
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 38E
Urea, a compound formed in the liver, is one of the ways humans excrete nitrogen. The Lewis structure for urea is
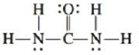
Using hybrid orbitals for carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, determine which orbitals overlap to form the various bonds in urea.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing
150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3
Ag+ + S20
Ag(S203)¯
K₁ = 7.4 × 108
Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203)
K₂ = 3.9 x 104
ΗΝ,
cyclohexanone
pH 4-5
Draw Enamine
I
I
CH3CH2Br
THF, reflux
H3O+
I
Drawing
Draw Iminium Ion
:0: :0:
Select to Add Arrows
:0:
(CH3)2NH
:0:
■ Select to Add Arrows
:0:
:0:
(CH3)2NH
■ Select to Add Arrows
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry
Ch. 9 - Why do we hybtidize atomic orbitals to explain the...Ch. 9 - What hybridization is required for central atoms...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in H2S, CH4, H2CO and HCN...Ch. 9 - What hybridization is required for central atoms...Ch. 9 - Electrons in bonding molecular orbitals are most...Ch. 9 - What are molecular orbitals? How do they compare...Ch. 9 - Explain the difference between the and MOs for...Ch. 9 - Compare Figs. 4-47 and 4-49. Why are they...Ch. 9 - Which of the following would you expect to be more...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for HCN. Indicate the...
Ch. 9 - Which is the more correct statement: The methane...Ch. 9 - Compare and contrast the MO model with the local...Ch. 9 - What are the relationships among bond order, bond...Ch. 9 - The molecules N2 and CO are isoelectronic but...Ch. 9 - Do lone pairs about a central atom affect the...Ch. 9 - In the hybrid orbital model, compare and contrast ...Ch. 9 - In the molecular orbital mode l, compare and...Ch. 9 - Why are d orbitals sometimes used to form hybrid...Ch. 9 - The atoms in a single bond can rotate about the...Ch. 9 - As compared with CO and O2, CS and S2 are very...Ch. 9 - Compare and contrast bonding molecular orbitals...Ch. 9 - What modification to the molecular orbital model...Ch. 9 - Why does the molecular orbital model do a better...Ch. 9 - The three NO bonds in NO3 are all equivalent in...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - The space-filling models of ethane and ethanol are...Ch. 9 - The space-filling models of hydrogen cyanide and...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - For each of the following molecules, write the...Ch. 9 - For each of the following molecules or ions that...Ch. 9 - Prob. 35ECh. 9 - The allene molecule has the following Lewis...Ch. 9 - Indigo is the dye used in coloring blue jeans. The...Ch. 9 - Urea, a compound formed in the liver, is one of...Ch. 9 - Biacetyl and acetoin are added to margarine to...Ch. 9 - Many important compounds in the chemical industry...Ch. 9 - Two molecules used in the polymer industry are...Ch. 9 - Hot and spicy foods contain molecules that...Ch. 9 - One of the first drugs to be approved for use in...Ch. 9 - Minoxidil (C9H15N15O) is a compound produced by...Ch. 9 - Consider the following molecular orbitals formed...Ch. 9 - Sketch the molecular orbital and label its type (...Ch. 9 - Which of the following are predicted by the...Ch. 9 - Which of the following are predicted by the...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - Consider the following electron configuration:...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model to describe the...Ch. 9 - A Lewis structure obeying the octet rule can be...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - In which of the following diatomic molecules would...Ch. 9 - In terms of the molecular orbital model, which...Ch. 9 - Show how two 2p atomic orbitals can combine to...Ch. 9 - Show how a hydrogen 1s atomic orbital and a...Ch. 9 - Use Figs. 4-54 and 4-55 to answer the following...Ch. 9 - Acetylene (C2H2) can be produced from the reaction...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in NO+, NO, and NO, using...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in the O3 molecule and the...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in the CO32 ion using the...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures, predict the molecular...Ch. 9 - The antibiotic thiarubin-A was discovered by...Ch. 9 - Two structures can be drawn for cyanuric acid: a....Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization for the molecular...Ch. 9 - Vitamin B6 is an organic compound whose deficiency...Ch. 9 - Aspartame is an artificial sweetener marketed...Ch. 9 - Prob. 73AECh. 9 - The three most stable oxides of carbon are carbon...Ch. 9 - Complete the following resonance structures for...Ch. 9 - Prob. 77AECh. 9 - The transport of O2 in the blood is carried out by...Ch. 9 - Using molecular orbital theory, explain why the...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in the first excited state of...Ch. 9 - Using an MO energy-level diagram, would you expect...Ch. 9 - Show how a dxz. atomic orbital and a pz, atomic...Ch. 9 - What type of molecular orbital would result from...Ch. 9 - Consider three molecules: A, B, and C. Molecule A...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures for TeCl4, ICl5, PCl5,...Ch. 9 - A variety of chlorine oxide fluorides and related...Ch. 9 - Pelargondin is the molecule responsible for the...Ch. 9 - Complete a Lewis structure for the compound shown...Ch. 9 - Which of the following statements concerning SO2...Ch. 9 - Consider the molecular orbital electron...Ch. 9 - Place the species B2+ , B2, and B2 in order of...Ch. 9 - Consider the following computer-generated model of...Ch. 9 - Cholesterol (C27liu;O) has the following...Ch. 9 - Cyanamide (H2NCN), an important industrial...Ch. 9 - A flask containing gaseous N2 is irradiated with...Ch. 9 - Values of measured bond energies may vary greatly...Ch. 9 - Use the MO model to explain the bonding in BeH2....Ch. 9 - Prob. 101CPCh. 9 - Arrange the following from lowest to highest...Ch. 9 - Use the MO model to determine which of the...Ch. 9 - Given that the ionization energy of F2 is 290...Ch. 9 - Carbon monoxide (CO) forms bonds to a variety of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 106CPCh. 9 - As the bead engineer of your starship in charge of...Ch. 9 - Determine the molecular structure and...Ch. 9 - Although nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) is a thermally...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- answer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forward
- answer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardC app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals LCAO; Author: Edmerls;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nq1zwrAIr4c;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Quantum Molecular Orbital Theory (PChem Lecture: LCAO and gerade ungerade orbitals); Author: Prof Melko;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l59CGEstSGU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY