
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals of carbon atoms in the given molecules are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Hybridization is the combining of atomic orbitals to form hybrid orbitals.
To determine hybridization of an atom, first draw the Lewis structure of the molecule.
Find the number of electron domains around an atom so as to get the number of hybrid orbitals used by the atom for bonding.
When atomic orbitals combine, they form equal number of hybrid orbitals.
The s orbital combines with one, two, or three p orbitals to form
Answer to Problem 36QP
Solution:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
a)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of
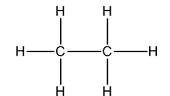
In this, the two carbon atoms are bonded to each other and the three hydrogen atoms by single bonds. Thus, there are four electron domains around each carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict thepresence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in both carbon atoms
b)
The Lewis structure of
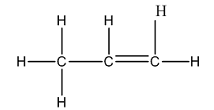
The carbon on the left is bonded to three hydrogen atoms by single bonds and to a carbon atom by a single bond. Thus, there are four electron domains around each carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict thepresence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in this carbon
The central carbon is bonded to one carbon atom by a single bond, to another by double bond and to a hydrogen by a single bond. Thus, there are three electron domains around this carbon atom. Three electron domainsdepict thepresence of three hybrid orbitals. Thus, hybridization of the central carbon is
The carbon on the right is bonded to two hydrogen atoms by a single bond and to a carbon by a double bond. Thus, there are three electron domains around this carbon atom. Three electron domainsdepict thepresence of three hybrid orbitals. Thus, hybridization of the carbon on the right is
Thus, the hybridizations of the carbon atoms, from left to right in the molecule, are
c)
The Lewis structure of
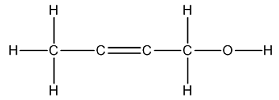
The carbon on left is bonded to three hydrogen atoms by single bonds and to a carbon atom by single bond. Thus, there are four electron domains around each carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict thepresence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in this carbon,
The two carbon atoms in the center are bonded to each other by double bonds and to a carbon by a single bond. Thus, there are two electron domains around each carbon atom. Two electron domains depict the presence of two hybrid orbitals. Thus, in these two carbons, sp hybrid orbitals are present.
The carbon on the right is bonded to two hydrogen atoms by single bonds, to a carbon atom by a single bond and to an oxygen by a single bond. Thus, there are four electron domains around this carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict the presence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in this carbon,
Thus, the hybridizations of the carbon atoms from left to right in the molecule are
d)
The Lewis structure of
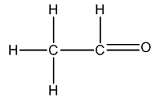
The carbon on the left is bonded to three hydrogen atoms by single bonds and to a carbon atom by a single bond. Thus, there are four electron domains around each carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict the presence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in this carbon
The carbon on the right is bonded to a hydrogen atom by a single bond and to an oxygen atom by a double bond. Thus, there are three electron domains around this carbon atom. Three electron domainsdepict the presence of three hybrid orbitals. Thus, the hybridization of the carbon atom on the right is
Thus, the hybridizations of carbon atoms from left to right in the molecule are
e)
The Lewis structure of
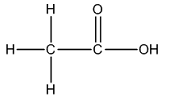
The carbon on left is bonded to three hydrogen atoms by single bonds and to carbon atom by single bond. Thus, there are four electron domains around each carbon atom. Four electron domainsdepict the presence of four hybrid orbitals. Thus, in this carbon
The carbon on the right is bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond and to another oxygen atom by a single bond. Thus, there are three electron domains around this carbon atom. Three electron domainsdepict the presence of three hybrid orbitals. Thus, the hybridization of the carbonatomon the right is
Thus, the hybridizations of carbon atoms from left to right in the molecule are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

