
Concept explainers
a.
To write:
An equation describing the possible values of x and y .
a.
Answer to Problem 30E
The equation
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The rectangle shown has a perimeter of 16 inches.

Calculation:
We know that the perimeter of a rectangle is sum of two times length and two times width. Upon representing our given information in an equation, we will get:
Therefore, the equation
b.
To graph:
The equation from part (a) using intercepts.
b.
Answer to Problem 30E
x -intercept:
y -intercept:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The rectangle shown has a perimeter of 16 inches.

Calculation:
To find x -intercept, we will substitute
Therefore, the x -intercept of our given equation is
To find y- intercept, we will substitute
Therefore, the y -intercept of our given equation is
Upon graphing our given equation, we will get our required graph as shown below:
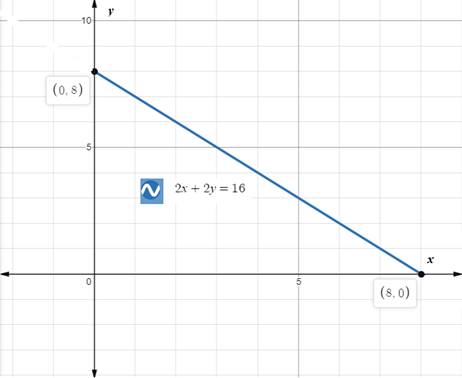
c.
To give:
Three pairs of whole number values of x and y that could represent side lengths of rectangle.
c.
Answer to Problem 30E
Our required pairs would be
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The rectangle shown has a perimeter of 16 inches.

Calculation:
To get three possible pairs for side lengths, we need to identify 3 points on the line graphed in part (b).
We can see that the points
Therefore, the points
d.
To explain:
Does either the x -intercept or the y -intercept represent a possible side length of the rectangle.
d.
Answer to Problem 30E
Neither x -intercept nor the y -intercept represent a possible side length of the rectangle.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The rectangle shown has a perimeter of 16 inches.

Calculation:
We know that the x -intercept is the point on x -axis, where the value of y is 0. The y -intercept is the point on y -axis, where the value of x is 0.
We also know that to form a rectangle we need two sides and both sides should be greater than 0. At the both intercepts, one side will be 0.
Therefore, neither x -intercept nor the y -intercept represent a possible side length of the rectangle.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
- Please use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward
- 33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forwardUse the infinite geometric sum to convert .258 (the 58 is recurring, so there is a bar over it) to a ratio of two integers. Please go over the full problem, specifying how you found r. Thank you.arrow_forwardH.w: Find the Eigen vectors for the largest Eigen value of the system X1+ +2x3=0 3x1-2x2+x3=0 4x1+ +3x3=0arrow_forward
- need help with 5 and 6 pleasearrow_forward1) Given matrix A below, answer the following questions: a) What is the order of the matrix? b) What is the element a13? c) What is the element a₁₁? 4 -1arrow_forward[25 points] Given the vector let v = ER² and the collection of vectors ε = E-{)·()}-{☹) (9)} = {(A)·(9)}· B: = and C = · {(6)·(})}· answer the following question. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) verify Verify is a basis for R² and find the coordinate [] of under ε. Verify B is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []B of ʊ Verify C is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []c of under ε. under ε. Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]+B from basis B to basis ε, and EE+BUB Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]B+ε from basis Ɛ to basis B, and verify [U]B= [] B+EVEarrow_forward
- Explain the following terms | (a) linear span (b) dimension of vector space (c) linearly independent (d) linearly dependent (e) rank of matrix Aarrow_forward3. Let u = 3/5 √ = and = -4/5 -() Define V span{ū, }. (a) (b) (c) Show that {u, } is orthonormal and forms a basis for V. Explicitly compute Projy w. Explicitly give a non-zero vector in V+.arrow_forwardIs 1.1 0.65 -3.4 0.23 0.4 -0.44 a basis for R3? You must explain your answer 0arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





