
a.
To write:
A system of equations describing the total cost of buying and operating each printer.
a.
Answer to Problem 25E
Our required system of equations would be:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
You are trying to decide whether to buy an inkjet printer for $100 or a laser printer for $400. The operating costs are estimated to be $0.15 per page for the inkjet printer and $0.03 per page for the laser printer.
Calculation:
Letxrepresent number of pages and y represent total cost.
The cost of printing x pages by inkjet printer would be
The cost of printing x pages by laser printer would be
Therefore, our required system of equations would be:
b.
To solve:
The system of equations using a graphing calculator. After how many pages are the total costs of the printers equal.
b.
Answer to Problem 25E
The total costs of both printers will be equal after 2500 pages.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
You are trying to decide whether to buy an inkjet printer for $100 or a laser printer for $400. The operating costs are estimated to be $0.15 per page for the inkjet printer and $0.03 per page for the laser printer.
Calculation:
Using an online graphing tool, we will get:
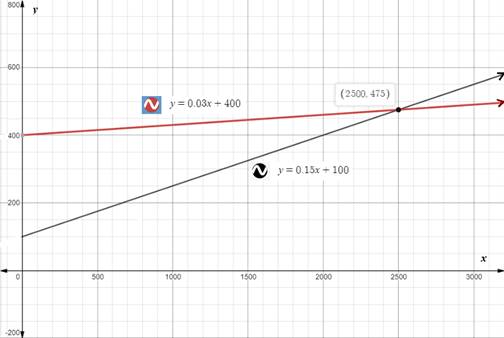
We can see that both lines intersect at
c.
To solve:
The system of equations using the given verbal model.
c.
Answer to Problem 25E
The total costs of both printers will be equal after 2500 pages.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
You are trying to decide whether to buy an inkjet printer for $100 or a laser printer for $400. The operating costs are estimated to be $0.15 per page for the inkjet printer and $0.03 per page for the laser printer.

Calculation:
To solve the given system of equations, we will equate both equations as:
Let us solve for x .
Therefore, the total costs of both printers will be equal after 2500 pages.
d.
To compare and contrast:
The methods used in part (b) and part (c). When would you use each method?
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
You are trying to decide whether to buy an inkjet printer for $100 or a laser printer for $400. The operating costs are estimated to be $0.15 per page for the inkjet printer and $0.03 per page for the laser printer.

Calculation:
We can see that we got same answer using graphing method and solving the system algebraically.
We will use graphing method when the equations contain complicated expressions.
We will solve system of equations manually, when the equations contain easy numbers and are easily computable.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Nasir invested $415 into a savings account that earns 2.5% annual interest. Tiana invested $295 into a saving account that earns 6.8% annual interest. Who will have more money after 7 years? How much more money will the person have?arrow_forwardSolve for the variable. 62k = 7776k- 8arrow_forwardSolve questionsarrow_forward
- Patterns in Floor Tiling A square floor is to be tiled with square tiles as shown. There are blue tiles on the main diagonals and red tiles everywhere else. In all cases, both blue and red tiles must be used. and the two diagonals must have a common blue tile at the center of the floor. If 81 blue tiles will be used, how many red tiles will be needed?arrow_forwardFind the values of n, if the points (n + 1, 2n), (3n, 2n + 3) and (5n + 1,5n) are collinear. Find the value of k that the four points (4,1,2), (5, k, 6), (5,1,-1) and (7,4,0) are coplanar. Find the value of r if the area of the triangle is formed by the points (-3,6),(4,4) and (r,-2) is 12 sq units. Find the volume of tetrahedron whose vertices are A(1,1,0), B(-4,3,6), C(-1,0,3) and D(2,4,-5).arrow_forward- Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables a,b,c,d: 5a-3b 7c - 2d = 2 2ab 2c+ 5d = -3 → (*) 4a 3b 5d = 3 6a b+2c+ 7d = −7 (a) Solve the system (*) by using Gauss elimination method. (b) Solve the system (*) by using Cramer's rule method.arrow_forward
- Solve for a 25 55 30 a=?arrow_forward9:41 … 93 Applying an Exponential Function to Newton's Law of Cooling 60. Water in a water heater is originally Aa ← 122°F. The water heater is shut off and the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding air, which is 60°F. The water cools slowly because of the insulation inside the heater, and the value of k is measured as 0.00351. a. Write a function that models the temperature T (t) (in °F) of the water t hours after the water heater is shut off. b. What is the temperature of the water 12 hr after the heater is shut off? Round to the nearest degree. c. Dominic does not like to shower with water less than 115°F. If Dominic waits 24 hr. will the water still be warm enough for a shower? Mixed Exercises ger-ui.prod.mheducation.comarrow_forwardPlease use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward
- 8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





