the bond strength be expected to weaken as an... Problem 58E: In terms of the molecular orbital model, which species in each of the following two pairs will roost... Problem 59E: Show how two 2p atomic orbitals can combine to form a or a molecular orbital. Problem 60E: Show how a hydrogen 1s atomic orbital and a fluorine 2p atomic orbital overlap to form bonding and... Problem 61E: Use Figs. 4-54 and 4-55 to answer the following questions. a. Would the bonding molecular orbital in... Problem 63E: Acetylene (C2H2) can be produced from the reaction of calcium carbide (CaC2) with water. Use both... Problem 64E: Describe the bonding in NO+, NO, and NO, using both the localized electron and molecular orbital... Problem 65E: Describe the bonding in the O3 molecule and the NO2 ion, using the localized electron model. How... Problem 66E: Describe the bonding in the CO32 ion using the localized electron model. How would the molecular... Problem 67AE: Draw the Lewis structures, predict the molecular structures, and describe the bonding (in terms of... Problem 68AE: The antibiotic thiarubin-A was discovered by studying the feeding habits of wild chimpanzees in... Problem 69AE: Two structures can be drawn for cyanuric acid: a. Are these two structures the same molecule?... Problem 70AE: Give the expected hybridization for the molecular structures illustrated in the previous question. Problem 71AE: Vitamin B6 is an organic compound whose deficiency in the human body can cause apathy, irritability,... Problem 72AE: Aspartame is an artificial sweetener marketed under the name Nutra-Sweet. A partial Lewis structure... Problem 73AE Problem 74AE: The three most stable oxides of carbon are carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and carbon... Problem 76AE: Complete the following resonance structures for POCl3. a. Would you predict the same molecular... Problem 77AE Problem 78AE: The transport of O2 in the blood is carried out by hemoglobin. Carbon monoxide (CO) can interfere... Problem 79AE: Using molecular orbital theory, explain why the removal of one electron in O2 strengthens bonding,... Problem 80AE: Describe the bonding in the first excited state of N2 (the one closest in energy to the ground... Problem 81AE: Using an MO energy-level diagram, would you expect F2 to have a lower or higher first ionization... Problem 82AE: Show how a dxz. atomic orbital and a pz, atomic orbital combine to form a bonding molecular orbital.... Problem 83AE: What type of molecular orbital would result from the in-phase combination of the two dxz atomic... Problem 84AE: Consider three molecules: A, B, and C. Molecule A has a hybridization of sp3 Molecule B has two more... Problem 86CWP: Draw the Lewis structures for TeCl4, ICl5, PCl5, KrCl4, and XeCl2. Which of the compounds exhibit at... Problem 87CWP: A variety of chlorine oxide fluorides and related cations and anions are known. They tend to be... Problem 88CWP: Pelargondin is the molecule responsible for the red color of the geranium flower. It also... Problem 89CWP: Complete a Lewis structure for the compound shown below, then answer the following questions. What... Problem 90CWP: Which of the following statements concerning SO2 is(are) true? a. The central sulfur atom is sp2... Problem 91CWP: Consider the molecular orbital electron configurations for N2, N2+, and N2. For each compound or... Problem 92CWP: Place the species B2+ , B2, and B2 in order of increasing bond length and increasing bond energy. Problem 93CP: Consider the following computer-generated model of caffeine: Complete a Lewis structure for caffeine... Problem 94CP: Cholesterol (C27liu;O) has the following structure: In such shorthand structures, each point where... Problem 95CP: Cyanamide (H2NCN), an important industrial chemical, is produced by the following steps: Calcium... Problem 97CP: A flask containing gaseous N2 is irradiated with 25-nm light. a. Using the following information,... Problem 99CP: Values of measured bond energies may vary greatly depending on the molecule studied. Consider the... Problem 100CP: Use the MO model to explain the bonding in BeH2. When constructing the MO energy-level diagram,... Problem 101CP Problem 102CP: Arrange the following from lowest to highest ionization energy: O, O2, O2 , O2+. Explain your... Problem 103CP: Use the MO model to determine which of the following has the smallest ionization energy: N2, O2,... Problem 104CP: Given that the ionization energy of F2 is 290 kJ/mol, do the following: a. Calculate the bond energy... Problem 105CP: Carbon monoxide (CO) forms bonds to a variety of metals and metal ions. liS ability to bond to iron... Problem 106CP Problem 107IP: As the bead engineer of your starship in charge of the warp drive, you notice that the supply of... Problem 109IP: Determine the molecular structure and hybridization of the central atom X in the polyatomic ion XY3+... Problem 110IP: Although nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is a thermally stable compound, nitrogen triiodide (NI3) is... format_list_bulleted



 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




