
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398235
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., John T. DeWolf, David F. Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.3, Problem 34P
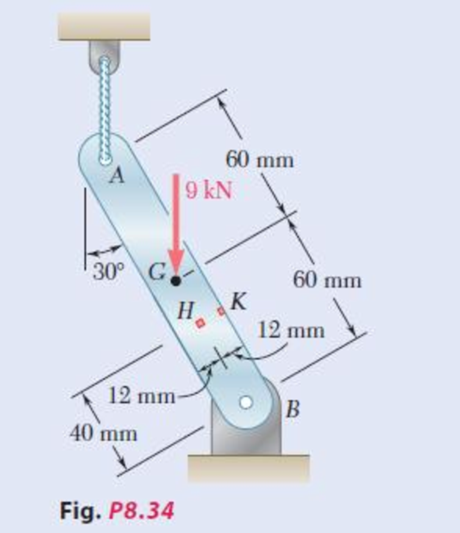
8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform rectangular cross section of 10 × 24 mm. For the loading shown, determine the normal and shearing stresses at (a) point H, (b) point K.
Fig. P8.34
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The member having a rectangular cross-section, Fig. a, is designed to resist a moment of 40 N # m. In order to increase its strength and rigidity, it is proposed that two small ribs be added at its bottom, Fig. b. Determine the maximum normal stress in the member for both cases.
Problem 8.5 A circular ring is subjected to a pull of 15 kN. The
ring is of T-section as shown in Fig. 8.12 and the internal radius is 10
cm. Determine the maximum and minimum stresses in the ring.
2cm
12cm
10cm
2
cm
Fig. 8.12
8.49 A 40-kN axial load is applied to a short wooden post that is sup-
ported by a concrete footing resting on undisturbed soil. Deter-
mine (a) the maximum bearing stress on the concrete footing,
(b) the size of the footing for which the average bearing stress in
the soil is 145 kPa.
|P = 40 kN
120 mm
100 mm
Fig. P8.49
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Ch. 8.2 - A W10 = 39 rolled-steel beam supports a load P as...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.1, assuming that P = 22.5 kips and a...Ch. 8.2 - An overhanging W920 449 rolled-steel beam...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.3, assuming that P = 850 kN and a =...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...
Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Using the notation of Sec. 8.2 and neglecting the...Ch. 8.2 - The 4-kN force is parallel to the x axis, and the...Ch. 8.2 - The vertical force P1 and the horizontal force P2...Ch. 8.2 - The two 500-lb forces are vertical and the force P...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shafts ABC and DEF and the gears shown...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - The cantilever beam AB has a rectangular cross...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the pipe AB as shown....Ch. 8.3 - Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pile AB has a 100-mm outer diameter and...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to a 4-in.-diameter plate...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pipe AB has a 72-mm outer diameter and a...Ch. 8.3 - A 13-kN force is applied as shown to the...Ch. 8.3 - A vertical force P of magnitude 60 lb is applied...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the machine component...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 57PCh. 8.3 - Four forces are applied to a W8 28 rolled-steel...Ch. 8.3 - A force P is applied to a cantilever beam by means...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 60PCh. 8.3 - A 5-kN force P is applied to a wire that is...Ch. 8.3 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8 - (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all = 14.5 ksi,...Ch. 8 - Neglecting the effect of fillets and of stress...Ch. 8 - Knowing that rods BC and CD are of diameter 24 mm...Ch. 8 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 450 rpm and...Ch. 8 - A 6-kip force is applied to the machine element AB...Ch. 8 - A thin strap is wrapped around a solid rod of...Ch. 8 - A close-coiled spring is made of a circular wire...Ch. 8 - Forces are applied at points A and B of the solid...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the bracket AB has a uniform...Ch. 8 - For the post and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8 - The cantilever beam AB will be installed so that...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6.13arrow_forwardanswer quicklyarrow_forwardPROBLEM 7.26 0.2 m The axle of an automobile is acted upon by the forces and couple shown. Knowing that the diameter of the solid axle is 32 mm, determine (a) the principal planes and principal stresses at point H located on top of the axle, (b) the maximum shearing stress at the same point. 3 kN 350 N- m 3 kN Omax = 18.67 MPa = -158,5 MPa O minarrow_forward
- A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by the 3 kN-m couple shown. Know-ing that E= 165 GPa and neglecting the effect of fillets, determine (a) the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in the casting and (b) the radius of curvature of the castingarrow_forwardQue 5.6. A crane hook trapezoidal horizontal cross-section is 50 mm wide inside and 30 mm wide outside. Thickness of the section is 60 mm. The crane hook carries a vertical load of 20 kN whose line of action is 50 mm from the inside edge of the section. The center of curvature is 60 mm from the inside edge. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in the section.arrow_forwardCorrect and complete solution please don't copyarrow_forward
- Problem 9.83 Determine the principal stress in ksi Determine the absolute maximum shear stress in ksi.arrow_forwardTwo wooden members of uniform rectangular cross section of sides a = 100 mm and b = 60 mm are joined by a simple glued joint as shown. Knowing that the ultimate stresses for the joint are σU =1.26 MPa in tension and τU = 1.50 MPa in shear and that P =6 kN, determine the factor of safety for the joint when (a) α =20°,(b) α =35°, (c) α =45°. For each of these values of α, also determine whether the joint will fail in tension or in shear if P is increased until rupture occurs.arrow_forwardTwo horizontal 5-kip forces are applied to pin B of the assembly shown. Knowing that a pin of 0.8-in. diameter is used at each connection, determine the maximum value of the average normal stress (a) in link AB, (b) in link BC. 0.5 in. 1.S in. 5 kips 5 lips 0,5 in. 60 1.8 in. Fig. P8.8arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license