
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398235
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., John T. DeWolf, David F. Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 66RP
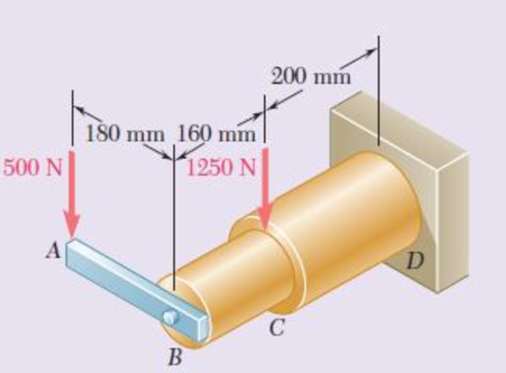
Neglecting the effect of fillets and of stress concentrations, determine the smallest permissible diameters of the solid rods BC and CD. Use τall = 60 MPa.
Fig. P8.66 and P8.67
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A spherical gas tank is fabricated by bolting together two thin-walled
hemispherical shells with an inner diameter of 8 m. The gas is
pressurized to 2.0 MPa. The shells have an allowable normal stress
of 150 MPa, and the 25 mm-diameter bolts have an allowable normal
stress of 250 MPa.
(a) Determine the minimum thickness of the walls of the tank to the
nearest mm.
(b) Determine the minimum number of bolts to connect the hemispheres.
2.
(a) A steel cylinder of 60 mm inner radius and 80 mm outer radius is
subjected to an internal pressure of 30 MNm ². Determine the
resulting hoop stress values at the inner and outer surfaces and
graphically represent (sketch) the general form of hoop stress
variation through the thickness of the cylinder wall.
(b)
(c)
The cylinder in (a) is to be used as a shrink-fitted sleeve to
strengthen a hydraulic cylinder manufactured of the same steel.
The cylinder bore radius is 40 mm. When the hydraulic cylinder
is not subjected to internal pressure, the interference pressure
generated due to the shrink fit alone is 30 MNm2. Note: This is
the same value of pressure as in the problem analysed in part
(a).
Determine the resulting hoop stress values at the inner and outer
walls of the inner cylinder.
Graphically represent the general form of hoop stress variation
through the wall thickness in the combination indicating the key
values as calculated in parts (a) and (b).
(d)
If the Young's…
A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is fabricated from 10-mm thick plate by welding along a helix that forms an angle of 20° with a plane perpendicular to the axis of the pipe. Knowing that a 280-kN axial force P is applied to the pipe, determine the normal and shearing stresses in directions respectively normal and tangential to the weld. (Input the answer with the appropriate sign.)
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Ch. 8.2 - A W10 = 39 rolled-steel beam supports a load P as...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.1, assuming that P = 22.5 kips and a...Ch. 8.2 - An overhanging W920 449 rolled-steel beam...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.3, assuming that P = 850 kN and a =...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...
Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Using the notation of Sec. 8.2 and neglecting the...Ch. 8.2 - The 4-kN force is parallel to the x axis, and the...Ch. 8.2 - The vertical force P1 and the horizontal force P2...Ch. 8.2 - The two 500-lb forces are vertical and the force P...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shafts ABC and DEF and the gears shown...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - The cantilever beam AB has a rectangular cross...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the pipe AB as shown....Ch. 8.3 - Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pile AB has a 100-mm outer diameter and...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to a 4-in.-diameter plate...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pipe AB has a 72-mm outer diameter and a...Ch. 8.3 - A 13-kN force is applied as shown to the...Ch. 8.3 - A vertical force P of magnitude 60 lb is applied...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the machine component...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 57PCh. 8.3 - Four forces are applied to a W8 28 rolled-steel...Ch. 8.3 - A force P is applied to a cantilever beam by means...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 60PCh. 8.3 - A 5-kN force P is applied to a wire that is...Ch. 8.3 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8 - (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all = 14.5 ksi,...Ch. 8 - Neglecting the effect of fillets and of stress...Ch. 8 - Knowing that rods BC and CD are of diameter 24 mm...Ch. 8 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 450 rpm and...Ch. 8 - A 6-kip force is applied to the machine element AB...Ch. 8 - A thin strap is wrapped around a solid rod of...Ch. 8 - A close-coiled spring is made of a circular wire...Ch. 8 - Forces are applied at points A and B of the solid...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the bracket AB has a uniform...Ch. 8 - For the post and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8 - The cantilever beam AB will be installed so that...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 20 mm diameter steel rod passes concentrically through a bronze tube (200+SN) mm long, 50 mm external diameter and 40 mm internal diameter. The ends of the steel rod are threaded and provided with nuts and washers which are adjusted initially so that there is no end play at 25°C.. 1. Assuming that there is no change in the thickness of the washers, if the stress produced in the steel is (200+SN) MN/m2 when one of the nuts is tightened, the pitch of the thread being 1 mm. Find the number of turns for the nut and stress in bronze tube.2. If the temperature of the steel and bronze is then raised to 4O°C find the changes that will occur in the stresses in both materials. The coefficient of linear expansion per C is 10 x10-6 for steel and 17 x10-6 for bronze. E for steel = 210 GN/m2. E %3D for bronze = 100 GN/m2.. Note: SN = %3D Student number Student Number =32arrow_forwardA lightweight lever consists of a 0.8m solid bar rigidly mounted to a large structure and a 0.5m solid lever welded to the solid bar. Using the loading indicated and assuming the material has a Young's Modulus of 200 GPa and a shear modulus of 86 GPa, calculate: (a) the maximum stress at Point A on the Cross-section a-a, (b) the vertical displacement of the knob when the load is applied relative to Cross-section a-a. B C 50 mm Section ad a 0.8 m 0.5 m 100 N 38 mm Focusarrow_forward6. Link BD consists of a single bar 30 mm wide and 12 mm thick. Knowing that each pin has a 10 mm diameter, determine the maximum value of the average normal stress in link BD if (a) 0 = 0°, (b) 0 = 90°. 150 m 00 mm 5B Page 2 of 3arrow_forward
- Problem No. 2 A cylindrical boiler with an outside diameter of 2.75 m and a wall thickness of 32 mm is made of a steel alloy that has a yield stress of 340 MPa. Determine: (a) the maximum normal stress produced by an internal pressure of 2.3 MPa.(b) the maximum allowable pressure if a factor of safety of 4.5 with respect to yield is requiredarrow_forwardThree forces, each of magnitude P = 3 kN, are applied to the structure shown. Determine the cross-sectional area of the uniform portion of rod BE for which the normal stress in that portion is +100 MPa. The cross-sectional area of the uniform portion of rod BE is mm2.arrow_forwardA timber column, 8 in. by 8 in. in cross section, is reinforced on all four sides by steel plates, each plate being 8 in. wide and t in. thick. Determine the smallest value of tfor which the column can support an axial load of 300 kips if the working stresses are 1200 psi for timber and 20 ksi for steel. The moduli of elasticity are 1.5 x106psi for timber and 29 x 106psi for steel.arrow_forward
- Parvinbhaiarrow_forwardTwo links BF are made of steel with a 450-MPa ultimate normal stress and has a 6x12–mm uniform rectangular cross section. Links BF are connected to members ABD and CDEF by 8-mm diameter pins; ABD and CDEF are connected together by a 10-mm diameter pin; CDEF is connected to the support by a 10-mm diameter pin; all of the pins are made of steel with a 170 MPa ultimate shearing stress. Knowing that a factor of safety of 3 is desired, determine the largest load P that may be appliedarrow_forwardProblem 1: Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown below. Knowing that P = 8 kips, find the average normal stress at the midsection of (a) rod AB, and (b) rod BC. Begin your solution on this page. 30 in. 25 in. B C P - 1.25 in. 12 kips 0.75 in.arrow_forward
- Q # 2 The state of plane stress shown is expected to 6 |13 MPа occur in an aluminum casting. Knowing that for the aluminum alloy used oUT =100 MPa and Ouc = 250 MPa and using Mohr's criterion, determine whether rupture of the casting will occur or not. 21 MPa 46 MPaarrow_forwardKnowing that a 0.02-in. gap exists when the temperature is 75°F, determine (a) the temperature at which the normal stress in the alumi-num bar will be equal to –11 ksi, (b) the corresponding exact length of the aluminum bar.arrow_forwardA draw bar between a tractor and a trailer is made from a length of steel with a rectangular cross-section 100 mm by 12 mm. The load is transmitted to the bar via a pin through a 25 mm diameter hole at each end as shown in Fig. 4c. for 100 Fig. 4c If the load P in the bar is 100 kN, determine the following: The stress at the section X-X, shown in Fig. 4c. i (6 marks) ii The stress at the section Y-Y, shown in Fig. 4c. (5 marks)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY