
Concept explainers
a.
Iswind speed a function of advisory number?
a.
Answer to Problem 22E
Yes, the wind speed is a function of advisory number.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
In 1995, a total of 32 regular weather advisories were issued during the storm that became hurricane Opal. The graph shows the wind speed inside Opal at the time of each advisory.
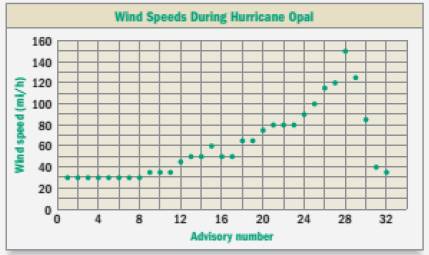
Calculation:
Open looking at our given graph, we can see that the horizontal axis represents advisory number and vertical axis represents wind speed.
We can see that each advisory number corresponds to a specific wind speed.
Therefore, the wind speed is a function of advisory number.
b.
An ocean storm is considered a hurricane if its wind speed is at least 74 miles per hour. For which advisories did Opal qualify as a hurricane?
b.
Answer to Problem 22E
Opal qualifies as a hurricane for 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, and 30 number advisories.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
In 1995, a total of 32 regular weather advisories were issued during the storm that became hurricane Opal. The graph shows the wind speed inside Opal at the time of each advisory.
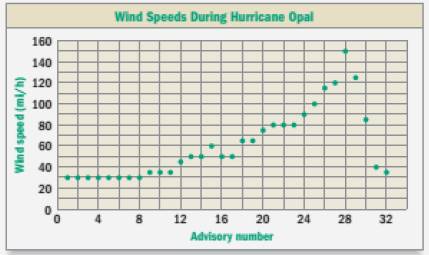
Calculation:
First of all, we will draw a horizontal line at
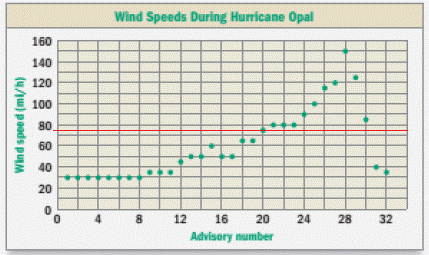
We can see that the advisories with number 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, and 30 has wind speed greater than 74 miles per hour.
Therefore, Opal qualifies as a hurricane for 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, and 30 number advisories.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- Please use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward
- 33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forwardUse the infinite geometric sum to convert .258 (the 58 is recurring, so there is a bar over it) to a ratio of two integers. Please go over the full problem, specifying how you found r. Thank you.arrow_forwardH.w: Find the Eigen vectors for the largest Eigen value of the system X1+ +2x3=0 3x1-2x2+x3=0 4x1+ +3x3=0arrow_forward
- need help with 5 and 6 pleasearrow_forward1) Given matrix A below, answer the following questions: a) What is the order of the matrix? b) What is the element a13? c) What is the element a₁₁? 4 -1arrow_forward[25 points] Given the vector let v = ER² and the collection of vectors ε = E-{)·()}-{☹) (9)} = {(A)·(9)}· B: = and C = · {(6)·(})}· answer the following question. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) verify Verify is a basis for R² and find the coordinate [] of under ε. Verify B is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []B of ʊ Verify C is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []c of under ε. under ε. Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]+B from basis B to basis ε, and EE+BUB Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]B+ε from basis Ɛ to basis B, and verify [U]B= [] B+EVEarrow_forward
- Explain the following terms | (a) linear span (b) dimension of vector space (c) linearly independent (d) linearly dependent (e) rank of matrix Aarrow_forward3. Let u = 3/5 √ = and = -4/5 -() Define V span{ū, }. (a) (b) (c) Show that {u, } is orthonormal and forms a basis for V. Explicitly compute Projy w. Explicitly give a non-zero vector in V+.arrow_forwardIs 1.1 0.65 -3.4 0.23 0.4 -0.44 a basis for R3? You must explain your answer 0arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





