
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398235
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., John T. DeWolf, David F. Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 23P
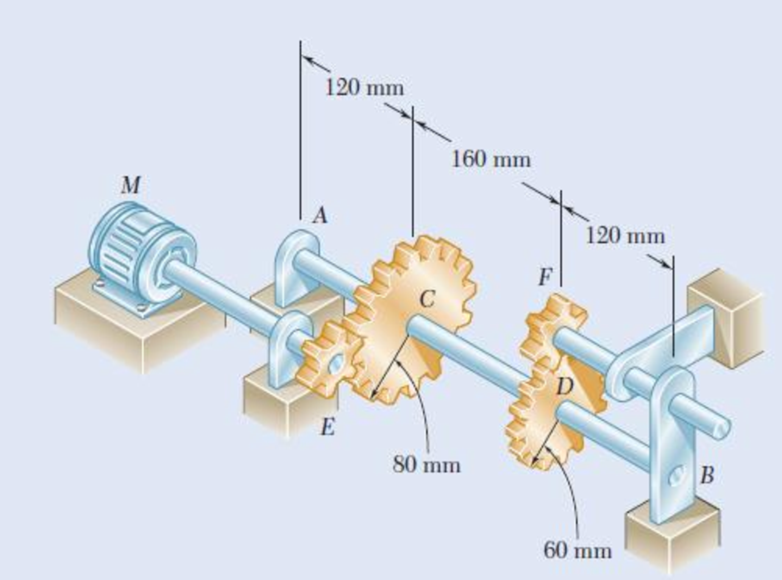
The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and transmits 80 kW from the motor M to a machine tool connected to gear F. Knowing that τall = 60 MPa, determine the smallest permissible diameter of shaft AB.
Fig. P8.23
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
100 mm
75 mm
150 mm
200 mm
100 mm
150 mm
100 mm
CE
PROBLEM 8.29
The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and
transmits 45 kW from the motor M to machine
tools connected to gears G and H. Knowing that
Tall = 55 MPa and that 30 kW is taken off at gear
G and 15 kW is taken off at gear H, determine the
smallest permissible diameter of shaft AE.
machine tools connected to gears G and H. Knowing that Tall= 50 Mpa and that 30
kW is taken off at gear G and 15 kW is taken off at gear H, determine the smallest
permissible diameter of shaft AE
The solid shaft AE rotates at 500 rpm and transmits 45 kW from the motor M to the
100 mm
150 mm
200 mm
150 mm
C.
75 mm
100 mm
100 mm
The design specifications for the gear-and-shaft system shown require that the same diameter be used for both shafts and that the angle through which pulley A will rotate when subjected to a 2-kip·in. torque TA while pulley D is held fixed will not exceed 7.5°. Determine the required diameter of the shafts if both shafts are made of a steel with G= 11.2 × 106 psi and τall= 12 ksi.assuming that both shafts are made of a brass with G= 5.6 × 106 psi and τall= 8 ksi.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Ch. 8.2 - A W10 = 39 rolled-steel beam supports a load P as...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.1, assuming that P = 22.5 kips and a...Ch. 8.2 - An overhanging W920 449 rolled-steel beam...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.3, assuming that P = 850 kN and a =...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...
Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Using the notation of Sec. 8.2 and neglecting the...Ch. 8.2 - The 4-kN force is parallel to the x axis, and the...Ch. 8.2 - The vertical force P1 and the horizontal force P2...Ch. 8.2 - The two 500-lb forces are vertical and the force P...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shafts ABC and DEF and the gears shown...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - The cantilever beam AB has a rectangular cross...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the pipe AB as shown....Ch. 8.3 - Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pile AB has a 100-mm outer diameter and...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to a 4-in.-diameter plate...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pipe AB has a 72-mm outer diameter and a...Ch. 8.3 - A 13-kN force is applied as shown to the...Ch. 8.3 - A vertical force P of magnitude 60 lb is applied...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the machine component...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 57PCh. 8.3 - Four forces are applied to a W8 28 rolled-steel...Ch. 8.3 - A force P is applied to a cantilever beam by means...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 60PCh. 8.3 - A 5-kN force P is applied to a wire that is...Ch. 8.3 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8 - (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all = 14.5 ksi,...Ch. 8 - Neglecting the effect of fillets and of stress...Ch. 8 - Knowing that rods BC and CD are of diameter 24 mm...Ch. 8 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 450 rpm and...Ch. 8 - A 6-kip force is applied to the machine element AB...Ch. 8 - A thin strap is wrapped around a solid rod of...Ch. 8 - A close-coiled spring is made of a circular wire...Ch. 8 - Forces are applied at points A and B of the solid...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the bracket AB has a uniform...Ch. 8 - For the post and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8 - The cantilever beam AB will be installed so that...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pravinbhaiarrow_forwardThe composite shaft shown consists of a 0.2-in.-thick brass jacket (Gbrass= 5.6 × 106 psi) bonded to a 1.2-in.-diameter steel core (Gsteel=11.2 × 106 psi). Knowing that the shaft is being subjected to the torques shown, determine the largest angle through which it can be twisted if the following allowable stresses are not to be exceeded: τsteel=15 ksi and τbrass= 8 ksi.arrow_forward3) The electric motor exerts a torque of 600 N.m on the steel shaft ABCD when it is rotating at a constant speed. Design specifications require that the diameter of the shaft be uniform from A to D and that the angle of twist between A and D not exceed 1.5°. Knowing that t max < 65 MPa and G = 77 GPa, determine the minimum diameter the shaft that can be used. 200 N.m 400 N.m 0.6 m -0.8m -0.3m-arrow_forward
- A 1.5-m-long tubular steel shaft of 38-mm outer diameter d1 is to be made of a steel for which τall = 65 MPa and G = 77.2 GPa. Knowing that the angle of twist must not exceed 4° when the shaft is subjected to a torque of 660 N·m, determine the largest inner diameter d2 that can be specified in the design. The largest inner diameter d2 that can be specified is mm.arrow_forwardThe design of the gear-and-shaft system shown requires that steel shafts of the same diameter be used for both AB and CD. It is further required that tmay s 60 MPa and that the angle op through which end D of shaft CD rotates not exceed 1.5 degrees. Knowing that G = 77.2 GPa, determine the required diameter of the shafts. 40 mm T = 1000 N-m D 100 mm 400 mm 600 mm ANSWER: mm (use 3 significant figures)arrow_forward30 mm PROBLEM 3.36 30 mm The torques shown are exerted on pulleys B, C, and D. Knowing that the entire shaft is made of steel (G = 27 GPa), determine the angle of twist between (a) C and B, (b) D and B. 400 N. m 36 mm 900 N- m 36 mm 500 N- m u 90. 0.8 m 1 m 0.5 m PBC = 8.54° PBD = 2.11° %3Darrow_forward
- A circular shaft AB consists of a 10-in.-long, 78-in.-diameter steel cylinder, in which a 5-in.-long, 58-in.-diameter cavity has been drilled from end B. The shaft is attached to fixed supports at both ends, and a 90 lb?ft torque is applied at its midsection . Determine the torque exerted on the shaft by each of the supports.arrow_forwardTwo shafts, each of 78-in.-diameter, are connected by the gears shown. Knowing that G= 11.2 ×106 psi and that the shaft at F is fixed, deter-mine the angle through which end A rotates when a 1.2 kip·in.-torque is applied at A.arrow_forwardA 1.5-m-long tubular steel shaft of 38-mm outer diameter d1 is to be made of a steel for which τall = 65 MPa and G = 77.2 GPa. Knowing that the angle of twist must not exceed 4° when the shaft is subjected to a torque of 540 N·m, determine the largest inner diameter d2 that can be specified in the design.arrow_forward
- The design of the gear-and-shaft system shown requires that steel shafts of the same diameter be used for both AB and CD. It is further required that τmax ≤ 60 MPa and that the angle φD through which end D of shaft CD rotates not exceed 1.5°. Knowing that G = 77.2 GPa, determine the required diameter of the shafts.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardThe design specifications of a 1.2-m-long solid transmission shaft require that the angle of twist of the shaft not exceed 4° when a torque of 750 N·m is applied. Determine the required diameter of the shaft, knowing that the shaft is made of a steel with an allowable shearing stress of 90 MPa and a modulus of rigidity of 77.2 GPa.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License