
(a.)
The plot of
The plot of
Given:
As a pendulum swings toward and away from a motion detector, its distance (in meters) from the detector is given by the position function
Concept used:
Parametric equations
Calculation:
The given parametric equations are
Plotting these parametric equations on the
plane as follows:
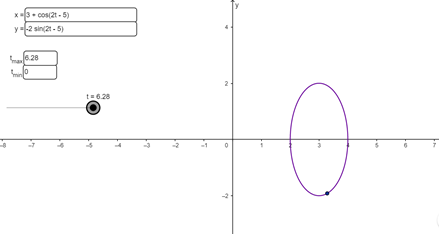
Conclusion:
The plot of
(b.)
The equation of the resulting conic in standard form, in terms of
It has been determined that the equation of the resulting conic in standard form, in terms of
Given:
As a pendulum swings toward and away from a motion detector, its distance (in meters) from the detector is given by the position function
Concept used:
Parametric equations
Calculation:
The given parametric equations are
Simplifying,
Squaring both sides of each equation,
Adding both equations,
Using trigonometric identity;
Converting to standard form,
This is the required equation of the resulting conic in standard form.
Conclusion:
It has been determined that the equation of the resulting conic in standard form, in terms of
Chapter 8 Solutions
PRECALCULUS:GRAPHICAL,...-NASTA ED.
- Question 1. (10 points) A researcher is studying tumours in mice. The growth rate for the volume of the tumour V(t) in cm³ is given by dV = 1.45V(2 In(V+1)). dt (a) (4 pts) Find all the equilibria and determine their stability using the stability condition. (b) (2 pts) Draw the phase plot f(V) versus V where f(V) = V'. You may find it helpful to use Desmos or Wolfram Alpha to plot the graph of f(V) versus V (both are free to use online), or you can plot it by hand if you like. On the plot identify each equilibrium as stable or unstable. (c) (4 pts) Draw direction arrows for the case where the tumour starts at size 3cm³ and for the case where the tumour starts at size 9cm³. Explain in biological terms what happens to the size of each of these tumours at time progresses.arrow_forwardFor the system consisting of the two planes:plane 1: -x + y + z = 0plane 2: 3x + y + 3z = 0a) Are the planes parallel and/or coincident? Justify your answer. What does this tell you about the solution to the system?b) Solve the system (if possible). Show a complete solution. If there is a line of intersection express it in parametric form.arrow_forwardQuestion 2: (10 points) Evaluate the definite integral. Use the following form of the definition of the integral to evaluate the integral: Theorem: Iff is integrable on [a, b], then where Ax = (ba)/n and x₂ = a + i^x. You might need the following formulas. IM³ L² (3x² (3x²+2x- 2x - 1)dx. n [f(z)dz lim f(x)Az a n→∞ i=1 n(n + 1) 2 n i=1 n(n+1)(2n+1) 6arrow_forward
- For the system consisting of the three planes:plane 1: -4x + 4y - 2z = -8plane 2: 2x + 2y + 4z = 20plane 3: -2x - 3y + z = -1a) Are any of the planes parallel and/or coincident? Justify your answer.b) Determine if the normals are coplanar. What does this tell you about the system?c) Solve the system if possible. Show a complete solution (do not use matrix operations). Classify the system using the terms: consistent, inconsistent, dependent and/or independent.arrow_forwardFor the system consisting of the three planes:plane 1: -4x + 4y - 2z = -8plane 2: 2x + 2y + 4z = 20plane 3: -2x - 3y + z = -1a) Are any of the planes parallel and/or coincident? Justify your answer.b) Determine if the normals are coplanar. What does this tell you about the system?c) Solve the system if possible. Show a complete solution (do not use matrix operations). Classify the system using the terms: consistent, inconsistent, dependent and/or independent.arrow_forwardOpen your tool box and find geometric methods, symmetries of even and odd functions and the evaluation theorem. Use these to calculate the following definite integrals. Note that you should not use Riemann sums for this problem. (a) (4 pts) (b) (2 pts) 3 S³ 0 3-x+9-dz x3 + sin(x) x4 + cos(x) dx (c) (4 pts) L 1-|x|dxarrow_forward
- An engineer is designing a pipeline which is supposed to connect two points P and S. The engineer decides to do it in three sections. The first section runs from point P to point Q, and costs $48 per mile to lay, the second section runs from point Q to point R and costs $54 per mile, the third runs from point R to point S and costs $44 per mile. Looking at the diagram below, you see that if you know the lengths marked x and y, then you know the positions of Q and R. Find the values of x and y which minimize the cost of the pipeline. Please show your answers to 4 decimal places. 2 Miles x = 1 Mile R 10 miles miles y = milesarrow_forwardAn open-top rectangular box is being constructed to hold a volume of 150 in³. The base of the box is made from a material costing 7 cents/in². The front of the box must be decorated, and will cost 11 cents/in². The remainder of the sides will cost 3 cents/in². Find the dimensions that will minimize the cost of constructing this box. Please show your answers to at least 4 decimal places. Front width: Depth: in. in. Height: in.arrow_forwardFind and classify the critical points of z = (x² – 8x) (y² – 6y). Local maximums: Local minimums: Saddle points: - For each classification, enter a list of ordered pairs (x, y) where the max/min/saddle occurs. Enter DNE if there are no points for a classification.arrow_forward
- Suppose that f(x, y, z) = (x − 2)² + (y – 2)² + (z − 2)² with 0 < x, y, z and x+y+z≤ 10. 1. The critical point of f(x, y, z) is at (a, b, c). Then a = b = C = 2. Absolute minimum of f(x, y, z) is and the absolute maximum isarrow_forwardThe spread of an infectious disease is often modeled using the following autonomous differential equation: dI - - BI(N − I) − MI, dt where I is the number of infected people, N is the total size of the population being modeled, ẞ is a constant determining the rate of transmission, and μ is the rate at which people recover from infection. Close a) (5 points) Suppose ẞ = 0.01, N = 1000, and µ = 2. Find all equilibria. b) (5 points) For the equilbria in part a), determine whether each is stable or unstable. c) (3 points) Suppose ƒ(I) = d. Draw a phase plot of f against I. (You can use Wolfram Alpha or Desmos to plot the function, or draw the dt function by hand.) Identify the equilibria as stable or unstable in the graph. d) (2 points) Explain the biological meaning of these equilibria being stable or unstable.arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. Check Answer: 7x 4 + 1x dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





